StarIntro_sb12
... The enormous pressure and heat in a star’s core convert matter into energy. Stars consist of controlled atomic reactions called nuclear fusion in which hydrogen (nuclei) atoms fuse to form ...
... The enormous pressure and heat in a star’s core convert matter into energy. Stars consist of controlled atomic reactions called nuclear fusion in which hydrogen (nuclei) atoms fuse to form ...
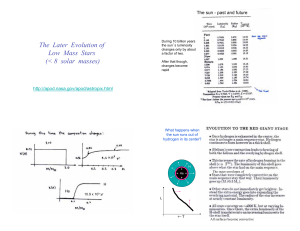
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
Document
... Cutaway drawing of the interior structure of an Asymptotic Giant Branch or AGB star. Hydrogen an helium burning shells are both active, though not necessarily both at the same time. The He and H burning regions are much thinner than this diagram suggests. The outer layers are convective. The C-O cor ...
... Cutaway drawing of the interior structure of an Asymptotic Giant Branch or AGB star. Hydrogen an helium burning shells are both active, though not necessarily both at the same time. The He and H burning regions are much thinner than this diagram suggests. The outer layers are convective. The C-O cor ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
The Northern Winter Constellations
... a fuzzy blur of stars closely grouped. These are the Pleiades, or the Seven Sisters. ...
... a fuzzy blur of stars closely grouped. These are the Pleiades, or the Seven Sisters. ...
Eyeing the retina nebula
... Planetary nebulae play a key role in recycling these materials throughout the universe. Without them rocky planets like the Earth and carbon-based life forms like us would not exist. The image of the Retina Nebula has been enhanced to dramatize its beauty. The difference in brightness between the ce ...
... Planetary nebulae play a key role in recycling these materials throughout the universe. Without them rocky planets like the Earth and carbon-based life forms like us would not exist. The image of the Retina Nebula has been enhanced to dramatize its beauty. The difference in brightness between the ce ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... Their temperatures are not that high (2000— 6000K) but they are very luminous by Stefan-Boltzmann law they must be very large (big surface area) Outer parts of the Sun’s atmosphere will engulf Earth and Mars when it becomes a red supergiant! ...
... Their temperatures are not that high (2000— 6000K) but they are very luminous by Stefan-Boltzmann law they must be very large (big surface area) Outer parts of the Sun’s atmosphere will engulf Earth and Mars when it becomes a red supergiant! ...
Study Guide for the Comprehensive Final Exam
... Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. State or identify a characteristic temperature for an O star, a G2 star and an M star. Solve problems with the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R T similar to HW problems. State the contribution of binary stars to o ...
... Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. State or identify a characteristic temperature for an O star, a G2 star and an M star. Solve problems with the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R T similar to HW problems. State the contribution of binary stars to o ...
Learning About Stars
... does not appear to move like the rest of the stars. In fact…all of the stars seem to circle Polaris. Look at the Star Trail photo. The camera was left on to record the movement of the stars. The North Star doesn’t appear blurry or have a trail because it is in the same position the whole time. ...
... does not appear to move like the rest of the stars. In fact…all of the stars seem to circle Polaris. Look at the Star Trail photo. The camera was left on to record the movement of the stars. The North Star doesn’t appear blurry or have a trail because it is in the same position the whole time. ...
Eyes to the Sky
... Our own galaxy seen edge-on; this faint band crossing the sky is the combined light of millions of stars. ...
... Our own galaxy seen edge-on; this faint band crossing the sky is the combined light of millions of stars. ...
The birth and life of stars
... about 100 million K, the thermonuclear process of helium fusion begins. This process converts helium to carbon, then to oxygen. In a massive giant, helium fusion begins gradually. In a less massive giant, it begins suddenly in a process called helium flash. The age of a stellar cluster can be esti ...
... about 100 million K, the thermonuclear process of helium fusion begins. This process converts helium to carbon, then to oxygen. In a massive giant, helium fusion begins gradually. In a less massive giant, it begins suddenly in a process called helium flash. The age of a stellar cluster can be esti ...
Red Giant Red Giant White Giant Red Giant White Giant White Giant
... High mass star that consumes hydrogen rapidly. The star’s enormous weight crushes the core with so much pressure that fusion is possible. Mass: 4 - 10 SM StarPower Points: 9 ...
... High mass star that consumes hydrogen rapidly. The star’s enormous weight crushes the core with so much pressure that fusion is possible. Mass: 4 - 10 SM StarPower Points: 9 ...
Galileo Galilei From The Starry Messenger (1610) and The Assayer
... to the unaided vision, adding countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty ea ...
... to the unaided vision, adding countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty ea ...
ASTR2100 - Saint Mary's University | Astronomy & Physics
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
Letot STELLAR EVOLUTION By Kyle Letot Grade Level: 6
... covering of rubber on the balloon is holding the air in. (I will include that stars do NOT have a membrane such as the balloon, rather the balloon has visual similarities that students can see and touch without the harming effects of an actual star.) Next I will point out how the air we used to blow ...
... covering of rubber on the balloon is holding the air in. (I will include that stars do NOT have a membrane such as the balloon, rather the balloon has visual similarities that students can see and touch without the harming effects of an actual star.) Next I will point out how the air we used to blow ...
Slide 1
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true: a) A reindeer grows a new set of antlers every year b) Reindeers have a poisonous spine on their back legs c) The reindeer is the only species where the males AND females grow antlers d) A reindeer’s antlers can grow up to 1.3m long ...
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true: a) A reindeer grows a new set of antlers every year b) Reindeers have a poisonous spine on their back legs c) The reindeer is the only species where the males AND females grow antlers d) A reindeer’s antlers can grow up to 1.3m long ...
The Sun and other Stars
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
Explores Angular Size - Chandra X
... appears to be about 1/2 degree in diameter. The planet Venus, when it is closest to Earth, appears to be even smaller - only about 1/60 of a degree. This small angle is called the arc-minute. There are 60 arcminutes in one degree. What we really would like to know is, physically, how big something i ...
... appears to be about 1/2 degree in diameter. The planet Venus, when it is closest to Earth, appears to be even smaller - only about 1/60 of a degree. This small angle is called the arc-minute. There are 60 arcminutes in one degree. What we really would like to know is, physically, how big something i ...
Neutron Stars
... Clicker Question: Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a ...
... Clicker Question: Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.