What is a star?
... • Apparent magnitude is the measure of a star’s brightness as seen from Earth. • Ancient astronomers, using only their eyes, described star brightness by magnitude. • They called the brightest stars they could see first magnitude and the faintest stars they could see sixth magnitude. ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the measure of a star’s brightness as seen from Earth. • Ancient astronomers, using only their eyes, described star brightness by magnitude. • They called the brightest stars they could see first magnitude and the faintest stars they could see sixth magnitude. ...
objects in telescope are farther than they appear
... because all have the same Airy Disk radius. However, the star image diameter seen by a telescope user like Galileo depends not just on the Airy Disk radius, but also on factors that set a limit on the intensity of light that can be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.1 ...
... because all have the same Airy Disk radius. However, the star image diameter seen by a telescope user like Galileo depends not just on the Airy Disk radius, but also on factors that set a limit on the intensity of light that can be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.1 ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Journey to the Stars: Activities for Grades 9-12
... Have students read this online article to learn how light transmits information about the composition of distant celestial objects. These objects are so distant that even if we could travel at the speed of light, it would take us thousands of years to reach them. Ask students: What types of informat ...
... Have students read this online article to learn how light transmits information about the composition of distant celestial objects. These objects are so distant that even if we could travel at the speed of light, it would take us thousands of years to reach them. Ask students: What types of informat ...
Spectra of Star Clusters
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
Why is there a main sequence?
... Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence, and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer four important questions: • Why is there a main seq ...
... Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence, and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer four important questions: • Why is there a main seq ...
Distance Ladder
... •Typically 300 km/s or so How to to determine distances: is moving away from us at •Measure v using Doppler shift 2100 km/s? A) 1 Mly D) 484 Mly •Deduce the distance from: B) 10 Mly E) 4,840 Mly v = H0d C) 100 Mly F) 48,400 Mly ...
... •Typically 300 km/s or so How to to determine distances: is moving away from us at •Measure v using Doppler shift 2100 km/s? A) 1 Mly D) 484 Mly •Deduce the distance from: B) 10 Mly E) 4,840 Mly v = H0d C) 100 Mly F) 48,400 Mly ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... • Horizontal branch from giant branch to above the MS turnoff point • Horizontal branch often populated only with variable RR Lyrae stars ...
... • Horizontal branch from giant branch to above the MS turnoff point • Horizontal branch often populated only with variable RR Lyrae stars ...
3 Nightly Motions
... For a star rising in northeastern sky: Stars first rise in the northeast, rise very high into the sky as they approach the meridian, and then set in the northwestern sky. ...
... For a star rising in northeastern sky: Stars first rise in the northeast, rise very high into the sky as they approach the meridian, and then set in the northwestern sky. ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
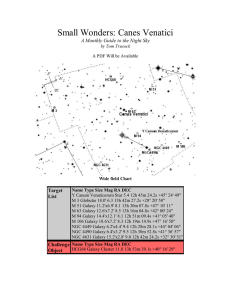
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
Properties of Stars
... Sometimes the orbital plane is lined up so that the stars pass in front of each other as seen from the Earth. Each eclipse will cause the total light from the system to decrease. The amount of the decrease will depend on how much of each star is covered up (they can have different sizes) and on the ...
... Sometimes the orbital plane is lined up so that the stars pass in front of each other as seen from the Earth. Each eclipse will cause the total light from the system to decrease. The amount of the decrease will depend on how much of each star is covered up (they can have different sizes) and on the ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... • 95% of the brightest stars are more luminous than the Sun. • The average absolute magnitude of a bright star is –1.2, equivalent to 300 solar luminosities. ...
... • 95% of the brightest stars are more luminous than the Sun. • The average absolute magnitude of a bright star is –1.2, equivalent to 300 solar luminosities. ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... a) cannot explain how the Sun is stable. b) detect only one-third the number of neutrinos expected by theory. c) cannot detect neutrinos easily. d) are unable to explain how neutrinos oscillate between other types. e) cannot create controlled fusion reactions on Earth. ...
... a) cannot explain how the Sun is stable. b) detect only one-third the number of neutrinos expected by theory. c) cannot detect neutrinos easily. d) are unable to explain how neutrinos oscillate between other types. e) cannot create controlled fusion reactions on Earth. ...
The Milky Way - Midlandstech
... fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). ...
... fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). ...
Shocking Truth about Massive Stars Lidia Oskinova Chandra’s First Decade of Discovery
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
Astronomy (C) - North Carolina Science Olympiad
... galaxy of Milky Way As with 47 Tucanae, more than one population of stars visible Suggests that many globular clusters have rich history of interaction with galaxies & molecular clouds ...
... galaxy of Milky Way As with 47 Tucanae, more than one population of stars visible Suggests that many globular clusters have rich history of interaction with galaxies & molecular clouds ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... Combine parallax and brightness Canopus has twice the parallax of Spica. Since distance α 1 / parallax, Spica must be at twice the distance of Canopus. (The numbers are 100 pc and 200 pc, but you don’t need to know that.) The more distant star (Spica) appears fainter. Since it is twice as distant a ...
... Combine parallax and brightness Canopus has twice the parallax of Spica. Since distance α 1 / parallax, Spica must be at twice the distance of Canopus. (The numbers are 100 pc and 200 pc, but you don’t need to know that.) The more distant star (Spica) appears fainter. Since it is twice as distant a ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool because of their great mass • At the very top of the main sequence, massive stars being very hot and active • In the middle of the main sequence, with very hot but less massive stars positioned higher and massive red giant stars pos ...
... • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool because of their great mass • At the very top of the main sequence, massive stars being very hot and active • In the middle of the main sequence, with very hot but less massive stars positioned higher and massive red giant stars pos ...
The Mighty Hunter in the Winter Sky By Shannon Jackson
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.