Earth Science – Quiz 2
... A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen D) 1.5 times those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen 21. Which one of the ...
... A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen D) 1.5 times those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen 21. Which one of the ...
Name_______________________Period_________Date
... The disk of dust and gas that formed the Sun and planets is known as the solar nebula. Dense concentration at center became the Sun. Temperature differed, Hotter at center and cooler at edges disk Due to temp differences different compounds were able to condense depending on distance from Su ...
... The disk of dust and gas that formed the Sun and planets is known as the solar nebula. Dense concentration at center became the Sun. Temperature differed, Hotter at center and cooler at edges disk Due to temp differences different compounds were able to condense depending on distance from Su ...
hw1
... apparent motions of objects in the sky. The two principle motions of the earth are – rotation (the spinning of earth about its own axis, which is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees from the vertical) and revolution (orbital motion of the earth around the sun). The rotation of the earth results in th ...
... apparent motions of objects in the sky. The two principle motions of the earth are – rotation (the spinning of earth about its own axis, which is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees from the vertical) and revolution (orbital motion of the earth around the sun). The rotation of the earth results in th ...
The Milky Way
... you see in the sky, and now you are ready to understand one of the most sweeping revolutions in human thought: the realization that we live on a planet. In this chapter, you will discover how astronomers of the Renaissance overthrew an ancient theory and found a new way to understand Earth. Here you ...
... you see in the sky, and now you are ready to understand one of the most sweeping revolutions in human thought: the realization that we live on a planet. In this chapter, you will discover how astronomers of the Renaissance overthrew an ancient theory and found a new way to understand Earth. Here you ...
Astro Ch 4 astronomers
... the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required the revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s place. By the 16th century, many astronomers were un ...
... the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required the revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s place. By the 16th century, many astronomers were un ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required the revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s place. By the 16th century, many astronomers were un ...
... the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required the revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s place. By the 16th century, many astronomers were un ...
AstroProjectDay3
... • Write this as the heading for the next page in your notebook • We will go out into the hallway where a scale model of our solar system is set up • BE QUIET when we are out there!! Other classes are in session • Take your notebook with you ...
... • Write this as the heading for the next page in your notebook • We will go out into the hallway where a scale model of our solar system is set up • BE QUIET when we are out there!! Other classes are in session • Take your notebook with you ...
Review 2
... Structure of a comet. The asteroid belt and the Oort cloud. Why do we have meteor showers during specific days of a year? Chapter 16: How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the ...
... Structure of a comet. The asteroid belt and the Oort cloud. Why do we have meteor showers during specific days of a year? Chapter 16: How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the ...
Extract, Datei
... R = 1 AU from the Sun, where one astronomical unit (AU) is the annual mean Sun-Earth distance (for an overview see Lean 1991; Fröhlich & Lean 2004). With the TSI being primary energy source of Earth, it is interesting to study its variations. ...
... R = 1 AU from the Sun, where one astronomical unit (AU) is the annual mean Sun-Earth distance (for an overview see Lean 1991; Fröhlich & Lean 2004). With the TSI being primary energy source of Earth, it is interesting to study its variations. ...
Our Solar System
... Fourth planet from sun Appears as bright reddish color in the night sky Surface features volcanoes and huge dust storms Has 2 moons: Phobos and Deimos ...
... Fourth planet from sun Appears as bright reddish color in the night sky Surface features volcanoes and huge dust storms Has 2 moons: Phobos and Deimos ...
The SUN
... Solar flares burst and sometimes knock out our electricity.!! No solar eclipse can last more than 7 minutes and 58 seconds ...
... Solar flares burst and sometimes knock out our electricity.!! No solar eclipse can last more than 7 minutes and 58 seconds ...
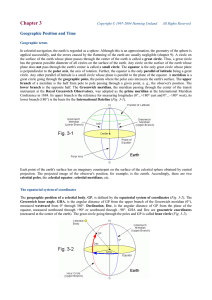
The Geographic Position of a Celestial Body
... The Greenwich hour angle of the imaginary mean vernal equinox of date (traveling along the celestial equator at a constant rate) defines Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time, GMST. The difference to GMST is called equation of the equinoxes, EQ, or nutation in right ascension. EQ can be predicted precisely. ...
... The Greenwich hour angle of the imaginary mean vernal equinox of date (traveling along the celestial equator at a constant rate) defines Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time, GMST. The difference to GMST is called equation of the equinoxes, EQ, or nutation in right ascension. EQ can be predicted precisely. ...
The Sun
... Do you see the light? • Everything in the solar system reflects light. • Everything also absorbs light and heats up producing blackbody radiation. • Q: Where does this light come from? • A: The Sun. ...
... Do you see the light? • Everything in the solar system reflects light. • Everything also absorbs light and heats up producing blackbody radiation. • Q: Where does this light come from? • A: The Sun. ...
384 kb
... partly driven by intense magnetic fields whose origin is not well understood. Nevertheless, being able to predict solar activity is of great importance for our technological society.” An anomalous solar cycle The lecture will feature spectacular videos of the Sun’s surface taken from Hinode. The obs ...
... partly driven by intense magnetic fields whose origin is not well understood. Nevertheless, being able to predict solar activity is of great importance for our technological society.” An anomalous solar cycle The lecture will feature spectacular videos of the Sun’s surface taken from Hinode. The obs ...
Mars Land Rover ASTEROID BELT
... • Pluto’ s largest moon Charon, is half the size of Pluto. • Since 2000 astronomers realized that Pluto is not like all eight planets. • Pluto is actually smaller than one of Neptune’ s moon Triton. ...
... • Pluto’ s largest moon Charon, is half the size of Pluto. • Since 2000 astronomers realized that Pluto is not like all eight planets. • Pluto is actually smaller than one of Neptune’ s moon Triton. ...
Introduction and some basic concepts
... billions of light-years away. We are observing them as they appeared billions of years ago. ...
... billions of light-years away. We are observing them as they appeared billions of years ago. ...
The Sun
... Clicker Question: Earth’s rotation is slowing down because of the tidal interaction between Earth and the Moon at a rate of 2 milliseconds/century. If this rate remains constant at the present value, how long will it take for one day on Earth to become 2 seconds longer than it is now: A: 1000 years ...
... Clicker Question: Earth’s rotation is slowing down because of the tidal interaction between Earth and the Moon at a rate of 2 milliseconds/century. If this rate remains constant at the present value, how long will it take for one day on Earth to become 2 seconds longer than it is now: A: 1000 years ...
Email Template - Personal.psu.edu
... C. beyond the orbit of Saturn. D. between Jupiter and Saturn. E. [None of the above. No general statement can be made.] ...
... C. beyond the orbit of Saturn. D. between Jupiter and Saturn. E. [None of the above. No general statement can be made.] ...
The Sun and planets
... Sun occupies one of the two foci (Kepler’s First Law). In particular, planets move along orbits that are slightly eccentric, i.e. slightly squashed, and almost all on the same plane because of the mechanism with which they were created during the formation of our planetary system. Dwarf planets and ...
... Sun occupies one of the two foci (Kepler’s First Law). In particular, planets move along orbits that are slightly eccentric, i.e. slightly squashed, and almost all on the same plane because of the mechanism with which they were created during the formation of our planetary system. Dwarf planets and ...
CyclesOfTheSky
... So the horoscopes are off by about one whole constellation compared to the real sky. Astrologers now tell you that they use a different zodiac that is not aligned with the constellations. That zodiac has 12 “houses” of equal size. I personally give no credence to astrology, think it is wrong and ano ...
... So the horoscopes are off by about one whole constellation compared to the real sky. Astrologers now tell you that they use a different zodiac that is not aligned with the constellations. That zodiac has 12 “houses” of equal size. I personally give no credence to astrology, think it is wrong and ano ...
Announcements Ancient astronomers: Why did they do it? Why did
... Used experiments to show that objects in motion tend to remain in motion Many observations (with the new-fangled invention called the telescope showed that the heavens are far from perfect (e.g., spots on the Sun, jagged mountains and valleys on the Moon) The Milky Way indicated that stars are far m ...
... Used experiments to show that objects in motion tend to remain in motion Many observations (with the new-fangled invention called the telescope showed that the heavens are far from perfect (e.g., spots on the Sun, jagged mountains and valleys on the Moon) The Milky Way indicated that stars are far m ...
Astronomy
... To find the mean distances of the planets, beginning with the following simple sequence of numbers: ...
... To find the mean distances of the planets, beginning with the following simple sequence of numbers: ...