Microsoft Word - students_diffe
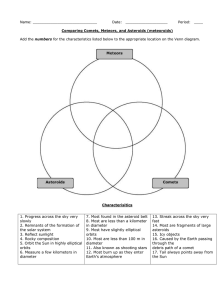
... Comparing Comets, Meteors, and Asteroids (meteoroids) Add the numbers for the characteristics listed below to the appropriate location on the Venn diagram. ...
... Comparing Comets, Meteors, and Asteroids (meteoroids) Add the numbers for the characteristics listed below to the appropriate location on the Venn diagram. ...
What is Sunology?
... The beginning of the circle represents the beginning of any process. As the circle is progressed through, concepts build on one another through to the end. The circle can be split into any number of steps. Sunology splits the circle into 30 steps. ...
... The beginning of the circle represents the beginning of any process. As the circle is progressed through, concepts build on one another through to the end. The circle can be split into any number of steps. Sunology splits the circle into 30 steps. ...
Members of the Solar System
... Solar System-the sun and all of the bodies that orbit it make up the solar system. This includes the planets and their moons, as well as comets, asteroids, meteoroids, and any other bits of rock or dust. The main parts of our solar system are eight planets, an asteroi d belt, and three dwarf planets ...
... Solar System-the sun and all of the bodies that orbit it make up the solar system. This includes the planets and their moons, as well as comets, asteroids, meteoroids, and any other bits of rock or dust. The main parts of our solar system are eight planets, an asteroi d belt, and three dwarf planets ...
What is the universe???
... Big Bang Balloon Quick Lab • Use a felt-tip pen/marker to make 5 dots in a row, 1 cm apart, on your balloon Label one “Earth” and the others A-D (these represent other galaxies) • Partially inflate the balloon (1-2 big breaths) and hold it…do not tie it! Use a piece of yarn to measure the distanc ...
... Big Bang Balloon Quick Lab • Use a felt-tip pen/marker to make 5 dots in a row, 1 cm apart, on your balloon Label one “Earth” and the others A-D (these represent other galaxies) • Partially inflate the balloon (1-2 big breaths) and hold it…do not tie it! Use a piece of yarn to measure the distanc ...
Astronomy Lecture 1a
... D.23.5 E.sun declination does not vary; it is always directly above the celestial equator ___ 22. ? is when a planet is opposite the Sun in the sky. A.opposition B.conjunction C.in both opposition and conjunction the planet is opposite the Sun in the sky ___ 23. The Prime Meridian is at zero degrees ...
... D.23.5 E.sun declination does not vary; it is always directly above the celestial equator ___ 22. ? is when a planet is opposite the Sun in the sky. A.opposition B.conjunction C.in both opposition and conjunction the planet is opposite the Sun in the sky ___ 23. The Prime Meridian is at zero degrees ...
Study Guide I (Chpts 1
... big bang occurred 15 billion years ago – all matter in universe came from this single explosion of matter (universe is still expanding) stars (and planets) were formed by gathering together of (cosmic) dust our solar system is part of Milky Way galaxy and formed ~ 5 billion years ago Milky Way is ~ ...
... big bang occurred 15 billion years ago – all matter in universe came from this single explosion of matter (universe is still expanding) stars (and planets) were formed by gathering together of (cosmic) dust our solar system is part of Milky Way galaxy and formed ~ 5 billion years ago Milky Way is ~ ...
The Seasons
... globe would the sun appear directly overhead on the summer solstice? (Use a globe for reference.) The sun is directly on the celestial equator, thus the sun is directly overhead on the equator. Compare the area of illumination at the equinox to the summer and winter solstices. The area of illuminati ...
... globe would the sun appear directly overhead on the summer solstice? (Use a globe for reference.) The sun is directly on the celestial equator, thus the sun is directly overhead on the equator. Compare the area of illumination at the equinox to the summer and winter solstices. The area of illuminati ...
Quiz 1 Review, Astronomy 1144 - astronomy.ohio
... 2. He measured the length of the shadows cast at noon in two different locations separated by a known North-South distance. The difference in these lengths gave him the angle between the two locations along Earth’s surface, allowing him to calculate the circumference of the Earth. • What is stellar ...
... 2. He measured the length of the shadows cast at noon in two different locations separated by a known North-South distance. The difference in these lengths gave him the angle between the two locations along Earth’s surface, allowing him to calculate the circumference of the Earth. • What is stellar ...
Montage of Jupiter and the Galilean satellites
... luminosity, in units of the SunΥsluminosity. The solid white lin es show where stars of different luminosity classes fall on the diagram; supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity cl ...
... luminosity, in units of the SunΥsluminosity. The solid white lin es show where stars of different luminosity classes fall on the diagram; supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity cl ...
Earth, Moon & Sun System
... • The Earth is a sphere (ball shape). Because of this only half can be lit by the sun at any one time. ...
... • The Earth is a sphere (ball shape). Because of this only half can be lit by the sun at any one time. ...
The sun, the earth, and the moon
... stick together these planets grew faster!! All gas giants are orbited by many moons ...
... stick together these planets grew faster!! All gas giants are orbited by many moons ...
1.1989 x 10 30 kg
... Scientists made the assessment after studying 18 years of data from the Ulysses satellite which has sampled the space environment all around our star. They expect the reduced output to have effects right across the Solar System. Indeed, one impact is to diminish slightly the influence the Sun has ov ...
... Scientists made the assessment after studying 18 years of data from the Ulysses satellite which has sampled the space environment all around our star. They expect the reduced output to have effects right across the Solar System. Indeed, one impact is to diminish slightly the influence the Sun has ov ...
Largest moon in the solar system
... Second largest dwarf planet in the solar system. Pluto’s companion, Charon , is half the size & doesn’t orbit around Pluto. Pluto & Charon are small enough to fit inside the United States. Pluto is smaller than the Earth's moon. Some astronomers believe that Pluto was once a moon of Neptune bu ...
... Second largest dwarf planet in the solar system. Pluto’s companion, Charon , is half the size & doesn’t orbit around Pluto. Pluto & Charon are small enough to fit inside the United States. Pluto is smaller than the Earth's moon. Some astronomers believe that Pluto was once a moon of Neptune bu ...
The Sun - SCHOOLinSITES
... magnetosphere that react with and excite the oxygen and nitrogen of Earth’s upper atmosphere; usually seen in the sky near Earth’s magnetic poles. – are the result of the interaction between the solar wind and Earth’s magnetosphere. – usually seen close to Earth’s magnetic poles because electrically ...
... magnetosphere that react with and excite the oxygen and nitrogen of Earth’s upper atmosphere; usually seen in the sky near Earth’s magnetic poles. – are the result of the interaction between the solar wind and Earth’s magnetosphere. – usually seen close to Earth’s magnetic poles because electrically ...
rotate
... What type of motion is this diagram showing? PROVE IT TO YOURSELF with the globes – counterclockwise in northern hemisphere and clockwise in southern hemisphere but always towards the east ...
... What type of motion is this diagram showing? PROVE IT TO YOURSELF with the globes – counterclockwise in northern hemisphere and clockwise in southern hemisphere but always towards the east ...
Astronomy
... asteroids – fragments of matter similar to planetary matter that orbit between Mars and Jupiter asteroid belt – the orbit of most asteroid located between Mars and Jupiter axis – the imaginary line around which an object rotates Big Bang theory – the most accepted theory for the origin of the univer ...
... asteroids – fragments of matter similar to planetary matter that orbit between Mars and Jupiter asteroid belt – the orbit of most asteroid located between Mars and Jupiter axis – the imaginary line around which an object rotates Big Bang theory – the most accepted theory for the origin of the univer ...
Precession
... spinning Earth’s axis to sweep around in a conical motion like the motion of a top’s axis. ...
... spinning Earth’s axis to sweep around in a conical motion like the motion of a top’s axis. ...
Unit 3 *The Solar System* 6th Grade Space Science
... Temperature is warmer or colder than Earth. Size is larger or smaller than Earth. What it is made of – mostly gas or mostly ...
... Temperature is warmer or colder than Earth. Size is larger or smaller than Earth. What it is made of – mostly gas or mostly ...
september 2013 - Holt Planetarium
... finally popped free of the heliosphere, the huge bubble of charged particles and magnetic fields that the sun puffs out around itself, on or around Aug. 25, 2012, becoming humanity's first envoy to the vast realms between the stars. Voyager 1 reached the boundary of the heliosphere in 2004, a milest ...
... finally popped free of the heliosphere, the huge bubble of charged particles and magnetic fields that the sun puffs out around itself, on or around Aug. 25, 2012, becoming humanity's first envoy to the vast realms between the stars. Voyager 1 reached the boundary of the heliosphere in 2004, a milest ...
Second Book: Student´s Reference Book ……
... Earth, third planet from the Sun and third largest in size of the nine main planets. The average distance of the Earth from the Sun is 149,503,000 km. It is the only planet known to have life, although some of the other planets have atmospheres and contain water. The Earth isn’t a perfect sphere but ...
... Earth, third planet from the Sun and third largest in size of the nine main planets. The average distance of the Earth from the Sun is 149,503,000 km. It is the only planet known to have life, although some of the other planets have atmospheres and contain water. The Earth isn’t a perfect sphere but ...
Einstein on Kepler
... a planet is actually located, but only in what direction it is visible at any given time from the Earth, which, however, is itself moving in an unknown way around the Sun. The difficulties seem all but insurmountable. Kepler had to find a way to bring order out of this chaos. First of all, he realiz ...
... a planet is actually located, but only in what direction it is visible at any given time from the Earth, which, however, is itself moving in an unknown way around the Sun. The difficulties seem all but insurmountable. Kepler had to find a way to bring order out of this chaos. First of all, he realiz ...
Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects
... make across the sky. The “actual motion” may be different. ...
... make across the sky. The “actual motion” may be different. ...