Presentation for perspective graduate students 2006
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distance ...
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distance ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... the sun the supernova will contract until so tight only neutrons can exist in the core ...
... the sun the supernova will contract until so tight only neutrons can exist in the core ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF STARS
... star’s absolute brightness is the brightness the star would have if all stars were the same standard distance form Earth. This allows astronomers to compare the brightness of all stars. Distances on Earth are often measured using kilometres and miles. However, distances between stars are so large th ...
... star’s absolute brightness is the brightness the star would have if all stars were the same standard distance form Earth. This allows astronomers to compare the brightness of all stars. Distances on Earth are often measured using kilometres and miles. However, distances between stars are so large th ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
... A constellation contains one or more asterisms (star groups) plus the surrounding region of the dark sky. Much the way that the United States is divided into 50 states, the sky is divided into 88 such constellations (i.e. regions). Each star technically belongs to just one constellation (although tr ...
... A constellation contains one or more asterisms (star groups) plus the surrounding region of the dark sky. Much the way that the United States is divided into 50 states, the sky is divided into 88 such constellations (i.e. regions). Each star technically belongs to just one constellation (although tr ...
LIGO Star Chart
... Betelgeuse appears redder than the other stars. It is located at a right angle to Orion’s belt. You may recall from reading your LIGO Explorer Sheet that Betelgeuse is a red super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to ...
... Betelgeuse appears redder than the other stars. It is located at a right angle to Orion’s belt. You may recall from reading your LIGO Explorer Sheet that Betelgeuse is a red super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... Several stars in and around the constellation Orion labeled with their names and apparent magnitudes. ...
... Several stars in and around the constellation Orion labeled with their names and apparent magnitudes. ...
Lecture10
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
NASC 1100
... The total energy production rate falls from its red giant phase peak. This reduces the star’s luminosity and decreases the star’s radius, making its surface hotter. In the H-R diagram, the star goes down and to the left. All low-mass stars fuse helium into carbon at nearly the same rate they have ...
... The total energy production rate falls from its red giant phase peak. This reduces the star’s luminosity and decreases the star’s radius, making its surface hotter. In the H-R diagram, the star goes down and to the left. All low-mass stars fuse helium into carbon at nearly the same rate they have ...
May 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Constellations - Jolie McLaine`s Senior Project
... • A constellation is a group of stars or an area of the sky that is associated with a name • Located near each other to form a pattern • We know that stars are hot balls of hydrogen and helium, with nuclear fusion at their core ...
... • A constellation is a group of stars or an area of the sky that is associated with a name • Located near each other to form a pattern • We know that stars are hot balls of hydrogen and helium, with nuclear fusion at their core ...
chapter8
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
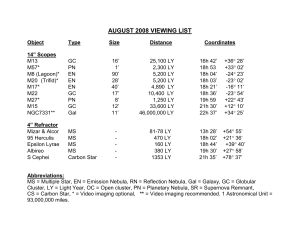
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... Energy is transferred to a thin shell of hydrogen surrounding the core, where hydrogen fusion continues and the shell expands. ...
... Energy is transferred to a thin shell of hydrogen surrounding the core, where hydrogen fusion continues and the shell expands. ...
3 sr -1
... 1 mag. difference gives a factor of 2.512 in apparent brightness (larger magnitude = fainter object!) 1st mag. stars appear 100 times brighter than 6th mag. stars ...
... 1 mag. difference gives a factor of 2.512 in apparent brightness (larger magnitude = fainter object!) 1st mag. stars appear 100 times brighter than 6th mag. stars ...
celestial equator
... make a star catalogue or star chart that is useful for observers at any location on the Earth. For example, the coordinates of Betelgeuse in the year 2000 were RA = 5 hours 55 minutes 10.3 seconds, DEC = +7 deg 24' 25”. ...
... make a star catalogue or star chart that is useful for observers at any location on the Earth. For example, the coordinates of Betelgeuse in the year 2000 were RA = 5 hours 55 minutes 10.3 seconds, DEC = +7 deg 24' 25”. ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... The distance (d) to a star can be determined from a measurement of the star’s parallax (p). The “intrinsic brightness” or luminosity (L) of a star can be determined from a measurement of the star’s apparent brightness (b) and a knowledge of the star’s distance. The surface temperature (T) of a star ...
... The distance (d) to a star can be determined from a measurement of the star’s parallax (p). The “intrinsic brightness” or luminosity (L) of a star can be determined from a measurement of the star’s apparent brightness (b) and a knowledge of the star’s distance. The surface temperature (T) of a star ...
April
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
read in advance to speed your work
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
star
... or black hole). These pairs of stars produce X-rays if the stars are close enough together that material is pulled off the normal star by the gravity of the dense, collapsed star. The X-rays come from the area around the collapsed star where the material that is falling toward it is heated to very h ...
... or black hole). These pairs of stars produce X-rays if the stars are close enough together that material is pulled off the normal star by the gravity of the dense, collapsed star. The X-rays come from the area around the collapsed star where the material that is falling toward it is heated to very h ...