Voir le texte intégral : Build a planet
... Shower, and our world will get a little bigger. Along with the Sun and all the planets of the Solar System, our world was mostly made some 4500 million years ago when a cloud of gas and dust collapsed. Little bits stuck together making bigger bits, and those bits hit other bits and the lumps got big ...
... Shower, and our world will get a little bigger. Along with the Sun and all the planets of the Solar System, our world was mostly made some 4500 million years ago when a cloud of gas and dust collapsed. Little bits stuck together making bigger bits, and those bits hit other bits and the lumps got big ...
Slide 1
... 300 million Light travels at a speed of ______________meters per second The distance that light travels in a year is called a 6 trillion light year. 1 light year = _____________________ miles. Sun 8 light minutes ...
... 300 million Light travels at a speed of ______________meters per second The distance that light travels in a year is called a 6 trillion light year. 1 light year = _____________________ miles. Sun 8 light minutes ...
The Stars
... There are more stars in the sky than anyone can easily count, but they are not scattered evenly, and they are not all the same in brightness or color. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sk ...
... There are more stars in the sky than anyone can easily count, but they are not scattered evenly, and they are not all the same in brightness or color. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sk ...
Grade 11 Cosmology PPT File
... Describes a relationship between the radius of the planets (average distance to the sun) and the time taken for one complete orbit. T2 is proportional to R3 Click for K3 Movie ...
... Describes a relationship between the radius of the planets (average distance to the sun) and the time taken for one complete orbit. T2 is proportional to R3 Click for K3 Movie ...
The odd planet
... - epicycles explain retrograde motion (Ptolemy) - based on simple observations and centuries of religious beliefs Heliocentric Model Sun-centred (Copernicus) - verified by Galileo’s telescope - proved by Newton - Elliptical orbits (Kepler) - Gravity (Newton) - Based on extensive observations and cal ...
... - epicycles explain retrograde motion (Ptolemy) - based on simple observations and centuries of religious beliefs Heliocentric Model Sun-centred (Copernicus) - verified by Galileo’s telescope - proved by Newton - Elliptical orbits (Kepler) - Gravity (Newton) - Based on extensive observations and cal ...
Set 2
... the Sun that involves measuring the time interval from the moment that the Earth and Jupiter are in opposition until the moment when they are next in quadrature. Earth and Jupiter are in quadrature when the Sun-Earth-Jupiter form a right angle. Using trigonometry, explain how Copernicus’ method work ...
... the Sun that involves measuring the time interval from the moment that the Earth and Jupiter are in opposition until the moment when they are next in quadrature. Earth and Jupiter are in quadrature when the Sun-Earth-Jupiter form a right angle. Using trigonometry, explain how Copernicus’ method work ...
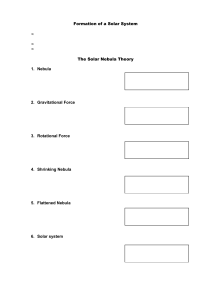
Formation of a Solar System • • • The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
HELIOSTAT II - MEASURING THE SOLAR ROTATION
... rotated between observations (treat E longitudes as negative, W longitudes as positive, and subtract the first longitude measurement from the second). Average your measurements from the different spots to produce your best estimate of the observed rotation angle. ...
... rotated between observations (treat E longitudes as negative, W longitudes as positive, and subtract the first longitude measurement from the second). Average your measurements from the different spots to produce your best estimate of the observed rotation angle. ...
Gravity and Motion Motion in astronomy Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The observed motion of the stars will depend on the latitude from which you are observing. Astronomy 1G 2011-12 ...
... The observed motion of the stars will depend on the latitude from which you are observing. Astronomy 1G 2011-12 ...
Motion in the Sky & Getting to know the Sky
... period of orbit about the sun (P) and the semimajor axis of its orbit (a) is ...
... period of orbit about the sun (P) and the semimajor axis of its orbit (a) is ...
Hands-On Tracking Sunspots!
... In the early 1600s, Galileo first recorded sunspots using a telescope. Sunspots can last for weeks or even several months and can be used to track the rotation rate of the Sun. In this activity, you will measure the motion of sunspots to determine how long it takes the sun to rotate! ...
... In the early 1600s, Galileo first recorded sunspots using a telescope. Sunspots can last for weeks or even several months and can be used to track the rotation rate of the Sun. In this activity, you will measure the motion of sunspots to determine how long it takes the sun to rotate! ...
Astronomy Notes
... negative pressure, which would have gravitational effects to account for the differences between the theoretical and observational results of gravitational effects on visible matter. ...
... negative pressure, which would have gravitational effects to account for the differences between the theoretical and observational results of gravitational effects on visible matter. ...
GRAVITY FIELD IN EXTERNAL PARTS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... Thus, part of the Kuiper belt objects and comets move in the interstellar medium, but remain deep within the incidence of the Sun. According to (Oort, 1950) exist cloud around the Sun of comet nuclei, called the Oort cloud. This cloud is not available observations. But if it exists, the comet nucleu ...
... Thus, part of the Kuiper belt objects and comets move in the interstellar medium, but remain deep within the incidence of the Sun. According to (Oort, 1950) exist cloud around the Sun of comet nuclei, called the Oort cloud. This cloud is not available observations. But if it exists, the comet nucleu ...
trek across the milky way
... • It is the brightest object in the sky besides the sun and the moon • Venus is composed mostly of carbon dioxide, which makes it unsuitable for life. • Said to be Earth’s sister planet because they are quite similar in all aspects, like size. • Has no known satellites ...
... • It is the brightest object in the sky besides the sun and the moon • Venus is composed mostly of carbon dioxide, which makes it unsuitable for life. • Said to be Earth’s sister planet because they are quite similar in all aspects, like size. • Has no known satellites ...
Celestial Equator - University of Maryland Astronomy
... when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. Spring and fall are in between. AXIS TILT is the key to the seasons; without it, we would not have seasons on Earth! ...
... when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. Spring and fall are in between. AXIS TILT is the key to the seasons; without it, we would not have seasons on Earth! ...
The sun is a star, and it is very large and very far away. Its distance
... The sun is a star, and it is very large and very far away. Its distance from Earth is about 149 million kilometres. The light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to get here, travelling at 300,000 kilometres per second. However, despite the fact that the sun is so far away, we're going to show you a ...
... The sun is a star, and it is very large and very far away. Its distance from Earth is about 149 million kilometres. The light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to get here, travelling at 300,000 kilometres per second. However, despite the fact that the sun is so far away, we're going to show you a ...
Homework #2 Solutions Astronomy 10, Section 2 due: Monday
... planet has one, and they are all slightly different. The question of seasons is completely different. Seasons will occur if there are significant changes in the surface temperatures with time. This can occur if a planetʼs rotation axis is tilted with respect to its own ecliptic. Table A-10 lists the ...
... planet has one, and they are all slightly different. The question of seasons is completely different. Seasons will occur if there are significant changes in the surface temperatures with time. This can occur if a planetʼs rotation axis is tilted with respect to its own ecliptic. Table A-10 lists the ...
THE SOLAR SYSTEM An Overview Astronomy is the study of the
... of time is not significantly affected by the motion of the earth around the sun. Synodic time is measured relative to the position in the sky of the sun. The revolution of the earth around the sun affects apparent positions relative to the sun. The sidereal period of the planet Mercury is 88 days. T ...
... of time is not significantly affected by the motion of the earth around the sun. Synodic time is measured relative to the position in the sky of the sun. The revolution of the earth around the sun affects apparent positions relative to the sun. The sidereal period of the planet Mercury is 88 days. T ...
Chap 2 Lecture(1)
... daylength. The variations in these are caused by various physical factors: Earth’s revolution around the sun Earth’s rotation around it’s axis Tilt of the earth’s axis Axial parallelism Sphericity ...
... daylength. The variations in these are caused by various physical factors: Earth’s revolution around the sun Earth’s rotation around it’s axis Tilt of the earth’s axis Axial parallelism Sphericity ...
solar system
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
The Solar System
... distances in the solar system. A.U.-equal to the average distance between the Earth and the sun This distance is 150 million km or 93 million miles. Light-year-equal to the distance light can travel in a vacuum in one year. Used to measure distances to the stars. ...
... distances in the solar system. A.U.-equal to the average distance between the Earth and the sun This distance is 150 million km or 93 million miles. Light-year-equal to the distance light can travel in a vacuum in one year. Used to measure distances to the stars. ...
E. Sci. Astronomy Notes
... Historically Earth was thought to be center of solar system (geocentric model) Heliocentric model is correct (Sun centered solar system) On Earth celestial objects appear to move from east to west in an arc pattern Sun/Stars Apparent Path #1 Looking North at Polaris #2 Looking West #3 Looking South ...
... Historically Earth was thought to be center of solar system (geocentric model) Heliocentric model is correct (Sun centered solar system) On Earth celestial objects appear to move from east to west in an arc pattern Sun/Stars Apparent Path #1 Looking North at Polaris #2 Looking West #3 Looking South ...
Astronomy Practice Test
... 28. Why have planets orbiting other stars not been directly observed? A. they are too dim B. They are too far away C. They are too small D. All of the above 29. The light from the most distant galaxies is A. shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. C. always ultraviolet ...
... 28. Why have planets orbiting other stars not been directly observed? A. they are too dim B. They are too far away C. They are too small D. All of the above 29. The light from the most distant galaxies is A. shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. C. always ultraviolet ...
123mt13a
... the celestial bodies may be described. While the Ptolemaic system which represent the planetary motions by combinations of circular motions - could take any point to be fixed, the choice of any particular point required some justification on other than astronomical grounds - there has to be some sen ...
... the celestial bodies may be described. While the Ptolemaic system which represent the planetary motions by combinations of circular motions - could take any point to be fixed, the choice of any particular point required some justification on other than astronomical grounds - there has to be some sen ...