The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
Luminosity
... These two stars have about the same luminosity— which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity— which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
Lecture 12: Evolution of the Galaxy
... • New stars which form therefore have higher values of heavy element mass fraction, Z, at the time of their birth. The youngest stars are therefore the most heavy-element rich, and the oldest ones (Population II stars) are the most deficient in heavy elements relative to the Sun. • Halo Population I ...
... • New stars which form therefore have higher values of heavy element mass fraction, Z, at the time of their birth. The youngest stars are therefore the most heavy-element rich, and the oldest ones (Population II stars) are the most deficient in heavy elements relative to the Sun. • Halo Population I ...
Chapter 13 The Life of a Star The Life of a Star Mass Is the Key The
... cools transforming the Sun into a red giant • After one billion years, the red giant’s core will be hot enough to begin fusing helium • The Sun will then transform into a pulsating yellow giant ...
... cools transforming the Sun into a red giant • After one billion years, the red giant’s core will be hot enough to begin fusing helium • The Sun will then transform into a pulsating yellow giant ...
Chapter 13
... star and creating bright blobs, “Herbig-Haro objects”, where the jet hits surrounding, distant gas ...
... star and creating bright blobs, “Herbig-Haro objects”, where the jet hits surrounding, distant gas ...
Stars - CBSD.org
... • Hipparchus decided that all the brightest stars in the night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’ ...
... • Hipparchus decided that all the brightest stars in the night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’ ...
Surveying the Stars
... other lines. Called them “F stars” • Yellow stars, with prominent double line in the yellow part of spectrum. Called them “G stars”. • Orange stars, with very weak H lines and tons of other lines. Skip some more letters and call them “K stars”. • Red stars, with no H lines, tons of lines, even big t ...
... other lines. Called them “F stars” • Yellow stars, with prominent double line in the yellow part of spectrum. Called them “G stars”. • Orange stars, with very weak H lines and tons of other lines. Skip some more letters and call them “K stars”. • Red stars, with no H lines, tons of lines, even big t ...
Ramin A. Skibba - Southern California Center for Galaxy Evolution
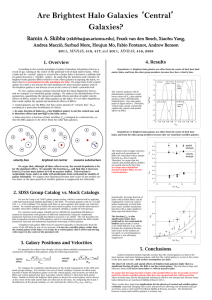
... Galaxy formation models typically assume that the central galaxy in a halo is the most massive and most luminous galaxy, and that the central galaxy is at rest at the center of the dark matter halo. Both of these assumptions are false. The observed velocity and spatial offsets of brightest halo gala ...
... Galaxy formation models typically assume that the central galaxy in a halo is the most massive and most luminous galaxy, and that the central galaxy is at rest at the center of the dark matter halo. Both of these assumptions are false. The observed velocity and spatial offsets of brightest halo gala ...
3-color photometry of stellar cluster - Kiepenheuer
... Beforehand one should decide which star cluster should be observed. In good practice one determines important properties (angular diameter, position, brightness...) of this specific cluster and then also looks for possible standard sources. One should also keep in mind that the specific object shoul ...
... Beforehand one should decide which star cluster should be observed. In good practice one determines important properties (angular diameter, position, brightness...) of this specific cluster and then also looks for possible standard sources. One should also keep in mind that the specific object shoul ...
Project Descriptions - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be mistaken for stars. However, their close proximity to the Earth also makes their apparent motion ...
... smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be mistaken for stars. However, their close proximity to the Earth also makes their apparent motion ...
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
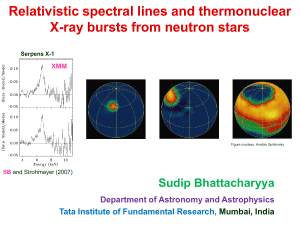
... common among various kinds of objects, such as proto-stars, Xray binaries and AGN. (b) Accretion onto black holes and neutron stars is possibly the most efficient energy source in the universe. (c) A study of accretion-ejection in X-ray binaries provides an important tool to probe the strong gravity ...
... common among various kinds of objects, such as proto-stars, Xray binaries and AGN. (b) Accretion onto black holes and neutron stars is possibly the most efficient energy source in the universe. (c) A study of accretion-ejection in X-ray binaries provides an important tool to probe the strong gravity ...
Astronomy
... 24. Where should you look to see the planets that wander among the stars? Why? Look to the ecliptic, because that is the plane on which all planets orbit the sun. 25. What is the tilt of the earth’s axis of rotation relative its plane of revolution? 23.5 degrees 26. What are circumpolar constellatio ...
... 24. Where should you look to see the planets that wander among the stars? Why? Look to the ecliptic, because that is the plane on which all planets orbit the sun. 25. What is the tilt of the earth’s axis of rotation relative its plane of revolution? 23.5 degrees 26. What are circumpolar constellatio ...
Question Paper - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... A amount of hydrogen and temperature. B amount of hydrogen and pressure. C density and pressure. D density and temperature. (Total for Question = 1 mark) 14 Current theories give a number of alternatives for the future evolution of our universe. According to current theory, an open universe A eventu ...
... A amount of hydrogen and temperature. B amount of hydrogen and pressure. C density and pressure. D density and temperature. (Total for Question = 1 mark) 14 Current theories give a number of alternatives for the future evolution of our universe. According to current theory, an open universe A eventu ...
It is now recognized that the vast majority of ellipticals are of
... • In contrast, E galaxies with close companions often have luminosity profiles which rise above a de Vaucouleurs law at large radii. These features may be plausibly blamed on tidal interactions. • E galaxies in closely interacting systems sometimes exhibit outer isophotes which are visibly eggshaped ...
... • In contrast, E galaxies with close companions often have luminosity profiles which rise above a de Vaucouleurs law at large radii. These features may be plausibly blamed on tidal interactions. • E galaxies in closely interacting systems sometimes exhibit outer isophotes which are visibly eggshaped ...
PHY2083
... If a star appears faint, is it because it is really (i.e. intrinsically) faint, or because it is very far away [or both] ? N.B. For stars at the same distance, the ratio of their fluxes = ratio of their luminosities ...
... If a star appears faint, is it because it is really (i.e. intrinsically) faint, or because it is very far away [or both] ? N.B. For stars at the same distance, the ratio of their fluxes = ratio of their luminosities ...
File - We All Love Science
... – Stars smaller than 0.1 are very rare. Why? – These low mass stars are very dim and are called “Brown Dwarf” stars due to their dim red light ...
... – Stars smaller than 0.1 are very rare. Why? – These low mass stars are very dim and are called “Brown Dwarf” stars due to their dim red light ...
The star Betelgeuse is about 500 light years away from us. If this star
... The big bang a. cannot be disproven as a scientific idea b. created the earth 4.5 billion years ago c. is the initial expansion of space d. was the emergence of the solar system from a black hole Our solar system is located in the a) Milky Way's galactic halo b) Milky Way's central nucleus c) Milky ...
... The big bang a. cannot be disproven as a scientific idea b. created the earth 4.5 billion years ago c. is the initial expansion of space d. was the emergence of the solar system from a black hole Our solar system is located in the a) Milky Way's galactic halo b) Milky Way's central nucleus c) Milky ...
English Summary
... wavelength the elements emit. These wavelengths are normally very small and are measured in units such as nanometers (1 nm = 0.000000001 meters). Since the light that we see is a combination of many wavelengths from different elements, how can we distinguish them? Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) solved ...
... wavelength the elements emit. These wavelengths are normally very small and are measured in units such as nanometers (1 nm = 0.000000001 meters). Since the light that we see is a combination of many wavelengths from different elements, how can we distinguish them? Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) solved ...
Evolution of low
... • Models for AGB stars, predict that Tc will be synthesized inbetween shell flashes and convected to the surface. • In 1952 Tc was detected for the first time in a star and now is routinely found in the spectra of AGB stars. This is direct proof of nucleosynthesis in stars and a powerful verificatio ...
... • Models for AGB stars, predict that Tc will be synthesized inbetween shell flashes and convected to the surface. • In 1952 Tc was detected for the first time in a star and now is routinely found in the spectra of AGB stars. This is direct proof of nucleosynthesis in stars and a powerful verificatio ...
Stellar Evolution
... 18. What does the core of a star at the end of being a main sequence star look like ? ...
... 18. What does the core of a star at the end of being a main sequence star look like ? ...
Lecture 16
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
Document
... The electrons in their core do not become degenerate until the final burning stages. The core at that point consists of iron. Other elements – hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen, and silicon, burn in successive layers (moving inward). The luminosity is almost constant, at all stages of the evolution. ...
... The electrons in their core do not become degenerate until the final burning stages. The core at that point consists of iron. Other elements – hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen, and silicon, burn in successive layers (moving inward). The luminosity is almost constant, at all stages of the evolution. ...
How Old is the Universe?
... over the luminosity of the RR Lyra stars which are used to determine the distances to globular clusters. Chaboyer (1997) gives a best estimate of 14.6 +/- 1.7 Gyr for the age of the globular clusters. But recent Hipparcos results show that the globular clusters are further away than previously thoug ...
... over the luminosity of the RR Lyra stars which are used to determine the distances to globular clusters. Chaboyer (1997) gives a best estimate of 14.6 +/- 1.7 Gyr for the age of the globular clusters. But recent Hipparcos results show that the globular clusters are further away than previously thoug ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.