Name____________________________________________________________________ Astronomy Packet 4
... ancient societies. Many astronomers believed it to Earths _______ albeit a hotter version. When it was first visited by the Soviet mission’s ___________ and________ it was discovered that that idea was totally ___________. In fact this planet is actually the solar systems_________ with an avg. surfa ...
... ancient societies. Many astronomers believed it to Earths _______ albeit a hotter version. When it was first visited by the Soviet mission’s ___________ and________ it was discovered that that idea was totally ___________. In fact this planet is actually the solar systems_________ with an avg. surfa ...
Chapter 14 Our Star The Sun is the Largest Object in the Solar
... The annual change in numbers of sunspots reveals that the Sun experiences an 11-year Sun Spot cycle ...
... The annual change in numbers of sunspots reveals that the Sun experiences an 11-year Sun Spot cycle ...
Pluto
... • Asteroids (“minor planets”) occupy a belt at ~2.8 AU from the Sun, where there could be a planet. • First one (Ceres) found in 1801; several others found shortly thereafter (1802, 1804) • Thousands are now known (105 or more?) • About 6 are larger than 300 km, but most are small (< 10 km). • 3 typ ...
... • Asteroids (“minor planets”) occupy a belt at ~2.8 AU from the Sun, where there could be a planet. • First one (Ceres) found in 1801; several others found shortly thereafter (1802, 1804) • Thousands are now known (105 or more?) • About 6 are larger than 300 km, but most are small (< 10 km). • 3 typ ...
Science Standards - Explore-It
... 4.2.3 Describe how human beings have made tools and machines, such as satellites to observe and do things that they could not otherwise sense or do at all, or as quickly or efficiently. 4.1.1 Recognize and describe how results of similar scientific investigations may turn out differently due to inco ...
... 4.2.3 Describe how human beings have made tools and machines, such as satellites to observe and do things that they could not otherwise sense or do at all, or as quickly or efficiently. 4.1.1 Recognize and describe how results of similar scientific investigations may turn out differently due to inco ...
Quiz 3
... • If a set of measurements has very high bias, can the set of measurements have a very high accuracy? 1. No. If there is a high bias, then the average of the measurements is far away from the true value. In order to have high accuracy, you need to have all measurements very close to the true value. ...
... • If a set of measurements has very high bias, can the set of measurements have a very high accuracy? 1. No. If there is a high bias, then the average of the measurements is far away from the true value. In order to have high accuracy, you need to have all measurements very close to the true value. ...
Solar Plasmas - Coalition for Plasma Science
... in such a bubble of particles is comparable to a hundred hurricanes. However, it is especially the magnetic energy of such plasma clouds that can upset technology here at earth. The sun goes through an 11-year cycle of activity, usually measured by the number of sunspots. At its peak, the sun often ...
... in such a bubble of particles is comparable to a hundred hurricanes. However, it is especially the magnetic energy of such plasma clouds that can upset technology here at earth. The sun goes through an 11-year cycle of activity, usually measured by the number of sunspots. At its peak, the sun often ...
space
... LlGHJ,YEAR-A measure of distance based on the speed of light (186,000 miles per second) ~ the total number ol seconds 'in a year's time .. ...
... LlGHJ,YEAR-A measure of distance based on the speed of light (186,000 miles per second) ~ the total number ol seconds 'in a year's time .. ...
Solar Instruments for Observing the Sun for Amateurs
... Solar Instruments for Observing the Sun ...
... Solar Instruments for Observing the Sun ...
Unit 1
... As light is blocked, shadows cast by opaque objects change. Earth rotates on an axis (one complete turn every 24 hours) creating day and night Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year = 1 complete revolution). Matter Unit: Air surrounds us, takes up space, and has mass. Matter (mass and volum ...
... As light is blocked, shadows cast by opaque objects change. Earth rotates on an axis (one complete turn every 24 hours) creating day and night Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year = 1 complete revolution). Matter Unit: Air surrounds us, takes up space, and has mass. Matter (mass and volum ...
God, science and you – 2 The solar system
... • Most of the other planets have one or more satellites. Their satellites may be called moons also. ...
... • Most of the other planets have one or more satellites. Their satellites may be called moons also. ...
Chaper 1 part b
... 2. REVOLUTION=the movement of the Earth in orbit around the sun. It takes one year for the Earth to complete one revolution. 3. PRECESSION=the slow conical (top-like) motion of the Earth’ Earth’s axis of rotation. It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to complete one cycle of precession. ...
... 2. REVOLUTION=the movement of the Earth in orbit around the sun. It takes one year for the Earth to complete one revolution. 3. PRECESSION=the slow conical (top-like) motion of the Earth’ Earth’s axis of rotation. It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to complete one cycle of precession. ...
The Science of Astronomy - Ohio Wesleyan University
... measurements of the positions of stars with positions measured by Greek astronomers about 170 years prior • Precession is a slow movement of the celestial poles with respect to the stars caused by shifting alignment of Earth’s rotational axis • Precession causes the coordinates of stars to change wi ...
... measurements of the positions of stars with positions measured by Greek astronomers about 170 years prior • Precession is a slow movement of the celestial poles with respect to the stars caused by shifting alignment of Earth’s rotational axis • Precession causes the coordinates of stars to change wi ...
As can be read from the textbook Fig. 8-9, or... transition has less energy and so a longer wavelength than... 4→3 3→2
... and set the luminosity equal to the rate at which this internal energy changes: GM 2 dR dU L = ------- = ------------ ------dt R 2 dt where I’m being sloppy with signs, but remembering that the sun must shrink in order to release energy. Putting in the relevant values for the sun, you find ...
... and set the luminosity equal to the rate at which this internal energy changes: GM 2 dR dU L = ------- = ------------ ------dt R 2 dt where I’m being sloppy with signs, but remembering that the sun must shrink in order to release energy. Putting in the relevant values for the sun, you find ...
ASTRONOMY
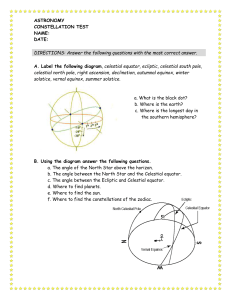
... D. Answer the Following questions with the most complete answer. 1. To which constellation does the big dipper belong? 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet ...
... D. Answer the Following questions with the most complete answer. 1. To which constellation does the big dipper belong? 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet ...
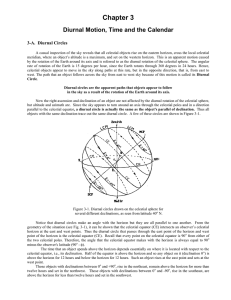
CHAPTER 3, Diurnal Motion - The College of New Jersey
... celestial sphere both change with time and location, but remember, the right ascension and declination do not. Hence, the horizon system is only useful for locating objects on the celestial sphere at a given location on the Earth and at a given instant of time. So, as the celestial sphere appears to ...
... celestial sphere both change with time and location, but remember, the right ascension and declination do not. Hence, the horizon system is only useful for locating objects on the celestial sphere at a given location on the Earth and at a given instant of time. So, as the celestial sphere appears to ...
Tycho Brahe & Johannes Kepler
... – made the most accurate observations of stars and planets up to that time. – was a flamboyant Danish nobleman who wore a silver nose when part of his nose was cut off in a duel! Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) ...
... – made the most accurate observations of stars and planets up to that time. – was a flamboyant Danish nobleman who wore a silver nose when part of his nose was cut off in a duel! Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) ...
Components of the Solar System Learning Targets
... blue color, Rotates top to bottom unlike other planets, at least 27 moons, rings Neptune –gas giant made mostly of hydrogen and helium, methane also in atmosphere that gives the planet i’s blue color, at least 13 moons with the largest one named Triton, gas/liquid/solid layers, rings Target 3: (The ...
... blue color, Rotates top to bottom unlike other planets, at least 27 moons, rings Neptune –gas giant made mostly of hydrogen and helium, methane also in atmosphere that gives the planet i’s blue color, at least 13 moons with the largest one named Triton, gas/liquid/solid layers, rings Target 3: (The ...
solutions - Las Cumbres Observatory
... D. Betelguese is 20 times the mass of the Sun and very near the end of its life. 1. It is 197 parsecs (640 light years) away, but how many magnitudes brighter than the Sun would it look if both stars were 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) away? Using absolute magnitude: MBetelgeuse = MSun - 2.5log ...
... D. Betelguese is 20 times the mass of the Sun and very near the end of its life. 1. It is 197 parsecs (640 light years) away, but how many magnitudes brighter than the Sun would it look if both stars were 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) away? Using absolute magnitude: MBetelgeuse = MSun - 2.5log ...
K-‐8 Earth and Space TEKS Cards
... (B) describe and illustrate the continuous movement of water above and on the surface of Earth through the water cycle and explain the role of the Sun as a major source of energy in this process; and (C) collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, ...
... (B) describe and illustrate the continuous movement of water above and on the surface of Earth through the water cycle and explain the role of the Sun as a major source of energy in this process; and (C) collect and analyze data to identify sequences and predict patterns of change in shadows, tides, ...
Solar System Marius A
... Earth (also the world, in Greek: Γαῖα Gaia, or in Latin: Terra) is the third planet from the Sun, the densest planet in the Solar System,the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 bi ...
... Earth (also the world, in Greek: Γαῖα Gaia, or in Latin: Terra) is the third planet from the Sun, the densest planet in the Solar System,the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 bi ...
SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and
... people use on refrigerators stick to? Any smooth surface? Any metal surface? 3. If a new force were discovered, perhaps related somehow to dark energy or dark matter, how would this force and its effects need to “fit in” with the known four forces? Could it replace one of the existing forces as the ...
... people use on refrigerators stick to? Any smooth surface? Any metal surface? 3. If a new force were discovered, perhaps related somehow to dark energy or dark matter, how would this force and its effects need to “fit in” with the known four forces? Could it replace one of the existing forces as the ...
Comparing the Chemical Compositions of the Sun and Earth
... are hard to reconcile with recent photospheric estimates of ∼ 1.2 (Asplund et al. 2005, Grevesse et al. 2005). However, the investigation of the systematic errors of these techniques is still in its infancy. The ∼ 1.5% of the mass of the Sun that is not H and not He, consists of oxygen (43.0%), carb ...
... are hard to reconcile with recent photospheric estimates of ∼ 1.2 (Asplund et al. 2005, Grevesse et al. 2005). However, the investigation of the systematic errors of these techniques is still in its infancy. The ∼ 1.5% of the mass of the Sun that is not H and not He, consists of oxygen (43.0%), carb ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... Answer the following Multiple Choice Questions by circling the correct response. 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that th ...
... Answer the following Multiple Choice Questions by circling the correct response. 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that th ...