AST 207 Test 1 28 September 2011
... star in the constellation Leo is a “morning star.” A morning star is a bright star that is seen close to the sun in the predawn sky. a. (3 pts.) What is the approximate date? Explain. I drew the horizon on 9/7 just before dawn. (The date must be after 8/21, the date on which the sun is in front of L ...
... star in the constellation Leo is a “morning star.” A morning star is a bright star that is seen close to the sun in the predawn sky. a. (3 pts.) What is the approximate date? Explain. I drew the horizon on 9/7 just before dawn. (The date must be after 8/21, the date on which the sun is in front of L ...
TEST1-WHITE Modern scientific theories are NOT: Testable
... b. The square of the planet’s orbital period is equal to the cube of its average distance c. A planet must move fastest in its obit when far from the Sun d. Epicycles are needed to explain the varying brightnesses of the planets e. Both c. and d. 14. What contribution of astronomy was made by Tycho ...
... b. The square of the planet’s orbital period is equal to the cube of its average distance c. A planet must move fastest in its obit when far from the Sun d. Epicycles are needed to explain the varying brightnesses of the planets e. Both c. and d. 14. What contribution of astronomy was made by Tycho ...
Physical Science Lecture Notes
... 1. Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five “stars” that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars. They called them Wander Stars “planets”. 2. “Wandering Stars” were: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn 3. Greek Astronomer Ptolemy (pronounced “tall-o ...
... 1. Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five “stars” that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars. They called them Wander Stars “planets”. 2. “Wandering Stars” were: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn 3. Greek Astronomer Ptolemy (pronounced “tall-o ...
What are stars?
... Compare the development of a less-massive star with that of a more-massive star. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________ ...
... Compare the development of a less-massive star with that of a more-massive star. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________ ...
Chapter 8, Lesson 4, 2nd Packet, pdf
... Compare the development of a less-massive star with that of a more-massive star. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________ ...
... Compare the development of a less-massive star with that of a more-massive star. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________ ...
Unit 2
... much larger than any solar system planet. The sun produces large amounts of heat and light. The sun is the largest object that can be seen ...
... much larger than any solar system planet. The sun produces large amounts of heat and light. The sun is the largest object that can be seen ...
Earth Science Curriculum Unit 1 Maps and Measurements
... Section 2 Galaxies and the Universe Time: 3 sessions 1. Describe evidence that supports the Big Bang theory. 2. Identify the three main types of galaxies. 3. List several characteristics of the Milky Way Galaxy. Section 3 Radiation from space Time: 2 sessions 1. Explain the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... Section 2 Galaxies and the Universe Time: 3 sessions 1. Describe evidence that supports the Big Bang theory. 2. Identify the three main types of galaxies. 3. List several characteristics of the Milky Way Galaxy. Section 3 Radiation from space Time: 2 sessions 1. Explain the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
Grade 9 Unit 4: Space
... remains of the formation of the solar system pieces of rock floating through space pieces of rock that have entered Earth’s atmosphere ...
... remains of the formation of the solar system pieces of rock floating through space pieces of rock that have entered Earth’s atmosphere ...
Used for stars w/in a few hundred LY
... Scientists do not want to work with large numbers, so they make up new units to measure distances in space with. The two units used in astronomy are: ...
... Scientists do not want to work with large numbers, so they make up new units to measure distances in space with. The two units used in astronomy are: ...
Objectives: Learn what units scientists measure distances in space
... Scientists do not want to work with large numbers, so they make up new units to measure distances in space with. The two units used in astronomy are: ...
... Scientists do not want to work with large numbers, so they make up new units to measure distances in space with. The two units used in astronomy are: ...
03jan13.ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... Axis tilt changes directness of sunlight during the year. ...
... Axis tilt changes directness of sunlight during the year. ...
The Earth in the Universe (solucionario)
... Solar system, while Light-Year is better for distances between stars and galaxies Star-Planet: Star emits its own radiation because nuclear reactions are occurring in it, while the planet doesn’t emit radiation. A.2. Se reproduce la tabla completa. Se marca en rojo la información que aparece ...
... Solar system, while Light-Year is better for distances between stars and galaxies Star-Planet: Star emits its own radiation because nuclear reactions are occurring in it, while the planet doesn’t emit radiation. A.2. Se reproduce la tabla completa. Se marca en rojo la información que aparece ...
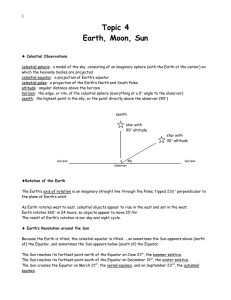
Topic 4: Earth-Moon-Sun
... “catch up” with the Moon’s orbit, the Moon rises 50 minutes later each day. Moon’s period of rotation = 27 days Moon’s period of revolution = 27 days Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the chang ...
... “catch up” with the Moon’s orbit, the Moon rises 50 minutes later each day. Moon’s period of rotation = 27 days Moon’s period of revolution = 27 days Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the chang ...
The long hunt for new objects in our expanding solar
... Earth's orbit. The Dutch astronomer Jan Hendrik which came to be known as Sedna. The discovery Oort hypothesised the existence of a spherical of this Kuiper belt object prompted further searches distribution of icy bodies. The Oort Cloud is thought and much speculation as to its origin – particularl ...
... Earth's orbit. The Dutch astronomer Jan Hendrik which came to be known as Sedna. The discovery Oort hypothesised the existence of a spherical of this Kuiper belt object prompted further searches distribution of icy bodies. The Oort Cloud is thought and much speculation as to its origin – particularl ...
Eratosthenes - Allendale School
... dominated western thought for almost 1500 years. In fact, the geocentric model he proposed is often referred to as the Ptolemaic System. One of the reasons that Ptolemy’s model was so compelling is that people could make accurate predictions based on the math he used. Since in reality, the solar sys ...
... dominated western thought for almost 1500 years. In fact, the geocentric model he proposed is often referred to as the Ptolemaic System. One of the reasons that Ptolemy’s model was so compelling is that people could make accurate predictions based on the math he used. Since in reality, the solar sys ...
INSTITUCIÓN EDUCATIVA LOS GÓMEZ PLAN DE APOYO FECHA
... There are seven other planets that travel around the sun, too. These planets, in order, include Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Earth is located between Venus and Mars. The path the planets use when traveling around the sun is oval-shaped and is called its orbit. Each of ...
... There are seven other planets that travel around the sun, too. These planets, in order, include Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Earth is located between Venus and Mars. The path the planets use when traveling around the sun is oval-shaped and is called its orbit. Each of ...
Seasons
... line around which Earth spins) every 23 hours & 56 minutes. • One day on Earth is one rotation of the Earth. ...
... line around which Earth spins) every 23 hours & 56 minutes. • One day on Earth is one rotation of the Earth. ...
Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
... The Orion Nebula is at the edge of an immense interstellar molecular cloud only 1,500 light-years away--the nearest large star-forming region. ...
... The Orion Nebula is at the edge of an immense interstellar molecular cloud only 1,500 light-years away--the nearest large star-forming region. ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... of the movement of the sun and the moon, and the planets, and the stars were good predictors of future positions of celestial bodies; models were verifiable simplicity (Occam's Razor or the Principle of Parsimony) - as few assumptions or rules as possible; no contradictions. ...
... of the movement of the sun and the moon, and the planets, and the stars were good predictors of future positions of celestial bodies; models were verifiable simplicity (Occam's Razor or the Principle of Parsimony) - as few assumptions or rules as possible; no contradictions. ...
Sun Lecture
... Source of the Sun’s Luminosity is _______________________________ Implications of the Sun’s Luminosity: The Sun produces energy by converting mass into energy. The luminosity of the Sun thus represents a continual mass loss. The Sun is currently converting 4.3 million metric tones of mass into ...
... Source of the Sun’s Luminosity is _______________________________ Implications of the Sun’s Luminosity: The Sun produces energy by converting mass into energy. The luminosity of the Sun thus represents a continual mass loss. The Sun is currently converting 4.3 million metric tones of mass into ...
A SHORT VIDEO What is the Solar System
... Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the solar system, orbiting the Sun once every 88 days. It can only be seen in the morning and evening twilight. Comparatively little is known about it; the first of two spacecraft to approach Mercury was Mariner 10 from 1974 to 1975, which mapped only ...
... Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the solar system, orbiting the Sun once every 88 days. It can only be seen in the morning and evening twilight. Comparatively little is known about it; the first of two spacecraft to approach Mercury was Mariner 10 from 1974 to 1975, which mapped only ...
Section 22.2 The Earth-Moon-Sun System
... Motions of Earth The two main motions of Earth are rotation and revolution. Precession is a third and very slow motion of Earth’s axis. Rotation Rotation is the turning, or spinning, of a body on its axis. Two measurements for rotation: Mean solar day is the time interval from one noon to the ne ...
... Motions of Earth The two main motions of Earth are rotation and revolution. Precession is a third and very slow motion of Earth’s axis. Rotation Rotation is the turning, or spinning, of a body on its axis. Two measurements for rotation: Mean solar day is the time interval from one noon to the ne ...
Star and Planet Formation Star and Planet - A
... 1. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, birds should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. Inadequate understanding of physics ! 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. Inadequate u ...
... 1. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, birds should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. Inadequate understanding of physics ! 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. Inadequate u ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements:
... • Kepler first tried to match Tycho’s observations with circular orbits • But an 8 arcminute discrepancy led him eventually to elliptical orbits… “If I had believed that we could ignore these eight minutes [of arc], I would have patched up my hypothesis accordingly. But, since it was not permissible ...
... • Kepler first tried to match Tycho’s observations with circular orbits • But an 8 arcminute discrepancy led him eventually to elliptical orbits… “If I had believed that we could ignore these eight minutes [of arc], I would have patched up my hypothesis accordingly. But, since it was not permissible ...