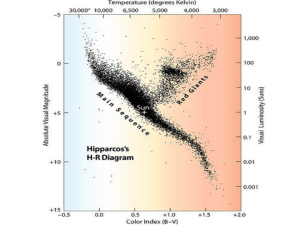
What tool do astronomers use to understand the evolution of stars?
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
Robert_Minchin_Galaxies_2011_REU
... tells us how gas-rich a galaxy is. – Gas-rich galaxies are often blue, late-type galaxies with active star formation. – Some are more intriguing objects with low SF rates. A number of these have been turned up by HI surveys. ...
... tells us how gas-rich a galaxy is. – Gas-rich galaxies are often blue, late-type galaxies with active star formation. – Some are more intriguing objects with low SF rates. A number of these have been turned up by HI surveys. ...
Constants and Equations
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
The cosmic distance scale
... Figure 2: Discovery image of SN2006X in M100. Earlier it was mentioned that all SN Ia ought to have the same absolute magnitude because the white dwarf star of the system explodes when it reaches a certain mass (which applies everywhere in the universe). This is however not exactly true, different w ...
... Figure 2: Discovery image of SN2006X in M100. Earlier it was mentioned that all SN Ia ought to have the same absolute magnitude because the white dwarf star of the system explodes when it reaches a certain mass (which applies everywhere in the universe). This is however not exactly true, different w ...
Structure of the solar system
... O ≥ 30,000 K blue (most massive) B 10,000–30,000 K blue to blue white A 7,500–10,000 K white F 6,000–7,500 K yellowish white G 5,200–6,000 K yellow K 3,700–5,200 K orange M ≤ 3,700 K red (least massive) Our star, The Sun, is a class G star and is yellowish. ...
... O ≥ 30,000 K blue (most massive) B 10,000–30,000 K blue to blue white A 7,500–10,000 K white F 6,000–7,500 K yellowish white G 5,200–6,000 K yellow K 3,700–5,200 K orange M ≤ 3,700 K red (least massive) Our star, The Sun, is a class G star and is yellowish. ...
17 The Deaths of Stars
... 1. A small star that is the extremely dense core of the original star made of helium, carbon, oxygen, or neon depending on the original size of the star. Gravitational contraction quickly forces the material into electron degeneracy. It is called a white dwarf. 2. An envelope expanding away from the ...
... 1. A small star that is the extremely dense core of the original star made of helium, carbon, oxygen, or neon depending on the original size of the star. Gravitational contraction quickly forces the material into electron degeneracy. It is called a white dwarf. 2. An envelope expanding away from the ...
Document
... spiral galaxy – 100,000 light years wide – 16,000 light years thick at the centre – has three distinct spiral arms - Sun is positioned in one of these arms about two-thirds of the way from the galactic center, at a distance of about 30,000 lightyears The Andromeda Galaxy, M31, is the nearest major ...
... spiral galaxy – 100,000 light years wide – 16,000 light years thick at the centre – has three distinct spiral arms - Sun is positioned in one of these arms about two-thirds of the way from the galactic center, at a distance of about 30,000 lightyears The Andromeda Galaxy, M31, is the nearest major ...
How do the most massive galaxies constrain theories of
... The two types are divided by a critical mass ~3x1010 Msun old, no recent star formation, ...
... The two types are divided by a critical mass ~3x1010 Msun old, no recent star formation, ...
Essay - CLC Charter School
... bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. For this to happen though, the star must be 10 times the size of the sun at least. So the supernova leaves a large core, and with no energy to fuse it doesn’t have any outward pressure, and that causes it to be very unbalan ...
... bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. For this to happen though, the star must be 10 times the size of the sun at least. So the supernova leaves a large core, and with no energy to fuse it doesn’t have any outward pressure, and that causes it to be very unbalan ...
1-1 H. Color Index: A color index is the difference of two color
... when seen from a distance of 10 parsecs (See Appendix A on measuring stellar distances). However, the absolute magnitude scale is a relative scale of absolute or intrinsic brightness. Astronomers use absolute magnitudes to express which stars are truly bright and which are truly faint, because dista ...
... when seen from a distance of 10 parsecs (See Appendix A on measuring stellar distances). However, the absolute magnitude scale is a relative scale of absolute or intrinsic brightness. Astronomers use absolute magnitudes to express which stars are truly bright and which are truly faint, because dista ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... magnitude of about -26.5 Sirius is next in line, with an apparent magnitude of -1.5; how many times brighter is the Sun than Sirius? a) 25 ...
... magnitude of about -26.5 Sirius is next in line, with an apparent magnitude of -1.5; how many times brighter is the Sun than Sirius? a) 25 ...
annie jump cannon
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
Northern and Southern Hemisphere Star Chart
... basically enormous balls of very hot gas, mainly hydrogen, with some helium and small amounts of a few other things. Inside the star huge quantities of energy are generated by a nuclear process called fusion. Planets, in contrast are balls of rock, metal and gas with no internal nuclear energy sourc ...
... basically enormous balls of very hot gas, mainly hydrogen, with some helium and small amounts of a few other things. Inside the star huge quantities of energy are generated by a nuclear process called fusion. Planets, in contrast are balls of rock, metal and gas with no internal nuclear energy sourc ...
2. - Quia
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on your chart? Why or why not? 2. The Voyager spacecraft were equipped with CDs that contain pictures and sounds depicting our world. One of the Voyager spacecraft is actually headed towards Sirius. If there is an inte ...
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on your chart? Why or why not? 2. The Voyager spacecraft were equipped with CDs that contain pictures and sounds depicting our world. One of the Voyager spacecraft is actually headed towards Sirius. If there is an inte ...
Lecture Notes – Galaxies
... Clusters of Galaxies Contain from 10 – 1000s of galaxies, and are gravitationally bound systems. Spacing of galaxies is realtively close, ≈ 100 times diameter of galaxy. (For comparison, in our Galaxy the spacing of stars ≈ 106 diameter of a typical star.) Rich clusters (> 100 members) contain mostl ...
... Clusters of Galaxies Contain from 10 – 1000s of galaxies, and are gravitationally bound systems. Spacing of galaxies is realtively close, ≈ 100 times diameter of galaxy. (For comparison, in our Galaxy the spacing of stars ≈ 106 diameter of a typical star.) Rich clusters (> 100 members) contain mostl ...
Some Facts and Hypotheses regard
... stars, which cannot be explained away by any supposition of mistaken entries, It may be that such stars are in reality periodic, possessing a periodicity far exceeding the limits of time within which the heavens have been observed with any scientific accuracy. In this case they will at some future e ...
... stars, which cannot be explained away by any supposition of mistaken entries, It may be that such stars are in reality periodic, possessing a periodicity far exceeding the limits of time within which the heavens have been observed with any scientific accuracy. In this case they will at some future e ...
Constellations - Brown University Wiki
... 4)a) Set your planimeter for midnight January 1. Notice that the visible sky is identical to the one on February 1 at 10 p.m. and at March 2 at 8 p.m.. Prove that this is to be expected, by making a sketch of the rotating and orbiting earth. b) Rotate the disc from midnight January 1 forward, to la ...
... 4)a) Set your planimeter for midnight January 1. Notice that the visible sky is identical to the one on February 1 at 10 p.m. and at March 2 at 8 p.m.. Prove that this is to be expected, by making a sketch of the rotating and orbiting earth. b) Rotate the disc from midnight January 1 forward, to la ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
color-stellar mass diagram
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.