Exam 1 Astronomy 100, Section 3 Select the most appropriate
... (B) The Earth travels about 30 degrees around the Sun in each month, and this adds 2 days between new moons. (C) One full Earth rotation takes less than 24 hrs, and it adds up to about 2 days in one month. (D) The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is not perfectly circular. (E) The Earth rotation axis i ...
... (B) The Earth travels about 30 degrees around the Sun in each month, and this adds 2 days between new moons. (C) One full Earth rotation takes less than 24 hrs, and it adds up to about 2 days in one month. (D) The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is not perfectly circular. (E) The Earth rotation axis i ...
The plane of the Moon`s orbit has an inclination of 5.15 degree to
... Some authorities believe that the value of the Cosmic Yuga mentioned above is the LCM of the sidereal periods of all the seven planets. It is not possible to verify such a claim mathematically based on the astronomical data available at present. Vishwamitra’s mystic number 3339 gives a better and a ...
... Some authorities believe that the value of the Cosmic Yuga mentioned above is the LCM of the sidereal periods of all the seven planets. It is not possible to verify such a claim mathematically based on the astronomical data available at present. Vishwamitra’s mystic number 3339 gives a better and a ...
The Science of Sunshine
... The Sun has spent its 4.5 billion years of existence maintaining a delicate equilibrium. The Sun contains a lot of material, equivalent to more than 330 000 Earths. This means its gravitational pull is very strong, if you could stand on the surface of the Sun, you would be nearly thirty times as hea ...
... The Sun has spent its 4.5 billion years of existence maintaining a delicate equilibrium. The Sun contains a lot of material, equivalent to more than 330 000 Earths. This means its gravitational pull is very strong, if you could stand on the surface of the Sun, you would be nearly thirty times as hea ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... Explanation: Yes it does look like Saturn, but Saturn is only one of four giant ringed planets in our Solar System. And while Saturn has the brightest rings, this system of rings and moons actually belongs to planet Uranus, imaged here in near-infrared light by the Antu telescope at the ESO Paranal ...
... Explanation: Yes it does look like Saturn, but Saturn is only one of four giant ringed planets in our Solar System. And while Saturn has the brightest rings, this system of rings and moons actually belongs to planet Uranus, imaged here in near-infrared light by the Antu telescope at the ESO Paranal ...
Key Stage 2: Teacher`s Pack
... 16. How does this demonstrate one advantage of building big telescopes? Increases collecting area, so can see fainter (and further) objects 17. What were bright radio sources originally called, when first discovered in the 1940s? Radio stars 18. Name the two brightest radio sources that are ‘visible ...
... 16. How does this demonstrate one advantage of building big telescopes? Increases collecting area, so can see fainter (and further) objects 17. What were bright radio sources originally called, when first discovered in the 1940s? Radio stars 18. Name the two brightest radio sources that are ‘visible ...
Day 1: How to Describe the Sky The Motions of the Stars
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
Lecture 2 - The University Centre in Svalbard
... The summer of 1609 Galileo Galilei (1564 – 1642) learned about a new invention in the Netherlands that could bring far objects to appear closer. An optician had made the first telescope. Galileo bought some lenses from his local optician and build his own telescope. When he pointed the telescope tow ...
... The summer of 1609 Galileo Galilei (1564 – 1642) learned about a new invention in the Netherlands that could bring far objects to appear closer. An optician had made the first telescope. Galileo bought some lenses from his local optician and build his own telescope. When he pointed the telescope tow ...
Lecture 1 – Astronomy
... The summer of 1609 Galileo Galilei (1564 – 1642) learned about a new invention in the Netherlands that could bring far objects to appear closer. An optician had made the first telescope. Galileo bought some lenses from his local optician and build his own telescope. When he pointed the telescope tow ...
... The summer of 1609 Galileo Galilei (1564 – 1642) learned about a new invention in the Netherlands that could bring far objects to appear closer. An optician had made the first telescope. Galileo bought some lenses from his local optician and build his own telescope. When he pointed the telescope tow ...
2016-0620-Mountain-Skies
... The planets: The planets and the moon circle our sky along a path that goes through twelve very famous constellations and one not so famous (Ophiuchus). As we look at the planets in the sky, we notice that they are not scattered all about but lie close to being in ...
... The planets: The planets and the moon circle our sky along a path that goes through twelve very famous constellations and one not so famous (Ophiuchus). As we look at the planets in the sky, we notice that they are not scattered all about but lie close to being in ...
The Night Sky
... beginning of July. The sun is now starting to move northward on its yearly cycle around the sky. As a result of this, sunsets start arriving later in the evening and sunrises start arriving earlier in the morning. January’s full moon, known in folklore as the wolf moon, rises at sunset on January 26 ...
... beginning of July. The sun is now starting to move northward on its yearly cycle around the sky. As a result of this, sunsets start arriving later in the evening and sunrises start arriving earlier in the morning. January’s full moon, known in folklore as the wolf moon, rises at sunset on January 26 ...
Eclipse of the Sun 1 September 2016
... Solar Eclipses have historically been viewed in the ancient past as omens that bring about death and destruction. King Henry's Eclipse: King Henry I died shortly after an eclipse in 1133, prompting the spread of the superstition that eclipses are bad omens for rulers ...
... Solar Eclipses have historically been viewed in the ancient past as omens that bring about death and destruction. King Henry's Eclipse: King Henry I died shortly after an eclipse in 1133, prompting the spread of the superstition that eclipses are bad omens for rulers ...
Complete the following review packet!
... 46. Approximately how long ago was the glaciation period that produced these moraines? ...
... 46. Approximately how long ago was the glaciation period that produced these moraines? ...
TOP 78 ASTRONOMY FACTS 1. The solar system consists of the
... 57. Nicolaus Copernicus (February 19, 1473 – May 24, 1543) was an astronomer who provided the first modern formulation of a heliocentric (sun-centered) theory of the solar system. His formulation of how the sun, rather than the earth, is at the center of the universe is considered one of the most im ...
... 57. Nicolaus Copernicus (February 19, 1473 – May 24, 1543) was an astronomer who provided the first modern formulation of a heliocentric (sun-centered) theory of the solar system. His formulation of how the sun, rather than the earth, is at the center of the universe is considered one of the most im ...
No Spring Picnic on Neptune
... from the Galileo spacecraft. All photos are visible light images except Uranus, which is an infrared image. Axis tilt source: The Solar System: The Cosmic ...
... from the Galileo spacecraft. All photos are visible light images except Uranus, which is an infrared image. Axis tilt source: The Solar System: The Cosmic ...
1 Timeline 2 Geocentric model
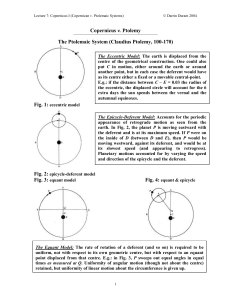
... • Ptolemy invented the device called the eccentric • The eccentric is the center of the deferent • Sometimes the eccentric was slightly off center from the center of the Earth Ptolemy’s Geocentric Model • Uniform circular motion could not account for speed of the planets thus Ptolemy used a device c ...
... • Ptolemy invented the device called the eccentric • The eccentric is the center of the deferent • Sometimes the eccentric was slightly off center from the center of the Earth Ptolemy’s Geocentric Model • Uniform circular motion could not account for speed of the planets thus Ptolemy used a device c ...
Chapter 13: Earth, Moon, and Beyond
... As Earth revolves around the sun, different parts of Earth are tilted toward Earth. When your part of Earth is tilted toward the sun, it is summer for you. The path that Earth moves on around the sun is called its orbit. ...
... As Earth revolves around the sun, different parts of Earth are tilted toward Earth. When your part of Earth is tilted toward the sun, it is summer for you. The path that Earth moves on around the sun is called its orbit. ...
Navigation Methods
... • Compass: Point to magnetic North, so you can follow a course by knowing our position in relation to North. • Loran C: radio transmissions from set positions on the surface of the Earth, that triangulate to give you a position. ...
... • Compass: Point to magnetic North, so you can follow a course by knowing our position in relation to North. • Loran C: radio transmissions from set positions on the surface of the Earth, that triangulate to give you a position. ...
astronomy 31 - UNC Physics
... D. Because Earth rotates, the stars appear to move around the north celestial pole in the northern hemisphere and the south celestial pole in the southern hemisphere. When standing at the north pole, the north celestial pole is directly overhead and when standing at the south pole the south celestia ...
... D. Because Earth rotates, the stars appear to move around the north celestial pole in the northern hemisphere and the south celestial pole in the southern hemisphere. When standing at the north pole, the north celestial pole is directly overhead and when standing at the south pole the south celestia ...
Lec 7 Copernicus I
... times as measured at Q. Uniformity of angular motion (though not about the centre) retained, but uniformity of linear motion about the circumference is given up. ...
... times as measured at Q. Uniformity of angular motion (though not about the centre) retained, but uniformity of linear motion about the circumference is given up. ...
HR Diagram
... 4. Select File> Run Exercise>HR Diagram of Cluster. 5. Under Tools choose HR Diagram Analysis. 6. Then select File>Load Plot>Select Cluster Data. Start with the intermediate age NGC 752. Double click to load graph. Under tools choose Zero Age Main Sequence. Adjust the V-Mv scroll bar to get the best ...
... 4. Select File> Run Exercise>HR Diagram of Cluster. 5. Under Tools choose HR Diagram Analysis. 6. Then select File>Load Plot>Select Cluster Data. Start with the intermediate age NGC 752. Double click to load graph. Under tools choose Zero Age Main Sequence. Adjust the V-Mv scroll bar to get the best ...
Lesson 3: what is the solar system?
... seems to have in the sky when it is observed from Earth. Lunar Cycle: the pattern of phases of the Moon. Lunar Eclipse: an event in which Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. Solar Eclipse: an event that occurs when the Moon blocks the sunlight from reaching Earth and the Moon’s shadow fall ...
... seems to have in the sky when it is observed from Earth. Lunar Cycle: the pattern of phases of the Moon. Lunar Eclipse: an event in which Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. Solar Eclipse: an event that occurs when the Moon blocks the sunlight from reaching Earth and the Moon’s shadow fall ...
question sheet
... 2. (A) Go to your diagram of the Earth/Sun system (from 3/24) and add an Earth (with axis) for Fall, an Earth (with axis) for Spring, and an Earth (w/axis) for Summer (use pencil!). LABEL the season for each Earth. (B) What parts of the diagram are unrealistically portrayed? Why do we use this diagr ...
... 2. (A) Go to your diagram of the Earth/Sun system (from 3/24) and add an Earth (with axis) for Fall, an Earth (with axis) for Spring, and an Earth (w/axis) for Summer (use pencil!). LABEL the season for each Earth. (B) What parts of the diagram are unrealistically portrayed? Why do we use this diagr ...
From Here on Earth
... Recorded on April 15th, this total lunar eclipse sequence looks south down icy Waterton Lake from the Waterton Lakes National Park in Alberta, Canada. An exposure every 10 minutes captured the Moon's position and eclipse phase, above the rugged skyline and town lights. The sequence actually effectiv ...
... Recorded on April 15th, this total lunar eclipse sequence looks south down icy Waterton Lake from the Waterton Lakes National Park in Alberta, Canada. An exposure every 10 minutes captured the Moon's position and eclipse phase, above the rugged skyline and town lights. The sequence actually effectiv ...
Constellations
... C. The number of weeks in a year D. The number of years in a decade 3. Astronomers recognize the Orion Nebula as a large celestial body. What can you infer about the Orion Nebula from its name? A. It is a star in the constellation Orion B. It plays an important role in the myth of Orion C. It is loc ...
... C. The number of weeks in a year D. The number of years in a decade 3. Astronomers recognize the Orion Nebula as a large celestial body. What can you infer about the Orion Nebula from its name? A. It is a star in the constellation Orion B. It plays an important role in the myth of Orion C. It is loc ...