ppt
... planet's size, distance from star, and orbital period. With velocity measurements, could then get planet's mass and hence density (rocky, gas giant?) *Massive planet like Jupiter that is very close to the star ...
... planet's size, distance from star, and orbital period. With velocity measurements, could then get planet's mass and hence density (rocky, gas giant?) *Massive planet like Jupiter that is very close to the star ...
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy
... research was done by analysis of photographs; this work was mostly done by women (called “computers,” as they did computations). Several of these women went on to become well-known astronomers in their own right. Their work enabled the advances made by Shapley as well as Hertzsprung and Russell, amo ...
... research was done by analysis of photographs; this work was mostly done by women (called “computers,” as they did computations). Several of these women went on to become well-known astronomers in their own right. Their work enabled the advances made by Shapley as well as Hertzsprung and Russell, amo ...
The Sun and Stars
... Reading H-R H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize diagrams stars into groups. Stars that fall in the band that stretches diagonally from cool, dim stars to hot, bright stars are called main sequence stars. Main sequence stars, like the sun, are in a very stable part of the ...
... Reading H-R H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize diagrams stars into groups. Stars that fall in the band that stretches diagonally from cool, dim stars to hot, bright stars are called main sequence stars. Main sequence stars, like the sun, are in a very stable part of the ...
Classifying Spectra PDF version - the Home Page for Voyager2
... The spectral classes are specified by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, M, L, T going hotter to colder. Each letter is subdivided by assigning a number 0 through 9 following the letter and going from hotter to colder. So B0 is colder than O9 and hotter than B1. Obviously not every type is shown. Origina ...
... The spectral classes are specified by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, M, L, T going hotter to colder. Each letter is subdivided by assigning a number 0 through 9 following the letter and going from hotter to colder. So B0 is colder than O9 and hotter than B1. Obviously not every type is shown. Origina ...
The Extragalactic Distance Database: Color–Magnitude Diagrams
... are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there are several images per filter available then these values are displayed for eac ...
... are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there are several images per filter available then these values are displayed for eac ...
Sky-High 2013 - Irish Astronomical Society
... couple of drawbacks. Each chart is correct for only one time on a given night, say 10 p.m. If you are observing two hours later you would need the following month's chart. These charts also show the planets visible for a particular month, so they can be confusing unless you tippex them out. When lea ...
... couple of drawbacks. Each chart is correct for only one time on a given night, say 10 p.m. If you are observing two hours later you would need the following month's chart. These charts also show the planets visible for a particular month, so they can be confusing unless you tippex them out. When lea ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
Stars in Their Youth
... spectra, and nuclear physics. It was George Gamow who sensitized physicists about the unsolved problems concerning stellar physics by convening a small conference in Washington, D.C. Hans Bethe and many of the leading physicists were at that conference. Within a few months of this, Hans Bethe had wo ...
... spectra, and nuclear physics. It was George Gamow who sensitized physicists about the unsolved problems concerning stellar physics by convening a small conference in Washington, D.C. Hans Bethe and many of the leading physicists were at that conference. Within a few months of this, Hans Bethe had wo ...
Document
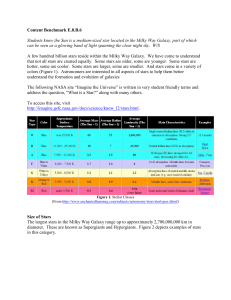
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... The brightness of stars, including our Sun, is measured in terms of magnitude and luminosity. This measurement is somewhat complicated by the fact that nearby dimmer stars might appear brighter than really bright distant stars. The further a star is below a magnitude of zero, the brighter it is. The ...
... The brightness of stars, including our Sun, is measured in terms of magnitude and luminosity. This measurement is somewhat complicated by the fact that nearby dimmer stars might appear brighter than really bright distant stars. The further a star is below a magnitude of zero, the brighter it is. The ...
Open access - ORBi
... Based on these requirements, we have chosen to work along the following lines. First, we identify all the known debris disk host stars with K < 5 and spectral type A, F, G and K. From this sample, we remove all the stars that are known to be binaries with angular separations smaller than 5′′ , as on ...
... Based on these requirements, we have chosen to work along the following lines. First, we identify all the known debris disk host stars with K < 5 and spectral type A, F, G and K. From this sample, we remove all the stars that are known to be binaries with angular separations smaller than 5′′ , as on ...
a MS Word version.
... galaxy evolution? What type of galaxy, usually found in the centers of rich galaxy clusters, is thought to be the result of galaxy mergers ("galactic cannibalism")? ...
... galaxy evolution? What type of galaxy, usually found in the centers of rich galaxy clusters, is thought to be the result of galaxy mergers ("galactic cannibalism")? ...
PHYS3380_110215_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... product. The core convection zone of these stars is overlaid by a radiation zone that is in thermal equilibrium and undergoes little or no mixing. •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the ...
... product. The core convection zone of these stars is overlaid by a radiation zone that is in thermal equilibrium and undergoes little or no mixing. •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star count data, which was considered necessary at that time to resolve Herschel’s “infinite universe” with Olb ...
... for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star count data, which was considered necessary at that time to resolve Herschel’s “infinite universe” with Olb ...
High Precision Parallax Collecting Satellite
... Many a night I saw the Pleiads, rising thro’ the mellow shade Glitter like a swarm of fireflies, tangled in a silver braid. ...
... Many a night I saw the Pleiads, rising thro’ the mellow shade Glitter like a swarm of fireflies, tangled in a silver braid. ...
Measuring the Milky Way
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
Observational properties of stars
... likely lost before the SN even. Helium is dominant in the spectrum. In ways this is very similar to the Type Ib and Ic SN. Possible origin could be from a merger of stars, though it is still being debated. IIL – light curve is linear in decline, due to the loss of much of the star’s hydrogen befor ...
... likely lost before the SN even. Helium is dominant in the spectrum. In ways this is very similar to the Type Ib and Ic SN. Possible origin could be from a merger of stars, though it is still being debated. IIL – light curve is linear in decline, due to the loss of much of the star’s hydrogen befor ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... A nova is a binary star system that suddenly brightens and then slowly fades back to normal. It is caused by an evolving star in a binary that is expanding past its Roche lobe and losing gas to a companion white dwarf. After a while, the material (primarily hydrogen) builds up on the white dwarf and ...
... A nova is a binary star system that suddenly brightens and then slowly fades back to normal. It is caused by an evolving star in a binary that is expanding past its Roche lobe and losing gas to a companion white dwarf. After a while, the material (primarily hydrogen) builds up on the white dwarf and ...
The Milky Way
... Spiral arms appear bright (newly formed, massive stars!) against the dark sky background… but dark (gas and dust in dense, star-forming clouds) against the bright background of the large galaxy Chance coincidence of small spiral galaxy in front of a large background galaxy ...
... Spiral arms appear bright (newly formed, massive stars!) against the dark sky background… but dark (gas and dust in dense, star-forming clouds) against the bright background of the large galaxy Chance coincidence of small spiral galaxy in front of a large background galaxy ...
Post main sequence evolution
... In case you did not notice, the Final is set for 03/21 from 12:00-3:00 pm. (This is posted on the class website) It will have about 80 questions, about 30 of them will be math problems. ...
... In case you did not notice, the Final is set for 03/21 from 12:00-3:00 pm. (This is posted on the class website) It will have about 80 questions, about 30 of them will be math problems. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.