Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
Astronomy in 1936 The History of the Universe
... Ωlp calculated from rotation curve for Milky Way. ...
... Ωlp calculated from rotation curve for Milky Way. ...
20 – N10/4/PHYSI/SP3/ENG/TZ0/XX Option E
... (iii) State why the method of parallax can only be used for stars at a distance of less than a few hundred parsecs from Earth. ...
... (iii) State why the method of parallax can only be used for stars at a distance of less than a few hundred parsecs from Earth. ...
First Stars II
... (H burning via CN cycle at several x10Msun) Accretion continues in low Mdot cases, while the stellar wind prohibit further accretion in high Mdot cases. ...
... (H burning via CN cycle at several x10Msun) Accretion continues in low Mdot cases, while the stellar wind prohibit further accretion in high Mdot cases. ...
Lecture 9: Stellar Spectra
... Example: the Effects of Dust There is gas and dust in between the stars. Dust particles are very small and scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are. A star’s color no longer tells you its tempertuare. But the spectrum still does! ...
... Example: the Effects of Dust There is gas and dust in between the stars. Dust particles are very small and scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are. A star’s color no longer tells you its tempertuare. But the spectrum still does! ...
ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... But the companion could have been ejected a few thousand years ago. FU Ori must in this picture be a close binary with a separation of roughly 10 AU, i.e. the system should be a triple. In the intervening years the newborn binary has had time to spiral together, reaching now the period of FUor ...
... But the companion could have been ejected a few thousand years ago. FU Ori must in this picture be a close binary with a separation of roughly 10 AU, i.e. the system should be a triple. In the intervening years the newborn binary has had time to spiral together, reaching now the period of FUor ...
–1– 2. Milky Way We know a great deal, perhaps more than any
... Fig. 1.— Panorama of the Milky Way (credit: Lund Observatory). Notice the dark patches caused by dust extinction. A Panorama of the Milky Way is shown in Fig. 1. The Galaxy appears as a thin band with dark patches which are caused by dust extinction. Many past astronomers often ignored such obvious ...
... Fig. 1.— Panorama of the Milky Way (credit: Lund Observatory). Notice the dark patches caused by dust extinction. A Panorama of the Milky Way is shown in Fig. 1. The Galaxy appears as a thin band with dark patches which are caused by dust extinction. Many past astronomers often ignored such obvious ...
astronomy practice test ch 9
... ____ 12. The absolute magnitude of a star is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were 10 pc from Earth. ____ 13. Lines in the spectra of supergiant stars are broader than the same spectral lines in main sequence stars of the same spectral type. ____ 14. Giant stars are members of luminosity c ...
... ____ 12. The absolute magnitude of a star is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were 10 pc from Earth. ____ 13. Lines in the spectra of supergiant stars are broader than the same spectral lines in main sequence stars of the same spectral type. ____ 14. Giant stars are members of luminosity c ...
Solar and Lunar Eclipse, the Sky,_x000b_The Milky
... The Milky Way & Constellations - In Northern cultures Solar eclipses There aren't many myths about solar eclipses due to Polar nights. Other reasons are that solar eclipses are in general rare in polar regions. In summer the temperature difference in significant during an eclipse and the people of t ...
... The Milky Way & Constellations - In Northern cultures Solar eclipses There aren't many myths about solar eclipses due to Polar nights. Other reasons are that solar eclipses are in general rare in polar regions. In summer the temperature difference in significant during an eclipse and the people of t ...
Nearby Stars - How far away is it
... Star Trek fans may recognize Wolf 359 as the scene of a great battle between the Federation and The Borg. Lalande 21185 - 8.32 light years Lalande 21185 is another dime red star. Recent analysis indicates that it may also be accompanied by at least two orbiting planets, but his has not been confirme ...
... Star Trek fans may recognize Wolf 359 as the scene of a great battle between the Federation and The Borg. Lalande 21185 - 8.32 light years Lalande 21185 is another dime red star. Recent analysis indicates that it may also be accompanied by at least two orbiting planets, but his has not been confirme ...
Stars and the Milky Way
... • the Milky Way is one of billions of galaxies in the universe • the Milky Way is made up of over 200 billion stars Other facts about the Milky Way • The Sun is just one of the stars in the Milky Way. • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of ligh ...
... • the Milky Way is one of billions of galaxies in the universe • the Milky Way is made up of over 200 billion stars Other facts about the Milky Way • The Sun is just one of the stars in the Milky Way. • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of ligh ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
Andromeda *ruler of men*
... Andromeda is an autumn constellation that is V shaped the best time of year to view Andromeda is during the month of November with the suggested time being 9pm. It occupies 722 square degrees and is located close to the North Pole in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be s ...
... Andromeda is an autumn constellation that is V shaped the best time of year to view Andromeda is during the month of November with the suggested time being 9pm. It occupies 722 square degrees and is located close to the North Pole in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be s ...
Lecture12
... A certain star has 100 times the luminosity of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? A. A high-mass main-sequence star B. A low-mass main-sequence star C. A red giant D. A red dwarf E. A white dwarf ...
... A certain star has 100 times the luminosity of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? A. A high-mass main-sequence star B. A low-mass main-sequence star C. A red giant D. A red dwarf E. A white dwarf ...
9 Dwarf Galaxies
... the star formation histories of dwarf galaxies Dwarf ellipticals are generally old (stars formed > 10 Gyr old), but some may have had more recent (a few Gyr ago) weaker episodes of star formation Dwarf irregulars tend to have quasi-continuous star formation (perhaps interspersed with bursts). Lower ...
... the star formation histories of dwarf galaxies Dwarf ellipticals are generally old (stars formed > 10 Gyr old), but some may have had more recent (a few Gyr ago) weaker episodes of star formation Dwarf irregulars tend to have quasi-continuous star formation (perhaps interspersed with bursts). Lower ...
uniview glossary - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
PH607lec10-4gal2
... the star formation histories of dwarf galaxies Dwarf ellipticals are generally old (stars formed > 10 Gyr old), but some may have had more recent (a few Gyr ago) weaker episodes of star formation Dwarf irregulars tend to have quasi-continuous star formation (perhaps interspersed with bursts). Lower ...
... the star formation histories of dwarf galaxies Dwarf ellipticals are generally old (stars formed > 10 Gyr old), but some may have had more recent (a few Gyr ago) weaker episodes of star formation Dwarf irregulars tend to have quasi-continuous star formation (perhaps interspersed with bursts). Lower ...
Lecture 15a - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... In general, science proceeds on the assumption of near-equilibrium. This assumption is valid because changes to systems usually transpire slowly… - stars evolve, but slowly; - mountains grow or erode, but slowly; - trees grow larger over time, but very slowly. Of course, many systems can move rapidl ...
... In general, science proceeds on the assumption of near-equilibrium. This assumption is valid because changes to systems usually transpire slowly… - stars evolve, but slowly; - mountains grow or erode, but slowly; - trees grow larger over time, but very slowly. Of course, many systems can move rapidl ...
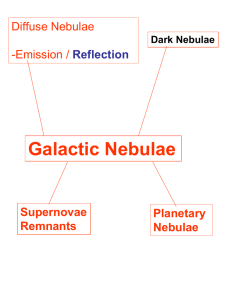
Galactic Nebulae
... Distance of 5000 light years and about 15 light years in diameter Omega Nebula represents over 800 solar masses of material Largest HII region – molecular cloud complex in inner part Of galaxy and one of closest to sun Cascade of star formation within M17 – open star cluster NGC6618 – obscured by ga ...
... Distance of 5000 light years and about 15 light years in diameter Omega Nebula represents over 800 solar masses of material Largest HII region – molecular cloud complex in inner part Of galaxy and one of closest to sun Cascade of star formation within M17 – open star cluster NGC6618 – obscured by ga ...
Lec09_ch11_lifecycleofstars
... becomes a pre-main-sequence star • PMS Stars evolve toward Main Sequence – Collapse continues somewhat – Stellar structure stabilizes – Nebular cloud push away by stellar wind – Rate of evolution depends on mass--higher mass, faster evolution! 2 Nov 2000 ...
... becomes a pre-main-sequence star • PMS Stars evolve toward Main Sequence – Collapse continues somewhat – Stellar structure stabilizes – Nebular cloud push away by stellar wind – Rate of evolution depends on mass--higher mass, faster evolution! 2 Nov 2000 ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen into helium every second 93 million miles or 150 million km from Earth (closer than any other star) A planet’s characteristics are often determined by distance from the Sun (ex- rocky, gaseous, temperature) ...
... 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen into helium every second 93 million miles or 150 million km from Earth (closer than any other star) A planet’s characteristics are often determined by distance from the Sun (ex- rocky, gaseous, temperature) ...
Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ - Eu-Hou
... Photometry is generally used to generate light curves of objects such as variable stars and supernovae, where the interest is the variation of total light energy output by the system over time. It can also be used to discover exoplanets, by measuring the intensity of a stars light over a period of t ...
... Photometry is generally used to generate light curves of objects such as variable stars and supernovae, where the interest is the variation of total light energy output by the system over time. It can also be used to discover exoplanets, by measuring the intensity of a stars light over a period of t ...
THE ORION CONSTELLATION the Great Hunter
... photographed objects in the night sky, and is among the most intensely studied celestial features. The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarf ...
... photographed objects in the night sky, and is among the most intensely studied celestial features. The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarf ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.