The Cosmic Near-Infrared Background: Remnant light form
... due to the mass spectrum could be large. •An accurate determination of the near-infrared background allows us to probe the formation history of early stars, which is difficult to constrain by other means. •A reasonable initial mass function, coupled with this star formation rate, does not overproduc ...
... due to the mass spectrum could be large. •An accurate determination of the near-infrared background allows us to probe the formation history of early stars, which is difficult to constrain by other means. •A reasonable initial mass function, coupled with this star formation rate, does not overproduc ...
The Scales of Things
... Cepheid variable stars are pulsating stars, named after the brightest member of the class, Delta Cephei. Cepheids are brightest when they are hottest, close to the minimum size. Since all Cepheids are about the same temperature, the size of a Cepheid determines its luminosity. Thus there is a per ...
... Cepheid variable stars are pulsating stars, named after the brightest member of the class, Delta Cephei. Cepheids are brightest when they are hottest, close to the minimum size. Since all Cepheids are about the same temperature, the size of a Cepheid determines its luminosity. Thus there is a per ...
What is a Star - Optics Institute of Southern California
... star as the internal pressure gradient balances against the force of gravity. Another way of thinking about this is to imagine the star as a large number of nested thin spherical shells (sort of like an onion). The inward forces on each shell consist of the gravitational pull from all the shells ins ...
... star as the internal pressure gradient balances against the force of gravity. Another way of thinking about this is to imagine the star as a large number of nested thin spherical shells (sort of like an onion). The inward forces on each shell consist of the gravitational pull from all the shells ins ...
Measuring Distances
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
What is a Star?
... a. absolute magnitude: actual brightness of a star (like absolute values in math) b. apparent magnitude: how bright a star appears based on its energy output, distance from you, & comparison to other stars ...
... a. absolute magnitude: actual brightness of a star (like absolute values in math) b. apparent magnitude: how bright a star appears based on its energy output, distance from you, & comparison to other stars ...
Globular Clusters
... some idea of how much better it must look further north. But it still can't compare with Omega Cen, 47 Tuc, M22, Pavo, or Ara globs - all of which are bigger, brighter, and closer. Even M5 is the same brightness and distance, but M13 claims first prize because it is bigger and higher in the Northern ...
... some idea of how much better it must look further north. But it still can't compare with Omega Cen, 47 Tuc, M22, Pavo, or Ara globs - all of which are bigger, brighter, and closer. Even M5 is the same brightness and distance, but M13 claims first prize because it is bigger and higher in the Northern ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
Star Cycle Balloons - Communicating Astronomy With The Public
... Time Allotment One class period (40 minutes) Hints The activity maybe conducted as a whole-class lesson or in small groups. The directions presented are for small groups of four. Vocabulary Nebula Planetary nebula Red giant White dwarf Black dwarf Red super giant Star Neutron Remnants ...
... Time Allotment One class period (40 minutes) Hints The activity maybe conducted as a whole-class lesson or in small groups. The directions presented are for small groups of four. Vocabulary Nebula Planetary nebula Red giant White dwarf Black dwarf Red super giant Star Neutron Remnants ...
sa`d al-malik - WordPress.com
... • It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. •It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Erida ...
... • It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. •It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Erida ...
Life Cycle of Stars Activity
... Time Allotment One class period (40 minutes) Hints The activity maybe conducted as a whole-class lesson or in small groups. The directions presented are for small groups of four. Vocabulary Nebula Planetary nebula Red giant White dwarf Black dwarf Red super giant Star Neutron Remnants ...
... Time Allotment One class period (40 minutes) Hints The activity maybe conducted as a whole-class lesson or in small groups. The directions presented are for small groups of four. Vocabulary Nebula Planetary nebula Red giant White dwarf Black dwarf Red super giant Star Neutron Remnants ...
lecture19 - Stony Brook University
... ray) intensity blinks on and off with a 0.24 sec. Period. ...
... ray) intensity blinks on and off with a 0.24 sec. Period. ...
shirley - Yancy L. Shirley`s Webpage
... How do you form a star with M > 10 Msun before radiation pressure stops accretion? ...
... How do you form a star with M > 10 Msun before radiation pressure stops accretion? ...
Stars - MrCrabtreesScience
... – Distance from the center of the black hole beyond which nothing can escape ...
... – Distance from the center of the black hole beyond which nothing can escape ...
3Nov_2014
... Stars begin as clouds of gas and dust, which collapse to form a stellar disk. This disk eventually becomes a star. The star eventually runs out of nuclear fuel and dies. The manner of its death depends on its mass. ...
... Stars begin as clouds of gas and dust, which collapse to form a stellar disk. This disk eventually becomes a star. The star eventually runs out of nuclear fuel and dies. The manner of its death depends on its mass. ...
Diapositiva 1
... and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1") resembles, on the best plates, a slightly diffuse star with a very short curved, nebulous "tail" extending for 5" in p.a. 52º. Its visual ma ...
... and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1") resembles, on the best plates, a slightly diffuse star with a very short curved, nebulous "tail" extending for 5" in p.a. 52º. Its visual ma ...
Characteristics of Stars
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
20_LectureOutline
... is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust cloud? (Then where is it?) Could its companion have been a red giant? (It became a white dwarf very quickly, then!) ...
... is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust cloud? (Then where is it?) Could its companion have been a red giant? (It became a white dwarf very quickly, then!) ...
Lecture 6: Stellar Distances and Brightness
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
SPA 302: THE EVOLUTION OF STARS LECTURE 1: BASICS OF
... proof that these elements are present in stars. The strength of the observed spectral lines can in some cases such as for Hydrogen indicate the abundance of the corresponding element. However, the line strength also depends on many other factors such as temperature, pressure and turbulence in stella ...
... proof that these elements are present in stars. The strength of the observed spectral lines can in some cases such as for Hydrogen indicate the abundance of the corresponding element. However, the line strength also depends on many other factors such as temperature, pressure and turbulence in stella ...
Distances of the Stars
... • it is intrinsically very luminous? • it is intrinsically faint but located nearby? ...
... • it is intrinsically very luminous? • it is intrinsically faint but located nearby? ...
PPT
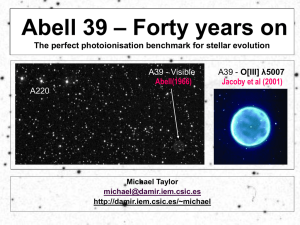
... higher brightness at left rim? Jacoby et al (2001) Conservation of momentum ΔM ≈ 0.05 M סּ 0.9 kms-1 ...
... higher brightness at left rim? Jacoby et al (2001) Conservation of momentum ΔM ≈ 0.05 M סּ 0.9 kms-1 ...
(as Main Sequence Stars)?
... (amount of energy put out every second in form of radiation). Luminosity also called “absolute brightness”. How bright a star appears to us is the “apparent brightness”, which depends on its luminosity and distance from us: apparent brightness ...
... (amount of energy put out every second in form of radiation). Luminosity also called “absolute brightness”. How bright a star appears to us is the “apparent brightness”, which depends on its luminosity and distance from us: apparent brightness ...
Low Mass
... Formation of Planetary Nebula • Double-shell burning causes strong stellar winds, star expels all of its outer layers • Expelled material, rich in heavy elements such as carbon and silicon, forms planetary nebula. • ~60% of mass is lost in planetary nebula • The process of expelling material and for ...
... Formation of Planetary Nebula • Double-shell burning causes strong stellar winds, star expels all of its outer layers • Expelled material, rich in heavy elements such as carbon and silicon, forms planetary nebula. • ~60% of mass is lost in planetary nebula • The process of expelling material and for ...
Participant Handout - Math Machines Home
... actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in watts (just like a light bulb) or in solar luminosities. Betelgeuse, for example, emits the same amount of light as a 20-nonillion watt light bulb. (That is 20x1030 or 20,000,0 ...
... actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in watts (just like a light bulb) or in solar luminosities. Betelgeuse, for example, emits the same amount of light as a 20-nonillion watt light bulb. (That is 20x1030 or 20,000,0 ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.