Celestial Coordinates Celestial Sphere: The celestial sphere is an
... meridian. The sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.1 seconds long. Sidereal Time: Official sidereal time is the day beginning at the hour angle of the vernal equinox. Star positions are given using this sidereal time. The position of a star with respect to the oberver's meridian is then relat ...
... meridian. The sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.1 seconds long. Sidereal Time: Official sidereal time is the day beginning at the hour angle of the vernal equinox. Star positions are given using this sidereal time. The position of a star with respect to the oberver's meridian is then relat ...
Document
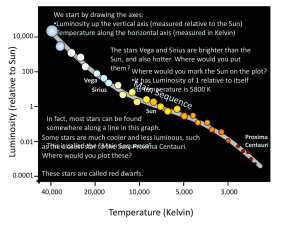
... Almost all stars we see are in one of these groups, but they don’t stay in the same place. ...
... Almost all stars we see are in one of these groups, but they don’t stay in the same place. ...
Planetarium Key Points
... most of this “flattening torque” is caused by the Moon and the Sun. But the Earth is rotating and therefore the torque cannot change the inclination of the equator relative to ecliptic, the rotation axis turns in a direction orthogonal to the axis and to the torque, thus describing a cone once in ro ...
... most of this “flattening torque” is caused by the Moon and the Sun. But the Earth is rotating and therefore the torque cannot change the inclination of the equator relative to ecliptic, the rotation axis turns in a direction orthogonal to the axis and to the torque, thus describing a cone once in ro ...
Document
... sustained for long as new observations will knock down incorrect ideas. Takes time! Leads to Theory! “Real” World ...
... sustained for long as new observations will knock down incorrect ideas. Takes time! Leads to Theory! “Real” World ...
Instructions for
... A. The distance between the Sun and Earth is 400 times greater than the distance between the Moon and Earth. B. This galaxy cannot be our galaxy (the Milky Way) because we are able to see the entire galaxy. It is not possible to travel outside of our galaxy to obtain an image like this one. If you c ...
... A. The distance between the Sun and Earth is 400 times greater than the distance between the Moon and Earth. B. This galaxy cannot be our galaxy (the Milky Way) because we are able to see the entire galaxy. It is not possible to travel outside of our galaxy to obtain an image like this one. If you c ...
View SKYTRACK_Glossary of Terms
... Tropical year – The length of time that the Sun, as viewed from the Earth, takes to return to the same position along the ecliptic, such as a solstice or equinox. The mean interval between two vernal equinoxes is 365.242 days long. The tropical year differs from the solar year by one part in about 2 ...
... Tropical year – The length of time that the Sun, as viewed from the Earth, takes to return to the same position along the ecliptic, such as a solstice or equinox. The mean interval between two vernal equinoxes is 365.242 days long. The tropical year differs from the solar year by one part in about 2 ...
Solar System powerpoint
... • Planetary Year-the length of time it takes a planet to revolve around the sun. ...
... • Planetary Year-the length of time it takes a planet to revolve around the sun. ...
Slayt 1
... • The closest star other than the Sun is about 4 light years away. • Mean separation between the stars is much greater than the mean diameters of the stars (approx. 50 million times). • It is very unlikely that two stars moving in the galaxy collide. ...
... • The closest star other than the Sun is about 4 light years away. • Mean separation between the stars is much greater than the mean diameters of the stars (approx. 50 million times). • It is very unlikely that two stars moving in the galaxy collide. ...
Earth in space
... Student pairs – one is the Sun, the other is the Earth. • ‘Sun’ writes down instructions for how the Earth should move over a 24h period. • ‘Earth’ writes down instructions for how Sun should move over a 24h period. ...
... Student pairs – one is the Sun, the other is the Earth. • ‘Sun’ writes down instructions for how the Earth should move over a 24h period. • ‘Earth’ writes down instructions for how Sun should move over a 24h period. ...
The Earth in Motion
... How fast does the Earth rotate? a. There are 360 degrees in a sphere b. There are 24 hours in one day. ...
... How fast does the Earth rotate? a. There are 360 degrees in a sphere b. There are 24 hours in one day. ...
Conditions for Life
... Part III The temperature on Earth does not go from one extreme to the other. There are areas of extreme cold and heat, but overall, the Earth’s climate is stable. This is due to Earth’s distance from the Sun as it orbits around it and its axial tilt during rotation. Look at a globe of Earth. Notice ...
... Part III The temperature on Earth does not go from one extreme to the other. There are areas of extreme cold and heat, but overall, the Earth’s climate is stable. This is due to Earth’s distance from the Sun as it orbits around it and its axial tilt during rotation. Look at a globe of Earth. Notice ...
Pocket Almanac - California Academy of Sciences
... two eclipses of the Sun and two of the Moon. The two solar eclipses feature one of each kind—total and annular—but neither is visible from the contiguous states of the U.S. The two lunar eclipses are penumbral and barely perceptible. ...
... two eclipses of the Sun and two of the Moon. The two solar eclipses feature one of each kind—total and annular—but neither is visible from the contiguous states of the U.S. The two lunar eclipses are penumbral and barely perceptible. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Planetary Configurations
... Earth longitude but for the sky; RA is measured Eastward starting from the Vernal Equinox • Declination (Dec) - similar to Earth latitude but for the sky; Dec is positive in the North Celestial Sphere and negative in the South • Celestial Poles - projection of North and South Poles onto the sky ...
... Earth longitude but for the sky; RA is measured Eastward starting from the Vernal Equinox • Declination (Dec) - similar to Earth latitude but for the sky; Dec is positive in the North Celestial Sphere and negative in the South • Celestial Poles - projection of North and South Poles onto the sky ...
Stream: sciences. E THIRD TERM ENGLISH EXAMINATION PART
... orbits the centre of our home galaxy, a spiral disk of 200 billion stars we call the Milky Way. The nearest large galaxy is the Andromeda Galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way but is 4 times as massive and is 2 million light years away. Our galaxy, one of billions of galaxies known, is tr ...
... orbits the centre of our home galaxy, a spiral disk of 200 billion stars we call the Milky Way. The nearest large galaxy is the Andromeda Galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way but is 4 times as massive and is 2 million light years away. Our galaxy, one of billions of galaxies known, is tr ...
Name
... degrees, distance from sun about 30 au. Set the time step to one year. Make the time go forward and notice which way the planets move (______________________). By the way, what is 1 au? ______________________________ Return to Earth, please. Unlock the sun. B. What did the solar system look like on ...
... degrees, distance from sun about 30 au. Set the time step to one year. Make the time go forward and notice which way the planets move (______________________). By the way, what is 1 au? ______________________________ Return to Earth, please. Unlock the sun. B. What did the solar system look like on ...
File
... popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the future - slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque (such as gravitational influence) acting to change the direction of the first axis – it means that we will have a ne ...
... popular name but smaller than a constellation 12. Explain precession and what it means in the future - slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque (such as gravitational influence) acting to change the direction of the first axis – it means that we will have a ne ...
What is a scientific model?
... in AUs and orbital periods) But: • This model was no more accurate than Ptolemaic model in predicting planetary positions, because still used perfect circles. ...
... in AUs and orbital periods) But: • This model was no more accurate than Ptolemaic model in predicting planetary positions, because still used perfect circles. ...
s*t*a*r chart - Ontario Science Centre
... MERCURY begins the year on the western horizon at twilight and reaches its greatest elongation west of the Sun, placing it at its highest point in our eastern morning sky on February 7. ...
... MERCURY begins the year on the western horizon at twilight and reaches its greatest elongation west of the Sun, placing it at its highest point in our eastern morning sky on February 7. ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known luminosity can be identified in distant galaxies • Cepheid Variable Stars ...
... stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known luminosity can be identified in distant galaxies • Cepheid Variable Stars ...
Homework # 2 1. For each of the following, make a sketch showing
... Galileo was able to resolve the band of the Milky Way into individual stars ...
... Galileo was able to resolve the band of the Milky Way into individual stars ...
Astronomy Quiz Units 1 to 3
... A conceptual model of the Sky Carries the stars Appears to rotate westward once every 23h 56m 4.09s NCP, SCP and Celestial Equator are aligned with the Earth’s north pole, south pole and equator respectively. Is divided into regions using Right Ascension and Declination. 8. What are specia ...
... A conceptual model of the Sky Carries the stars Appears to rotate westward once every 23h 56m 4.09s NCP, SCP and Celestial Equator are aligned with the Earth’s north pole, south pole and equator respectively. Is divided into regions using Right Ascension and Declination. 8. What are specia ...
Earth`s Place in the Universe Test 1
... D) the time it takes light to travel from Earth to the Sun. 3) Hunter goes outside and notices that the sun looks larger than the other stars he has seen. Why does the sun appear larger than the other stars? The Sun looks larger because it's closer to A) The Sun is the largest star in the sky. C) Ea ...
... D) the time it takes light to travel from Earth to the Sun. 3) Hunter goes outside and notices that the sun looks larger than the other stars he has seen. Why does the sun appear larger than the other stars? The Sun looks larger because it's closer to A) The Sun is the largest star in the sky. C) Ea ...