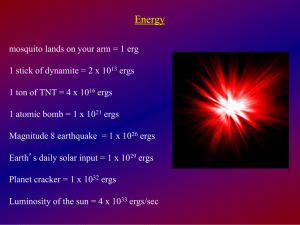
Lecture19
... earth, heading straight to towards the core. It would surface again on the opposite side of the planet, and fall again. Again and again it would fall until it settled at the center of the earth. ...
... earth, heading straight to towards the core. It would surface again on the opposite side of the planet, and fall again. Again and again it would fall until it settled at the center of the earth. ...
TRANSIT
... from the Trapezium, and the matching arc heading off in the opposite direction? With a low power lens, look for the faint splodge around a single bright star away from the Trapezium. This is de Mairan’s Nebula or M43. It is prominent in good observing conditions from all locations. Above and to the ...
... from the Trapezium, and the matching arc heading off in the opposite direction? With a low power lens, look for the faint splodge around a single bright star away from the Trapezium. This is de Mairan’s Nebula or M43. It is prominent in good observing conditions from all locations. Above and to the ...
Surveying the Stars
... images. These are relatively rare – need wide separations, like out to Pluto and beyond – to separate the stars on images • Spectroscopic binaries: by far the most common, binary pairs are usually so close you can only see a blended image of both stars. It is the Doppler Shifts in the spectra of one ...
... images. These are relatively rare – need wide separations, like out to Pluto and beyond – to separate the stars on images • Spectroscopic binaries: by far the most common, binary pairs are usually so close you can only see a blended image of both stars. It is the Doppler Shifts in the spectra of one ...
Although a wall looks real, solid to sight and feel, a wall is not a wall
... A dense world far, far away: Astronomers have detected the first rocky planet ever found outside our solar system. Until now, most of the some 500 “exoplanets” discovered orbiting distant stars have been Jupitersize gas giants. The latest find, named Kepler-10b, is only 40 percent larger than Earth, ...
... A dense world far, far away: Astronomers have detected the first rocky planet ever found outside our solar system. Until now, most of the some 500 “exoplanets” discovered orbiting distant stars have been Jupitersize gas giants. The latest find, named Kepler-10b, is only 40 percent larger than Earth, ...
Stars - CBSD.org
... Magnitudes • Hipparchus decided that all the brightest stars in the night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • ...
... Magnitudes • Hipparchus decided that all the brightest stars in the night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • ...
Scientists discover surprising importance of `I Love Q` for
... "Getting a paper accepted into 'Science' is very knowing the details of their internal structure. difficult," Yunes said. "It's a great honor to be accepted. This encourages us to continue working These relations – described in Yunes and Yagi's hard to make new, important discoveries." paper titled ...
... "Getting a paper accepted into 'Science' is very knowing the details of their internal structure. difficult," Yunes said. "It's a great honor to be accepted. This encourages us to continue working These relations – described in Yunes and Yagi's hard to make new, important discoveries." paper titled ...
ASTR100 Class 01 - University of Maryland Department of
... How can that be? Answer: one is bigger than the other! ...
... How can that be? Answer: one is bigger than the other! ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... • Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum. The Compositions of Stars • Scientists have learned that stars are made up of the same elements that compose Earth. • The most common element in sta ...
... • Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum. The Compositions of Stars • Scientists have learned that stars are made up of the same elements that compose Earth. • The most common element in sta ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
What Is a Light
... What is the nearest star to Earth? Our sun is the nearest star. It is about 150,000,000 km away. The next closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri is 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For ...
... What is the nearest star to Earth? Our sun is the nearest star. It is about 150,000,000 km away. The next closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri is 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For ...
White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe
... of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
... of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
Final Exam, Dec. 19, 2015 - Physics@Brock
... 47. The layer of the Sun that we normally see is the (a) corona. (b) chromosphere. (c) ionosphere. (d) photosphere. 48. The neutrinos interact with other elementary particles via (a) electrical force. (b) magnetic force. (c) strong nuclear force. (d) weak nuclear force. 49. The solar neutrino proble ...
... 47. The layer of the Sun that we normally see is the (a) corona. (b) chromosphere. (c) ionosphere. (d) photosphere. 48. The neutrinos interact with other elementary particles via (a) electrical force. (b) magnetic force. (c) strong nuclear force. (d) weak nuclear force. 49. The solar neutrino proble ...
Stellar Evolution - Lick Observatory
... UV photons from the hot, newly formed O stars ionize hydrogen atoms in the surrounding gas. • When electrons recombine with protons (ionized hydrogen atoms), the electrons cascade through the energy levels. A high probability step on the epath to the ground level is to drop from the 2nd excited leve ...
... UV photons from the hot, newly formed O stars ionize hydrogen atoms in the surrounding gas. • When electrons recombine with protons (ionized hydrogen atoms), the electrons cascade through the energy levels. A high probability step on the epath to the ground level is to drop from the 2nd excited leve ...
Birth of Stars
... astronomers need to refine, perhaps significantly, their current models of planetary formation Most of the extrasolar “planets” found are not at all like the ones in our own solar system Many of the extrasolar planets are similar to Jupiter in mass, or more massive, and have highly eccentric orbits ...
... astronomers need to refine, perhaps significantly, their current models of planetary formation Most of the extrasolar “planets” found are not at all like the ones in our own solar system Many of the extrasolar planets are similar to Jupiter in mass, or more massive, and have highly eccentric orbits ...
Is the Sun a Star? - Classroom Websites
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
Measuring Distance with Spectroscopic Parallax
... Finding Luminosity Using the HR Diagram At the end of this activity packet is an HR diagram that you made earlier in this course. The Luminosity of the stars (in units of Suns) is plotted versus the Temperature of the stars in Kelvin (in reverse order). When using this graph, remember that the verti ...
... Finding Luminosity Using the HR Diagram At the end of this activity packet is an HR diagram that you made earlier in this course. The Luminosity of the stars (in units of Suns) is plotted versus the Temperature of the stars in Kelvin (in reverse order). When using this graph, remember that the verti ...
The birth and life of stars
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
Learning About Stars
... http://www.redorbit.com/modules/reflib/article_images/6_15cc05865f89c4801c5ff2a85d74a93c.jpg ...
... http://www.redorbit.com/modules/reflib/article_images/6_15cc05865f89c4801c5ff2a85d74a93c.jpg ...
TRANSIT
... Researchers at the University of Southampton have developed a software package for modelling asteroid impacts that enables them to assess the potential human and economic consequences across the globe. The software, called NEOimpactor, has been specifically developed for measuring the impact of 'sma ...
... Researchers at the University of Southampton have developed a software package for modelling asteroid impacts that enables them to assess the potential human and economic consequences across the globe. The software, called NEOimpactor, has been specifically developed for measuring the impact of 'sma ...
Red supergiants and the past of Cygnus OB2
... Methods. Near-infrared star counts in the Cygnus region reveal moderate evidence for a peak in the areal density of bright, reddened stars approximately coincident with Cygnus OB2. A total of 11 sources are found within a circle of 1◦ radius centered on the association, of which 4 are non-supergiant ...
... Methods. Near-infrared star counts in the Cygnus region reveal moderate evidence for a peak in the areal density of bright, reddened stars approximately coincident with Cygnus OB2. A total of 11 sources are found within a circle of 1◦ radius centered on the association, of which 4 are non-supergiant ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.