LIFEPAC® 7th Grade Science Unit 3 Worktext - HomeSchool
... cloud of stars stretching across the sky. You can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is ...
... cloud of stars stretching across the sky. You can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is ...
Whiteq
... The densities of white dwarves are, of course, very high. Sirius B has a density of about 125,000 g/cm3. The densest may be as much as 10,000 times denser than this. The most dense materials on earth are only about 20 g/cm3. This is why the idea was initially regarded with skepticism. These densitie ...
... The densities of white dwarves are, of course, very high. Sirius B has a density of about 125,000 g/cm3. The densest may be as much as 10,000 times denser than this. The most dense materials on earth are only about 20 g/cm3. This is why the idea was initially regarded with skepticism. These densitie ...
An Introduction To Parallax
... Even the nearest star, Alpha Centauri, is more than 200,000 times further away than the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. This means that the shift in angle we observe in Alpha Centauri is less than 1 second of arc, or less than the thickness of a hair seen across a large rooma . It was not until the m ...
... Even the nearest star, Alpha Centauri, is more than 200,000 times further away than the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. This means that the shift in angle we observe in Alpha Centauri is less than 1 second of arc, or less than the thickness of a hair seen across a large rooma . It was not until the m ...
Chapter 15
... measurement of the distances to the globular clusters? a. The Sun is far from the center of the Milky Way. b. The Sun is near the center of the Milky Way. c. A period-luminosity relationship also exists for RR Lyrae variable stars. d. Globular clusters have 50,000 to 1,000,000 stars. e. Open cluster ...
... measurement of the distances to the globular clusters? a. The Sun is far from the center of the Milky Way. b. The Sun is near the center of the Milky Way. c. A period-luminosity relationship also exists for RR Lyrae variable stars. d. Globular clusters have 50,000 to 1,000,000 stars. e. Open cluster ...
Observations of gravitational microlensing events with OSIRIS
... structure of the Milky Way. Moreover, the nature of its parent star would be clarified by determining its mass to the same uncertainty. To our best knowledge only one microlensing event has been observed from two different vantage points already: OGLE-2005-SMC-001. This was done from Earth and Spitz ...
... structure of the Milky Way. Moreover, the nature of its parent star would be clarified by determining its mass to the same uncertainty. To our best knowledge only one microlensing event has been observed from two different vantage points already: OGLE-2005-SMC-001. This was done from Earth and Spitz ...
01-Star Atlas Project - Mapping the Heavens
... In the Trained Eye Star Atlas, there are two types of maps. Equatorial maps ring the sky around the celestial equator, polar maps show the stars around the north and south poles. Right ascension and declination are encoded on the two types of maps in different ways. On the equatorial maps, the celes ...
... In the Trained Eye Star Atlas, there are two types of maps. Equatorial maps ring the sky around the celestial equator, polar maps show the stars around the north and south poles. Right ascension and declination are encoded on the two types of maps in different ways. On the equatorial maps, the celes ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... In 1837 Argelander, of the Bonn Observatory and orginator of the BD catalogue, was able to derive an apex for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star ...
... In 1837 Argelander, of the Bonn Observatory and orginator of the BD catalogue, was able to derive an apex for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star ...
TISHTRIYA - Earth`s second Sun
... Although, to the naked eye, it looks like one Star it is composed of two Stars. In different research data there seems to be a wide inconsistency in the description of the size and brightness of each of the two stars. The larger and brighter of the two, Sirius A, averages 2-3 times the mass of our s ...
... Although, to the naked eye, it looks like one Star it is composed of two Stars. In different research data there seems to be a wide inconsistency in the description of the size and brightness of each of the two stars. The larger and brighter of the two, Sirius A, averages 2-3 times the mass of our s ...
Pegasus - Interactive Stars
... This monstrous being, whose name we still use to describe deception and delusion, had the body of a goat, the tail of a dragon, and the head of a lion, which belched out sulphur, smoke and flames. Bellerophon asked the goddess of reason, Athene, for help. His prayers were answered in a dream: the gr ...
... This monstrous being, whose name we still use to describe deception and delusion, had the body of a goat, the tail of a dragon, and the head of a lion, which belched out sulphur, smoke and flames. Bellerophon asked the goddess of reason, Athene, for help. His prayers were answered in a dream: the gr ...
Neutron stars and black holes
... Since the Schwarzschild radius of a black hole is rSch = 2 GM / c2, the radius of a black hole is proportional to its mass. A one billion solar mass black hole will have a radius of 3 X 109 km. Since one Astronomical Unit ~ 1.5 X 108 km, it follows that a one billion solar mass black hole has a rad ...
... Since the Schwarzschild radius of a black hole is rSch = 2 GM / c2, the radius of a black hole is proportional to its mass. A one billion solar mass black hole will have a radius of 3 X 109 km. Since one Astronomical Unit ~ 1.5 X 108 km, it follows that a one billion solar mass black hole has a rad ...
harrold_kajubi_astro1
... Mees Telescope with Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Camera Photometry with ATV ...
... Mees Telescope with Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Camera Photometry with ATV ...
Assessment Schedule
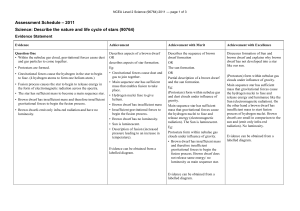
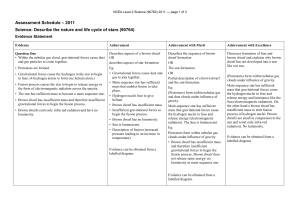
... • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to become a main sequence star. ...
... • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to become a main sequence star. ...
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to become a main sequence star. ...
... • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to become a main sequence star. ...
ph507lecnote07
... arcsec corresponds to 1 AU) EXAMPLE: Sirius: Also known as Alpha Canis Majoris, Sirius is the fifth closest system to Sol, at 8.6 light-years. Sirius is composed of a main-sequence star and a white dwarf stellar remnant. They form a close binary, Alpha Canis Majoris A and B, that is separated "on av ...
... arcsec corresponds to 1 AU) EXAMPLE: Sirius: Also known as Alpha Canis Majoris, Sirius is the fifth closest system to Sol, at 8.6 light-years. Sirius is composed of a main-sequence star and a white dwarf stellar remnant. They form a close binary, Alpha Canis Majoris A and B, that is separated "on av ...
01 Orders of Magnitude and Units
... Q2. There are about 1x1028 molecules of air in the lab. So by how many orders of magnitude are there more molecules in the Sun than in the lab? A. 1056 / 1028 = 1028 so 28 orders of magnitude more molecules in the Sun. Q3. Determine the ratio of the diameter of a hydrogen atom to the diameter of a ...
... Q2. There are about 1x1028 molecules of air in the lab. So by how many orders of magnitude are there more molecules in the Sun than in the lab? A. 1056 / 1028 = 1028 so 28 orders of magnitude more molecules in the Sun. Q3. Determine the ratio of the diameter of a hydrogen atom to the diameter of a ...
February - Fort Worth Astronomical Society
... Satrun onward though the night sky in a race for your attention. This month we will concentrate on Saturn. Saturn, with it's beautiful ring system, can be easily seen from just about any location (except under trees!) It is presently just north of Aldebaran in Taurus. Just about any size scope will ...
... Satrun onward though the night sky in a race for your attention. This month we will concentrate on Saturn. Saturn, with it's beautiful ring system, can be easily seen from just about any location (except under trees!) It is presently just north of Aldebaran in Taurus. Just about any size scope will ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Section 1
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.