Astronomy Exam review
... 19.At what latitude will the Sun be seen overhead on September 23? 20.What is the latitude of the tropic of Cancer? 21.How many stars are visible to the eye on a typical clear night? 22.Into how many constellations is the sky divided? 23.How many astronomical units are there between the Earth and su ...
... 19.At what latitude will the Sun be seen overhead on September 23? 20.What is the latitude of the tropic of Cancer? 21.How many stars are visible to the eye on a typical clear night? 22.Into how many constellations is the sky divided? 23.How many astronomical units are there between the Earth and su ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... argon, and chlorine; the density of these gases is above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Fie ...
... argon, and chlorine; the density of these gases is above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Fie ...
SNC1PL The Life Cycle of Stars
... quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronomers on Earth. ...
... quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronomers on Earth. ...
ASTR100 Homework #5 Solutions Chapter 11 #29, 31 Due
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
Lecture Summary (11/22)
... Stars more massive than the Sun are born as protostars in nebulae. Due to their great mass, they are forced to fuse hydrogen into helium at a higher core temperature and consume their hydrogen at a rapid rate. Their main sequence lifetimes are much shorter than our Sun. After becoming giants, these ...
... Stars more massive than the Sun are born as protostars in nebulae. Due to their great mass, they are forced to fuse hydrogen into helium at a higher core temperature and consume their hydrogen at a rapid rate. Their main sequence lifetimes are much shorter than our Sun. After becoming giants, these ...
Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
File
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
Star Name __Direction ___ Degrees
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
Chapter 11 - USD Home Pages
... 35. a. What is the approximate mass of a main sequence star that is 10,000 times as luminous as the Sun? b. What is the approximate lumniosuty of a main-sequence star whose mass is one-tenth that of the Sun? Answer: a. Reading Fig 11-14: Find 104 L on the vertical scale; trace horizontally until yo ...
... 35. a. What is the approximate mass of a main sequence star that is 10,000 times as luminous as the Sun? b. What is the approximate lumniosuty of a main-sequence star whose mass is one-tenth that of the Sun? Answer: a. Reading Fig 11-14: Find 104 L on the vertical scale; trace horizontally until yo ...
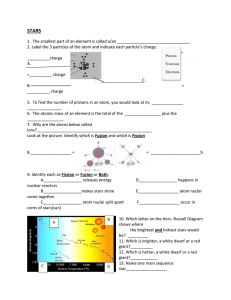
Stars - Madison County Schools
... up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most of its life is in this phase ...
... up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most of its life is in this phase ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
Stars and the Sun
... – Big enough to swallow first 3 planets – Uses He other elements for about 10 million years ...
... – Big enough to swallow first 3 planets – Uses He other elements for about 10 million years ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 55. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of the way from the center of the galaxy. 56. The Milky Way is classified as a(n) ____________________ galaxy. 57. In addition to size and shape, one of the major differences among galaxies is the ____________________ of their stars. 58. A(n) ____ ...
... 55. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of the way from the center of the galaxy. 56. The Milky Way is classified as a(n) ____________________ galaxy. 57. In addition to size and shape, one of the major differences among galaxies is the ____________________ of their stars. 58. A(n) ____ ...
1000
... star and you notice that the star you are watching has moved about 15 degrees, how long have you been watching? ...
... star and you notice that the star you are watching has moved about 15 degrees, how long have you been watching? ...
May 2016 night sky chart
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.