PH607lec08
... • When examined with sufficient resolution, 25% to more than 40% of E galaxies show features due to dust absorption. • The dust lanes seen in E galaxies imply that the absorbing material is distributed in rings or disks. Dust lanes may be aligned with either the major or minor axes, or they may be w ...
... • When examined with sufficient resolution, 25% to more than 40% of E galaxies show features due to dust absorption. • The dust lanes seen in E galaxies imply that the absorbing material is distributed in rings or disks. Dust lanes may be aligned with either the major or minor axes, or they may be w ...
Lecture 8: Spiral Structure
... Spiral structure 1- Spiral tracers • Spiral tracers are objects that are commonly found in spiral arms and so are used to trace spiral structure. • Photos in blue taken of nearby spiral galaxies such as M31 (Andromeda galaxy) show the bluish spiral arms distinctly. This appearance results from blui ...
... Spiral structure 1- Spiral tracers • Spiral tracers are objects that are commonly found in spiral arms and so are used to trace spiral structure. • Photos in blue taken of nearby spiral galaxies such as M31 (Andromeda galaxy) show the bluish spiral arms distinctly. This appearance results from blui ...
Small star patterns for telescopes and binoculars Demelza Ramakers
... The Golf Putter looks a bit like Kemble’s Cascade. There’s a long line of stars visible with an open star cluster on the end of it. The row ends with a bow. The open cluster NGC 752 forms the golf ball. Use a binocular for this asterism, because it is comparative large. Draw a line between the stars ...
... The Golf Putter looks a bit like Kemble’s Cascade. There’s a long line of stars visible with an open star cluster on the end of it. The row ends with a bow. The open cluster NGC 752 forms the golf ball. Use a binocular for this asterism, because it is comparative large. Draw a line between the stars ...
CO OBSERVATIONS OF SPIRAL STRUCTURE AND THE LIFETIME
... and on the other hand you show that they are gravitationally bound, what prevents these clouds from collapsing? Scoville: It is clear that there is some mechanism restraining the ob served clouds from free-fall collapse. It is also clear from observa tions of external galaxies that although dust c ...
... and on the other hand you show that they are gravitationally bound, what prevents these clouds from collapsing? Scoville: It is clear that there is some mechanism restraining the ob served clouds from free-fall collapse. It is also clear from observa tions of external galaxies that although dust c ...
3.1 Radio Astronomy Research Results For much of PY 2010, radio
... interference. PALFA now use longer observations (9 min instead of 4.5 min) for Galactic longitudes between ~30° and 45° to expand the effective search volume. In PY 2010, PALFA continued processing data via the Einstein@Home community, which was originally developed to process LIGO data for coheren ...
... interference. PALFA now use longer observations (9 min instead of 4.5 min) for Galactic longitudes between ~30° and 45° to expand the effective search volume. In PY 2010, PALFA continued processing data via the Einstein@Home community, which was originally developed to process LIGO data for coheren ...
The cosmological significance of high
... investigations of its stellar content. The H I mass of the cloud is 2.0 × 107 (d/27 kpc)2 M⊙ , making Complex H one of the most massive HVCs if its distance is more than ∼ 20 kpc. Virtually all similar H I clouds in other galaxy groups are associated with low surface brightness dwarf galaxies. We se ...
... investigations of its stellar content. The H I mass of the cloud is 2.0 × 107 (d/27 kpc)2 M⊙ , making Complex H one of the most massive HVCs if its distance is more than ∼ 20 kpc. Virtually all similar H I clouds in other galaxy groups are associated with low surface brightness dwarf galaxies. We se ...
GALEX and Star Formation
... complexes and stellar associations dissolve. They are very hot, therefore the UV wavelength range is ideal to detect and study them, because (i) UV colors are more sensitive to the temperatures of the hottest stars, enabling e.g. to discern O-types from late-O/early-B, while optical colors are satur ...
... complexes and stellar associations dissolve. They are very hot, therefore the UV wavelength range is ideal to detect and study them, because (i) UV colors are more sensitive to the temperatures of the hottest stars, enabling e.g. to discern O-types from late-O/early-B, while optical colors are satur ...
Ophiuchus Ascendant
... ASCENDANT~DESCENDANT~HIGH and the Flying Eagle (Christ Rising / SERPENT Rising Ascendant / Ophiuchus ). The USA chart with Sagittarius rising in the 9th degree has Uranus opposition Ascendant and both square Ceres and in aspect with Eris and Nessus. In this post. SelfMade HoroscopeI. Ascendant in Ca ...
... ASCENDANT~DESCENDANT~HIGH and the Flying Eagle (Christ Rising / SERPENT Rising Ascendant / Ophiuchus ). The USA chart with Sagittarius rising in the 9th degree has Uranus opposition Ascendant and both square Ceres and in aspect with Eris and Nessus. In this post. SelfMade HoroscopeI. Ascendant in Ca ...
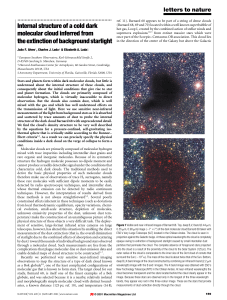
Internal structure of a cold dark molecular cloud inferred
... shells, a few of their most resilient dense cores will be left behind, embedded within the shell's hot interior. Remnant cores with just the right mass can establish pressure equilibrium with the hot gas within the shell and survive to become Bok globules. Eventually, as a result of the processes de ...
... shells, a few of their most resilient dense cores will be left behind, embedded within the shell's hot interior. Remnant cores with just the right mass can establish pressure equilibrium with the hot gas within the shell and survive to become Bok globules. Eventually, as a result of the processes de ...
Chapter 10 Formation and evolution of the Local Group
... Summary: The Local Group (LG) is the group of galaxies gravitationally associated with the Galaxy and M 31. Galaxies within the LG have overcome the general expansion of the universe. There are approximately 75 galaxies in the LG within a diameter of ∼3 Mpc having a total mass of 2-5 × 1012 M⊙ . A s ...
... Summary: The Local Group (LG) is the group of galaxies gravitationally associated with the Galaxy and M 31. Galaxies within the LG have overcome the general expansion of the universe. There are approximately 75 galaxies in the LG within a diameter of ∼3 Mpc having a total mass of 2-5 × 1012 M⊙ . A s ...
PHY 375 - DePaul University
... We will use the full relativistic Doppler effect formula to avoid faster than light recession velocity (but see posted lecture notes about why this step angers theoreticians, especially because faster than light motions are not a problem in general relativity; in fact, the preference is to keep dist ...
... We will use the full relativistic Doppler effect formula to avoid faster than light recession velocity (but see posted lecture notes about why this step angers theoreticians, especially because faster than light motions are not a problem in general relativity; in fact, the preference is to keep dist ...
Practical cosmology with the Local Volume galaxies
... The local Hubble flow around the LV groups is found to be very cold, with rms deviations of ~25 km/s that is a signature of the universe vacuum-dominated on small scales. The cold infall pattern around nearby groups provides us with a new method to determine the total mass of the groups independent ...
... The local Hubble flow around the LV groups is found to be very cold, with rms deviations of ~25 km/s that is a signature of the universe vacuum-dominated on small scales. The cold infall pattern around nearby groups provides us with a new method to determine the total mass of the groups independent ...
Gemini - www.BahaiStudies.net
... To look at Gemini is to look away from the Milky Way; as a result, there are comparatively few deep-sky objects of note. The Eskimo Nebula and Medusa Nebula, Messier object M35, and Geminga are those that attract the most attention. The Eskimo and Medusa nebulae are both planetary nebulae, the one a ...
... To look at Gemini is to look away from the Milky Way; as a result, there are comparatively few deep-sky objects of note. The Eskimo Nebula and Medusa Nebula, Messier object M35, and Geminga are those that attract the most attention. The Eskimo and Medusa nebulae are both planetary nebulae, the one a ...
A Stars
... stars of the same Temperature. – Means they must be smaller in radius. – L-R-T Relation predicts: R ~ 0.01 Rsun (~ size of Earth!) ...
... stars of the same Temperature. – Means they must be smaller in radius. – L-R-T Relation predicts: R ~ 0.01 Rsun (~ size of Earth!) ...
Gone in a flash: supernovae in the survey era
... brighter than a Type Ia supernova). The first of SLSN (Gal-Yam 2012), commonly defined as CFHT, or DECam on the Cerro Tololo Interevent, SCP 06F6, was identified in 2009 and had being brighter than –21 in absolute magnitude American Observatory 4 m Blanco telescope), broad, unexplained spectral abso ...
... brighter than a Type Ia supernova). The first of SLSN (Gal-Yam 2012), commonly defined as CFHT, or DECam on the Cerro Tololo Interevent, SCP 06F6, was identified in 2009 and had being brighter than –21 in absolute magnitude American Observatory 4 m Blanco telescope), broad, unexplained spectral abso ...
17_Testbank
... 38) What types of stars end their lives with supernovae? A) all stars that are red in color B) all stars that are yellow in color C) stars that are at least several times the mass of the Sun D) stars that are similar in mass to the Sun E) stars that have reached an age of 10 billion years Answer: C ...
... 38) What types of stars end their lives with supernovae? A) all stars that are red in color B) all stars that are yellow in color C) stars that are at least several times the mass of the Sun D) stars that are similar in mass to the Sun E) stars that have reached an age of 10 billion years Answer: C ...
Spectral Classification: The First Step in Quantitative Spectral Analysis
... How are spectral types determined? They are determined via direct comparison with standard stars The spectral region/resolution are of secondary importance, as spectral classification is no longer confined to the classical blue-violet region of the spectrum. ...
... How are spectral types determined? They are determined via direct comparison with standard stars The spectral region/resolution are of secondary importance, as spectral classification is no longer confined to the classical blue-violet region of the spectrum. ...
The role of black holes in galaxy formation and evolution
... Galaxies come in two basic types: ‗football-shaped‘ ellipticals and ‗disk-shaped‘ spirals (Fig. 1). Spirals contain plenty of cold gas, which forms stars, whereas the gas in ellipticals is too hot to form stars. Thus, ellipticals lack the young blue stars that are usually seen in spirals, and are g ...
... Galaxies come in two basic types: ‗football-shaped‘ ellipticals and ‗disk-shaped‘ spirals (Fig. 1). Spirals contain plenty of cold gas, which forms stars, whereas the gas in ellipticals is too hot to form stars. Thus, ellipticals lack the young blue stars that are usually seen in spirals, and are g ...
Gamma Ray Burst Afterglows and Host Galaxies
... GRBs in Obscured Starbursts? • Recently, two GRB host galaxies have been shown to have unusually high submillimeter wavelength brightness. • This suggests strong star formation activity hidden by dust. ...
... GRBs in Obscured Starbursts? • Recently, two GRB host galaxies have been shown to have unusually high submillimeter wavelength brightness. • This suggests strong star formation activity hidden by dust. ...
Observing Stellar Evolution
... sky can use one or more of the designations to identify a star, but not all. Astronomy is an old science and over time many names and catalogs have been developed. Those of us who are amateur astronomers will simply have to learn to live with this system. To help you along the way, here are some of ...
... sky can use one or more of the designations to identify a star, but not all. Astronomy is an old science and over time many names and catalogs have been developed. Those of us who are amateur astronomers will simply have to learn to live with this system. To help you along the way, here are some of ...
D ASTROPHYSICS
... A galaxy is a creation of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity and containing billions of stars. The Milky Way contains about 3 × 10 11 stars and, probably, at least this number of planets. Some galaxies exist in isolation but the majority of them occur in groups known as clusters that have ...
... A galaxy is a creation of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity and containing billions of stars. The Milky Way contains about 3 × 10 11 stars and, probably, at least this number of planets. Some galaxies exist in isolation but the majority of them occur in groups known as clusters that have ...
STELLAR AGE VERSUS MASS OF EARLY
... minor population of Virgo cluster early type galaxies with ongoing central star formation, a typical value for E(B − V ) of 0.1 was found for their centers (Lisker et al. 2006b), thus being much smaller for the galaxies as a whole, and certainly negligible for the vast majority of the sample. For ea ...
... minor population of Virgo cluster early type galaxies with ongoing central star formation, a typical value for E(B − V ) of 0.1 was found for their centers (Lisker et al. 2006b), thus being much smaller for the galaxies as a whole, and certainly negligible for the vast majority of the sample. For ea ...
Candidate star clusters toward the inner Milky Way discovered on
... The final list of identified cluster candidates contains nine objects. Their locations on the sky are shown in Fig. 4 and there appears to be some clustering: VVV CC 169 and VVV CC 170 have projected on-sky separation of ∼2 arcmin, but these objects have different extinctions and distances (Table 1) ...
... The final list of identified cluster candidates contains nine objects. Their locations on the sky are shown in Fig. 4 and there appears to be some clustering: VVV CC 169 and VVV CC 170 have projected on-sky separation of ∼2 arcmin, but these objects have different extinctions and distances (Table 1) ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.