Problem Sheet for Introduction to Astrophysics
... a) How much brighter will a star of 1st magnitude appear compared with one of 9th magnitude? b) What is the apparent magnitude of a star that appears 2.512 times less bright than the 0th magnitude star Vega? c) Two stars of identical luminosity are observed. The apparent brightness of the more dista ...
... a) How much brighter will a star of 1st magnitude appear compared with one of 9th magnitude? b) What is the apparent magnitude of a star that appears 2.512 times less bright than the 0th magnitude star Vega? c) Two stars of identical luminosity are observed. The apparent brightness of the more dista ...
ppt
... few galaxies (1-2 Mpc). Even Hubble Space Telescope cannot find Cepheids beyond the Virgo cluster (16 Mpc). Beyond 1-2Mpc, Hubble used… ...
... few galaxies (1-2 Mpc). Even Hubble Space Telescope cannot find Cepheids beyond the Virgo cluster (16 Mpc). Beyond 1-2Mpc, Hubble used… ...
65008_StarFinderPart2
... a. Name three special objects and their constellations visible in the SOUTH horizon. _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ ...
... a. Name three special objects and their constellations visible in the SOUTH horizon. _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ _______________________ in the constellation of _______________________ ...
Hubble`s Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a
... may explain why stars form there. The fact that we see star formation in spiral arms is evidence for the density wave theory, not the other way around. Similarly, the fact that we see star formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Als ...
... may explain why stars form there. The fact that we see star formation in spiral arms is evidence for the density wave theory, not the other way around. Similarly, the fact that we see star formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Als ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
9. Lectures on Star Formation.
... Star hasn’t yet reached the main sequence, no nuclear reactions at center, still contracting. These stars are only about 150,000 years old. ...
... Star hasn’t yet reached the main sequence, no nuclear reactions at center, still contracting. These stars are only about 150,000 years old. ...
Extragalactic AO Science
... reduce throughput further making it difficult to observe faint extended sources. Normal galaxy disks only achieve a maximum SB of K~16 mag/sq arcsec and this fades as (1+z)4. This means all normal disks are fainter than 22.5 mag within 0.05x0.05”. ...
... reduce throughput further making it difficult to observe faint extended sources. Normal galaxy disks only achieve a maximum SB of K~16 mag/sq arcsec and this fades as (1+z)4. This means all normal disks are fainter than 22.5 mag within 0.05x0.05”. ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... Most of the bright star have individual names. The names are often related to the part of the "picture". •Alhena in Gemini means "mark", pertaining to a mark on the foot of Gemini twin Pollux. •Betelgeuse (Orion) means “shoulder” (well ….) ...
... Most of the bright star have individual names. The names are often related to the part of the "picture". •Alhena in Gemini means "mark", pertaining to a mark on the foot of Gemini twin Pollux. •Betelgeuse (Orion) means “shoulder” (well ….) ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
star
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
... • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
... • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
Astronomy
... • Red Shift – when an object is moving away from us the wavelength increases, or gets longer. Think about two people holding a slinky between them and walking away from ...
... • Red Shift – when an object is moving away from us the wavelength increases, or gets longer. Think about two people holding a slinky between them and walking away from ...
Star Classification
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
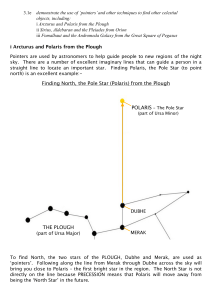
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... 3 types of galaxies are: 1. spiral- arms like a pinwheel ex our galaxy- Milky Way 2. elliptical- nearly spherical to flatdisks (older than other galaxies) 3. irregular- no orderly or definite shape, not very common Milky Way Galaxy- pinwheel shaped disk with bulge in center -the older stars are near ...
... 3 types of galaxies are: 1. spiral- arms like a pinwheel ex our galaxy- Milky Way 2. elliptical- nearly spherical to flatdisks (older than other galaxies) 3. irregular- no orderly or definite shape, not very common Milky Way Galaxy- pinwheel shaped disk with bulge in center -the older stars are near ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
galaxy.
... our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, it would have to be turning faster than the speed of light. • Spiral nebulae were never seen in ...
... our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, it would have to be turning faster than the speed of light. • Spiral nebulae were never seen in ...
Galaxy clusters - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... source, we can figure out the total mass in the lens. This provides an independent confirmation of dark matter. • A lense can act as a huge telescope. The deepest images of the most distant galaxies are obtained with clusters acting as gravitational lenses. ...
... source, we can figure out the total mass in the lens. This provides an independent confirmation of dark matter. • A lense can act as a huge telescope. The deepest images of the most distant galaxies are obtained with clusters acting as gravitational lenses. ...
galaxy_physics
... Disks are rotationally supported (dynamically cold) Bulges are dispersion supported (dynamically hot) Two extremes along a continuum Rotation asymmetric drift dispersion ...
... Disks are rotationally supported (dynamically cold) Bulges are dispersion supported (dynamically hot) Two extremes along a continuum Rotation asymmetric drift dispersion ...
Lab 2: The Planisphere
... distortion, constellations in the sky will not appear as they do on the planisphere, but the planisphere can help us identify bright stars and give us a general idea of where to look for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfor ...
... distortion, constellations in the sky will not appear as they do on the planisphere, but the planisphere can help us identify bright stars and give us a general idea of where to look for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfor ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
The Night Sky 12-07
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
Name: ____________ Period: ______ STAR BIOGRAPHY Name of
... Color and Temperature of Star Spectral class: The color of the star. Hot stars are bluer, cool stars are redder. In descending order from hottest (most blue) to coolest (most red), the spectral classes are: O B A F G K M. Each spectral class letter can be subdivided into ten smaller steps or gradat ...
... Color and Temperature of Star Spectral class: The color of the star. Hot stars are bluer, cool stars are redder. In descending order from hottest (most blue) to coolest (most red), the spectral classes are: O B A F G K M. Each spectral class letter can be subdivided into ten smaller steps or gradat ...
Interactive Vocabulary Review for Outer Space Indicator
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.