Indications for an influence of Hot Jupiters
... testing for tidal or magnetic interaction effects in samples of planet-hosting stars is difficult because stellar activity hinders exoplanet detection, so that stellar samples with detected exoplanets show a bias towards low activity for small exoplanets. Aims. We aim to test if exoplanets in close ...
... testing for tidal or magnetic interaction effects in samples of planet-hosting stars is difficult because stellar activity hinders exoplanet detection, so that stellar samples with detected exoplanets show a bias towards low activity for small exoplanets. Aims. We aim to test if exoplanets in close ...
The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027
... C HAPTER 2: The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 ...
... C HAPTER 2: The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 ...
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars
... • A star remains on the main sequence as long as it can fuse hydrogen into helium in its core. – About 90% of total lifetime is spent on main sequence – Stable energy generation during this phase. • Once the core H fuel is gone, the star evolves rapidly off the main-sequence, spending much o ...
... • A star remains on the main sequence as long as it can fuse hydrogen into helium in its core. – About 90% of total lifetime is spent on main sequence – Stable energy generation during this phase. • Once the core H fuel is gone, the star evolves rapidly off the main-sequence, spending much o ...
Heliacal Rising of Canopus in Indian Astronomy
... the northern hemisphere δ should be greater than 90° – 6 φ (i.e. φ > 90° – 6 δ). Such a star will be always above the horizon. Also, if the southern declination of a star is greater than 90° – 6φ such a star will never be seen in a northern latitude, be it Lubdhaka (Sirius) or Agastya (Canopus). Bhā ...
... the northern hemisphere δ should be greater than 90° – 6 φ (i.e. φ > 90° – 6 δ). Such a star will be always above the horizon. Also, if the southern declination of a star is greater than 90° – 6φ such a star will never be seen in a northern latitude, be it Lubdhaka (Sirius) or Agastya (Canopus). Bhā ...
The Milky Way thin disk structure as revealed by stars and young
... the solar system makes it difficult for us to understand the real nature, orientation, and extent of this structure. It was originally detected by Morgan et al. (1953, see Fig. 1), but its nature has been elusive to present days. It might be a real arm, like Perseus, or a kind of inter-arm feature, li ...
... the solar system makes it difficult for us to understand the real nature, orientation, and extent of this structure. It was originally detected by Morgan et al. (1953, see Fig. 1), but its nature has been elusive to present days. It might be a real arm, like Perseus, or a kind of inter-arm feature, li ...
PDF Full-text
... detectability of various molecules in optical and infrared spectra (e.g., [3,5,9]), and to test the effect of different UV flux illumination on the mixing ratios of many molecules (e.g., [3,5,10]). The assumed UV spectral-energy distributions for these models range from the minimal UV flux associate ...
... detectability of various molecules in optical and infrared spectra (e.g., [3,5,9]), and to test the effect of different UV flux illumination on the mixing ratios of many molecules (e.g., [3,5,10]). The assumed UV spectral-energy distributions for these models range from the minimal UV flux associate ...
Astronomy Astrophysics Circumstellar emission in Be/X-ray binaries of the Magellanic
... galaxy (MWG). Such relations had been established so far for isolated Be stars, that is to say, Be stars not known to be in binaries (Dachs et al. 1988, for bright field stars, Fabregat & Torrejón 1998, for Be stars in open clusters). Nevertheless, we now know that the circumstellar envelope of Be s ...
... galaxy (MWG). Such relations had been established so far for isolated Be stars, that is to say, Be stars not known to be in binaries (Dachs et al. 1988, for bright field stars, Fabregat & Torrejón 1998, for Be stars in open clusters). Nevertheless, we now know that the circumstellar envelope of Be s ...
When we look at a neighboring galaxy (such as M31, the
... supergiants from foreground stars—and that is through measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actuall ...
... supergiants from foreground stars—and that is through measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actuall ...
The HIRES science case
... predictions of disc migration. Recent results have shown that hot Jupiter planets on non-coplanar orbits are common, including some planets on retrograde orbits (Triaud et al. 2010). Those measurements have been interpreted as showing that dynamical events are probably not uncommon and that not all ...
... predictions of disc migration. Recent results have shown that hot Jupiter planets on non-coplanar orbits are common, including some planets on retrograde orbits (Triaud et al. 2010). Those measurements have been interpreted as showing that dynamical events are probably not uncommon and that not all ...
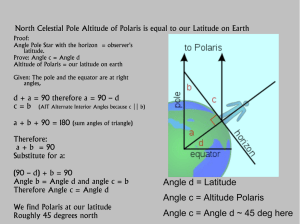
Angle d = Latitude Angle c = Altitude Polaris Angle c
... celestial equator to the zenith > latitude, say 50 deg, then Alt = 90 + (Phi + Dec) rather than (90 – Phi) + Dec Alt = 90 + Our Observing Latitude determines what celestial objects are seen above our local horizon ...
... celestial equator to the zenith > latitude, say 50 deg, then Alt = 90 + (Phi + Dec) rather than (90 – Phi) + Dec Alt = 90 + Our Observing Latitude determines what celestial objects are seen above our local horizon ...
IR Universe
... In the 1980's, astronomers using IRAS data discovered about two dozen stars which had infrared-emitting dust surrounding them, extending hundreds of astronomical units from the stars. This discovery inspired astronomers to make more detailed observations of these stars. What they found around ...
... In the 1980's, astronomers using IRAS data discovered about two dozen stars which had infrared-emitting dust surrounding them, extending hundreds of astronomical units from the stars. This discovery inspired astronomers to make more detailed observations of these stars. What they found around ...
PH607lec11-4gal2
... M101 is 9Mpc away;20x20 arcmin, mV= 7.9 M100 is 20Mpc away; 6x7 arcmin, mV= 9.3 Flocculent spiral: NGC 4414 ...
... M101 is 9Mpc away;20x20 arcmin, mV= 7.9 M100 is 20Mpc away; 6x7 arcmin, mV= 9.3 Flocculent spiral: NGC 4414 ...
6.1 Introduction
... in the gas from which stars have recently formed, such as the Orion nebula. Possibly these most metal-poor stars have been enriched by only one previous generation of stars which themselves presumably formed out of pristine gas. Thus, the chemical composition of the most metal-poor stars known is on ...
... in the gas from which stars have recently formed, such as the Orion nebula. Possibly these most metal-poor stars have been enriched by only one previous generation of stars which themselves presumably formed out of pristine gas. Thus, the chemical composition of the most metal-poor stars known is on ...
Direct Imaging Searches Around White Dwarfs - X
... progenitors: early-type stars (B,A,F), intermediate masses (1.5
... progenitors: early-type stars (B,A,F), intermediate masses (1.5
Chapter 12
... by which the star shifts is extremely small. It was not until the 1830s that the first parallax was measured by the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel at Königsberg Observatory (now in Kaliningrad). Even now, the method fails for most stars farther away than about 100 parsecs because the Earth’s atm ...
... by which the star shifts is extremely small. It was not until the 1830s that the first parallax was measured by the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel at Königsberg Observatory (now in Kaliningrad). Even now, the method fails for most stars farther away than about 100 parsecs because the Earth’s atm ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.