No Slide Title
... for 40 What is the rare astronomical event involving the explosion of the majority of the material in a star, which results in an extremely bright, short-lived object that gives off vast quantities of energy? ...
... for 40 What is the rare astronomical event involving the explosion of the majority of the material in a star, which results in an extremely bright, short-lived object that gives off vast quantities of energy? ...
Spectral Classification
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
Oct 06, 2001
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
Lecture 22 - Cosmic distance scale
... 3. Measure the flux of star B with same spectral type and luminosity class to be lower by a factor of 1600 ...
... 3. Measure the flux of star B with same spectral type and luminosity class to be lower by a factor of 1600 ...
BASIC PROPERTIES of STARS - 2
... (1) What is approximate time to get the return signal from Venus when it is at its closest to Earth? C = 3 x 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant position? (A 850; B 1700; C 2550; D 3400 sec ...
... (1) What is approximate time to get the return signal from Venus when it is at its closest to Earth? C = 3 x 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant position? (A 850; B 1700; C 2550; D 3400 sec ...
Measuring Astronomical Distances
... We can then use machine learning to improve the photometric redshift estimates ...
... We can then use machine learning to improve the photometric redshift estimates ...
Space astrometry 2: Scientific results from Hipparcos
... Search Optimisation for SETI (2/3) Search for solar twins: non-binary stars identical to the Sun in terms of: age, mass, luminosity, chemical composition, temperature, surface gravity, magnetic field, rotational velocity, chromospheric activity ...
... Search Optimisation for SETI (2/3) Search for solar twins: non-binary stars identical to the Sun in terms of: age, mass, luminosity, chemical composition, temperature, surface gravity, magnetic field, rotational velocity, chromospheric activity ...
Chapter 7: The Galaxy, structure and content File
... There is little doubt now that the distribution of stars in the region of the Milky Way bulge is triaxial – there is a (rotating) bar with the positive l side nearer to us and moving away. The evidence for this was at first indirect, and took the following form. Consider gas in the ring, which must ...
... There is little doubt now that the distribution of stars in the region of the Milky Way bulge is triaxial – there is a (rotating) bar with the positive l side nearer to us and moving away. The evidence for this was at first indirect, and took the following form. Consider gas in the ring, which must ...
Stars
... the stars core, the core _________________ releases a huge about of energy • A Supernova will occur about once every 50 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way – which means they occur about every second in the universe! ...
... the stars core, the core _________________ releases a huge about of energy • A Supernova will occur about once every 50 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way – which means they occur about every second in the universe! ...
Astronomy 114 – Summary of Important Concepts #2 1 Stars: key
... Q: A star has an absolute magnitude of 4 and lies 1 parsec from the Earth. Suppose that star is moved to a distance of 10 parsecs from the Sun. What is its absolute magnitude? A: The absolute magnitude is still 4. Absolute magnitude does not depend on distance. It measures the luminosity of the star ...
... Q: A star has an absolute magnitude of 4 and lies 1 parsec from the Earth. Suppose that star is moved to a distance of 10 parsecs from the Sun. What is its absolute magnitude? A: The absolute magnitude is still 4. Absolute magnitude does not depend on distance. It measures the luminosity of the star ...
Orion – The Hunter - Guild of Students
... the scorpion in the night sky as the constellations Orion and Scorpius. She placed the scorpion opposite him, so that never are the two visible at once. The sky shows him followed by his two fighting dogs, Canis Major and Minor, and fighting a bull, Taurus. Oddly, the bull is completely irrelevant t ...
... the scorpion in the night sky as the constellations Orion and Scorpius. She placed the scorpion opposite him, so that never are the two visible at once. The sky shows him followed by his two fighting dogs, Canis Major and Minor, and fighting a bull, Taurus. Oddly, the bull is completely irrelevant t ...
JimH This is Your Life - The Atlanta Astronomy Club
... Expanding envelope forms a ring nebula around the White Dwarf core. Ring is Ionized and heated by the hot central core of WD. Called planetary nebula because look like a tiny planet in a small telescope. •The nebula expands at the ~ 35,000 to 70,000 miles/hour. ...
... Expanding envelope forms a ring nebula around the White Dwarf core. Ring is Ionized and heated by the hot central core of WD. Called planetary nebula because look like a tiny planet in a small telescope. •The nebula expands at the ~ 35,000 to 70,000 miles/hour. ...
a MS Word version.
... series of equations, since there is actually more than one equation within some of the four equation "descriptions"), that describe the physics that can be used to calculate the internal structure and time evolution of the Sun and stars. For each equation give a short description of the physical pro ...
... series of equations, since there is actually more than one equation within some of the four equation "descriptions"), that describe the physics that can be used to calculate the internal structure and time evolution of the Sun and stars. For each equation give a short description of the physical pro ...
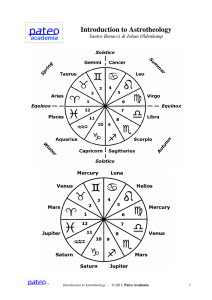
Introduction to Astrotheology
... The table below shows the bodily locations of common diseases, based on the moment of birth. This relation is based on the three decanates (or decans for short) per Zodiac sign. A decan is the division of the full period of a Zodiac sign (of 30 degrees of arc) into three equal periods (of 10 degree ...
... The table below shows the bodily locations of common diseases, based on the moment of birth. This relation is based on the three decanates (or decans for short) per Zodiac sign. A decan is the division of the full period of a Zodiac sign (of 30 degrees of arc) into three equal periods (of 10 degree ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between a main-sequence star’s mass and the total energy it emits. Distances to stars can be determined using their spectral types and luminosity classes. ...
... supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between a main-sequence star’s mass and the total energy it emits. Distances to stars can be determined using their spectral types and luminosity classes. ...
1 Name: Date: PARALLAX EXERCISE1 The goal of this
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. The most direct method of distance measurement is parallax, the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the change in position of the observer. To see an example of this, ...
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. The most direct method of distance measurement is parallax, the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the change in position of the observer. To see an example of this, ...
Plotting Supernova Light Curves
... For stars with masses of more than 15 times the mass of the Sun, their lives end in a violent explosion called a supernova. Nuclear fusion stops in the core of the star, which then collapses and bounces back outwards, ejecting most of its matter into space. During this explosion, the star increases ...
... For stars with masses of more than 15 times the mass of the Sun, their lives end in a violent explosion called a supernova. Nuclear fusion stops in the core of the star, which then collapses and bounces back outwards, ejecting most of its matter into space. During this explosion, the star increases ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... because you’re in one! Unfortunately, galaxies are massive, and we can’t see as much as we wish, and that is why with the assistance of telescopes, astronomers have been able to identify certain things in space. Our galaxy (the Milky Way, in case you didn’t know), is made up of stars, gas, dust, a s ...
... because you’re in one! Unfortunately, galaxies are massive, and we can’t see as much as we wish, and that is why with the assistance of telescopes, astronomers have been able to identify certain things in space. Our galaxy (the Milky Way, in case you didn’t know), is made up of stars, gas, dust, a s ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... The results from actual star counts in various Galactic fields are: i. Bright stars are nearly uniformly distributed between the pole and the plane of the Galaxy, but faint stars are clearly concentrated towards the Galactic plane. ii. Most of the light from the region of the Galactic poles comes f ...
... The results from actual star counts in various Galactic fields are: i. Bright stars are nearly uniformly distributed between the pole and the plane of the Galaxy, but faint stars are clearly concentrated towards the Galactic plane. ii. Most of the light from the region of the Galactic poles comes f ...
Document
... falls into another neutron star or black hole. The resulting explosion sends out particles and radiation all over the spectrum They are the most luminous things in the universe In May a GRB was seen at redshift 8. It is the farthest thing ever seen and occurred only 400 million years after the big b ...
... falls into another neutron star or black hole. The resulting explosion sends out particles and radiation all over the spectrum They are the most luminous things in the universe In May a GRB was seen at redshift 8. It is the farthest thing ever seen and occurred only 400 million years after the big b ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.