June 2010 - Denver Astronomical Society
... was a beautifully restored Alvan Clark 4-inch, circa 1917, brought up by Dan Schechter. We used this scope on its original, and very heavy, Clark #5 mount, with its battery of original eyepieces. The performance was very good. Then Dan mounted the tube assembly on his large Astro Physics GoTo mount ...
... was a beautifully restored Alvan Clark 4-inch, circa 1917, brought up by Dan Schechter. We used this scope on its original, and very heavy, Clark #5 mount, with its battery of original eyepieces. The performance was very good. Then Dan mounted the tube assembly on his large Astro Physics GoTo mount ...
Gone in a flash: supernovae in the survey era
... brighter than a Type Ia supernova). The first of SLSN (Gal-Yam 2012), commonly defined as CFHT, or DECam on the Cerro Tololo Interevent, SCP 06F6, was identified in 2009 and had being brighter than –21 in absolute magnitude American Observatory 4 m Blanco telescope), broad, unexplained spectral abso ...
... brighter than a Type Ia supernova). The first of SLSN (Gal-Yam 2012), commonly defined as CFHT, or DECam on the Cerro Tololo Interevent, SCP 06F6, was identified in 2009 and had being brighter than –21 in absolute magnitude American Observatory 4 m Blanco telescope), broad, unexplained spectral abso ...
Galaxies - senwiki
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
Carolina Kehrig
... There is still a lack of understanding of narrow HeII emitters even at low redshift WR features are not seen whenever narrow HeII is observed IFS spatial offset between nebular HeII-emitting zone and WR stars can be a possible explanation for the non-detection of WR features in some galaxy s ...
... There is still a lack of understanding of narrow HeII emitters even at low redshift WR features are not seen whenever narrow HeII is observed IFS spatial offset between nebular HeII-emitting zone and WR stars can be a possible explanation for the non-detection of WR features in some galaxy s ...
Chapter 20. Galaxies
... reflects variations in the accretion rate. The time scale for the variations can be as short as minutes, hours, days or months. When variable galaxies on these time scales were first discovered it was hard for people to believe, since no object bigger than a few light minutes could vary on time scal ...
... reflects variations in the accretion rate. The time scale for the variations can be as short as minutes, hours, days or months. When variable galaxies on these time scales were first discovered it was hard for people to believe, since no object bigger than a few light minutes could vary on time scal ...
... around 280 parts per million (ppm) to around 380 ppm now. Studies of ice core show that concentrations of CO2 have not been so high for nearly half a million years. At the current rate of increase, they will have reached 800 ppm by the end of the 21st century! Beyond 550 ppm it would not be liveable ...
The Milky Way: Spiral galaxies:
... metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns –! Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals –! Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars –! Nucl ...
... metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns –! Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals –! Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars –! Nucl ...
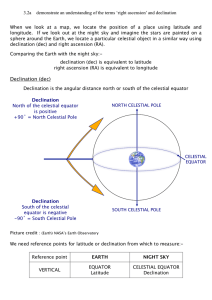
Altitude and Azimuth 4 page
... needs a coordinate system to find objects on the Earth. Navigators and geographers use latitude and longitude to find their way around on the surface of the Earth. Astronomers, though, have one problem that Earth-oriented people don't have. Objects in the sky appear to move over time with respect to ...
... needs a coordinate system to find objects on the Earth. Navigators and geographers use latitude and longitude to find their way around on the surface of the Earth. Astronomers, though, have one problem that Earth-oriented people don't have. Objects in the sky appear to move over time with respect to ...
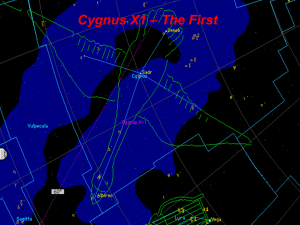
Cygnus X-1
... being a black hole. Cygnus X-1 is about 14,000 light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven th ...
... being a black hole. Cygnus X-1 is about 14,000 light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven th ...
Milky Way inner halo reveals its age | COSMOS magazine
... burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain approximately the mass of the Sun in a volume that is the size of the Earth. This means they are very dense ...
... burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain approximately the mass of the Sun in a volume that is the size of the Earth. This means they are very dense ...
Have You Seen Canopus Tonight?
... other bright stars on the sky, about 310 light years by current estimates. However, other very bright looking stars as Rigel (900 light years?) or Deneb (1,000 light years?) are more distant. Nevertheless, this still makes Canopus a splendid and imposing star as we shall see. We know, too, that Cano ...
... other bright stars on the sky, about 310 light years by current estimates. However, other very bright looking stars as Rigel (900 light years?) or Deneb (1,000 light years?) are more distant. Nevertheless, this still makes Canopus a splendid and imposing star as we shall see. We know, too, that Cano ...
Solution
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 19 Notes: The Stellar
... determine the star formation history in different parts of a nearby galaxy. They divided the galaxy into annuli, and in each annulus they made an HR diagram using stars as observed by the Hubble Space Telescope. They then tried to find a star formation history that would reproduce the observed HR di ...
... determine the star formation history in different parts of a nearby galaxy. They divided the galaxy into annuli, and in each annulus they made an HR diagram using stars as observed by the Hubble Space Telescope. They then tried to find a star formation history that would reproduce the observed HR di ...
Learning goals for Astronomy`s Final 2013
... Define and classify nebulae in galaxies, planetary nebula and star clusters Explain how galaxies were discovered Classify galaxies Explain galaxy formation ...
... Define and classify nebulae in galaxies, planetary nebula and star clusters Explain how galaxies were discovered Classify galaxies Explain galaxy formation ...
Star Formation in the Rosette Complex
... map of the Rosette Complex using the Arecibo telescope. They found that neutral gas in the Rosette Complex is distributed in three main regions which form a rough, extended shell of about 45 pc in radius around the nebula and extend beyond the molecular cloud. This shell would have a center of expan ...
... map of the Rosette Complex using the Arecibo telescope. They found that neutral gas in the Rosette Complex is distributed in three main regions which form a rough, extended shell of about 45 pc in radius around the nebula and extend beyond the molecular cloud. This shell would have a center of expan ...
presentation source
... Quasars have been observed to fluctuate in brightness with periods ranging from a few years to a few hours. Recall that this light variation places an upper limit on the size of the quasar’s energy source. If they are as distant as Hubble’s Law indicates then some mechanism must be producing energie ...
... Quasars have been observed to fluctuate in brightness with periods ranging from a few years to a few hours. Recall that this light variation places an upper limit on the size of the quasar’s energy source. If they are as distant as Hubble’s Law indicates then some mechanism must be producing energie ...
Stellar Properties
... • a star could be very bright because is was very close to us; not because it was truly bright • two stars in the same constellation might not be close to each other; one could be much farther away ...
... • a star could be very bright because is was very close to us; not because it was truly bright • two stars in the same constellation might not be close to each other; one could be much farther away ...
Thermonuclear supernovae and cosmology
... Instability, to collapse in self grav. field Chandrasekhar limit: degenerate electrons can’t support mass above MCh: P~ρ5/3, R~1/M for nonrelativistic electrons. P~ρ4/3 ,R(MCh)=0 for ultrarelat. e Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit for NS mass. ...
... Instability, to collapse in self grav. field Chandrasekhar limit: degenerate electrons can’t support mass above MCh: P~ρ5/3, R~1/M for nonrelativistic electrons. P~ρ4/3 ,R(MCh)=0 for ultrarelat. e Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit for NS mass. ...
astro-ph/0504597 PDF
... Supernovae are really bright – about 10 billion times as luminous as the Sun. They tend to fade over months or years. The energy output of a supernova surpasses that of the galaxy as a whole! When one such occurs in our own Galaxy, that can be seen even in day light for a few weeks. From ancient tim ...
... Supernovae are really bright – about 10 billion times as luminous as the Sun. They tend to fade over months or years. The energy output of a supernova surpasses that of the galaxy as a whole! When one such occurs in our own Galaxy, that can be seen even in day light for a few weeks. From ancient tim ...
Star Sizes - Fort Lewis College
... Parallax Measurements • Earth-based measurements can typically be made to 0.03”, or to a distance of ~30 parsecs (pc) • Distances to several thousand stars are known this way. • The Hipparcos satellite extends the distance to ~200 pc, so distances to nearly one million stars can be measured with pa ...
... Parallax Measurements • Earth-based measurements can typically be made to 0.03”, or to a distance of ~30 parsecs (pc) • Distances to several thousand stars are known this way. • The Hipparcos satellite extends the distance to ~200 pc, so distances to nearly one million stars can be measured with pa ...
Interacting Galaxies
... While galaxies collide, with very rare exceptions, the stars within them do not. This is because so much of a galaxy is simply empty space, with distances between stars about 100 million times larger than their stellar diameters. What collides is the gas and dust between the stars, which produces a ...
... While galaxies collide, with very rare exceptions, the stars within them do not. This is because so much of a galaxy is simply empty space, with distances between stars about 100 million times larger than their stellar diameters. What collides is the gas and dust between the stars, which produces a ...
The Fundamental Plane, Stellar Popula6ons
... Some of the (many) things we don’t know (at least not well)… What is the relaBon between stellar mass and dynamical mass, and how does this vary with parent halo mass & environment? How do the observed trends in stellar populaBons vary with ...
... Some of the (many) things we don’t know (at least not well)… What is the relaBon between stellar mass and dynamical mass, and how does this vary with parent halo mass & environment? How do the observed trends in stellar populaBons vary with ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.