Combined Background Field Removal and Reconstruction for
... Combined Background Field Removal and Reconstruction for Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Maximilian März ...
... Combined Background Field Removal and Reconstruction for Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Maximilian März ...
Gene Mutation Story
... the Alzheimer’s only gets worse. After a while, William begins to develop other mental problems, and can’t seem to complete the simplest of tasks due to forgetting where he put stuff, and generally what he was doing in the first place. William will eventually experience total memory loss and not be ...
... the Alzheimer’s only gets worse. After a while, William begins to develop other mental problems, and can’t seem to complete the simplest of tasks due to forgetting where he put stuff, and generally what he was doing in the first place. William will eventually experience total memory loss and not be ...
CH. 2 (BIOLOGY)
... tissues being studied. Next, you will be asked to lie down on a flat examination table that is moved into the center of a PET scanner—a doughnut-like shaped machine. This machine detects and records the energy given off by the tracer substance and, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converte ...
... tissues being studied. Next, you will be asked to lie down on a flat examination table that is moved into the center of a PET scanner—a doughnut-like shaped machine. This machine detects and records the energy given off by the tracer substance and, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converte ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... cortex: amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb These structures attach emotional “feelings” to survival-related functions Structures of the limbic system form in early development and provide a foundation for emotional memory, associating emotions with particular events or ...
... cortex: amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb These structures attach emotional “feelings” to survival-related functions Structures of the limbic system form in early development and provide a foundation for emotional memory, associating emotions with particular events or ...
Comparative approaches to cortical microcircuits
... Although these brain areas and their role in spatial navigation have been studied for decades in rats [36], it is only recently that their operations have been examined in flying mammals such as the Egyptian fruit bat [37,38], an animal with long-range foraging behavior and challenging navigational ...
... Although these brain areas and their role in spatial navigation have been studied for decades in rats [36], it is only recently that their operations have been examined in flying mammals such as the Egyptian fruit bat [37,38], an animal with long-range foraging behavior and challenging navigational ...
Of Toasters and Molecular Ticker Tapes
... are important for a given neuroscience question. As long as we cannot approach understanding the entire brain at the same time, it is highly useful to select what to stimulate and what to measure. (2) Get stimuli into the brain. To understand what neurons do, inputs need to be defined or known. (3) ...
... are important for a given neuroscience question. As long as we cannot approach understanding the entire brain at the same time, it is highly useful to select what to stimulate and what to measure. (2) Get stimuli into the brain. To understand what neurons do, inputs need to be defined or known. (3) ...
Cerebrum Renatus Conference (3)
... of the soul. It is partly due to Stenson that the blind loyalty to ancient scientific concepts was demolished, and the scientific method, and the interpretation of results based on proper analysis came into play in the scientific arena. He disagreed with Descartes’ opinion that the body is a machine ...
... of the soul. It is partly due to Stenson that the blind loyalty to ancient scientific concepts was demolished, and the scientific method, and the interpretation of results based on proper analysis came into play in the scientific arena. He disagreed with Descartes’ opinion that the body is a machine ...
Overview of brain anatomy
... injury – most commonly from stroke or trauma. The type of aphasia depends on the brain area affected. Broca’s area lies in the left frontal lobe. If this area is damaged, one may have difficulty moving the tongue or facial muscles to produce the sounds of speech. The individual can still read and un ...
... injury – most commonly from stroke or trauma. The type of aphasia depends on the brain area affected. Broca’s area lies in the left frontal lobe. If this area is damaged, one may have difficulty moving the tongue or facial muscles to produce the sounds of speech. The individual can still read and un ...
Brain Anatomy Overview
... injury – most commonly from stroke or trauma. The type of aphasia depends on the brain area affected. Broca’s area lies in the left frontal lobe. If this area is damaged, one may have difficulty moving the tongue or facial muscles to produce the sounds of speech. The individual can still read and un ...
... injury – most commonly from stroke or trauma. The type of aphasia depends on the brain area affected. Broca’s area lies in the left frontal lobe. If this area is damaged, one may have difficulty moving the tongue or facial muscles to produce the sounds of speech. The individual can still read and un ...
Vladimirov et al., Nature Methods, 2014
... motor behaviors. The first was the forward optomotor response (OMR)1,2, in which swimming is elicited by visual gratings moving in the tail-to-head direction. In our system, the OMR during light-sheet scanning was comparable to the OMR without the presence of the light sheets (Fig. 1c). We defined a ...
... motor behaviors. The first was the forward optomotor response (OMR)1,2, in which swimming is elicited by visual gratings moving in the tail-to-head direction. In our system, the OMR during light-sheet scanning was comparable to the OMR without the presence of the light sheets (Fig. 1c). We defined a ...
Brain_stemCh45
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
Biology
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
PSYCH-UNIT-2-0 -NOTES-BIO-INTRO
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
File - firestone falcons
... network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. ...
... network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. ...
Biology The Nervous System
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
... keep the Brain alert and conscious. The RAS also helps to control respiration and circulation and serves as a filtering system for incoming sensory signals. For example, we awaken to the sound of an alarm clock, to a bright light flash, or to a painful pinch because activity in the RAS that arouses ...
... keep the Brain alert and conscious. The RAS also helps to control respiration and circulation and serves as a filtering system for incoming sensory signals. For example, we awaken to the sound of an alarm clock, to a bright light flash, or to a painful pinch because activity in the RAS that arouses ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint Biological basis of behavior-
... Wrinkles on the brain are made by fissures and folds called gyri ...
... Wrinkles on the brain are made by fissures and folds called gyri ...
Neurogenesis - Brain Mind Forum
... related experiences. Very quickly, it has so much information stored in its neurons that some sort of hierarchy of focus develops to enable the organism to respond to imminent danger as fast as possible, while, at other times allowing the system to pause, reflect, evaluate and develop more efficient ...
... related experiences. Very quickly, it has so much information stored in its neurons that some sort of hierarchy of focus develops to enable the organism to respond to imminent danger as fast as possible, while, at other times allowing the system to pause, reflect, evaluate and develop more efficient ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... The Structure and Function of the Brain The brain processes information transmitted from the senses so that the body can react to changes in the external and internal environment. The brain makes up 2% of the body weight but may contain 15% of the blood supply and consumes 20% of the body’s oxy ...
... The Structure and Function of the Brain The brain processes information transmitted from the senses so that the body can react to changes in the external and internal environment. The brain makes up 2% of the body weight but may contain 15% of the blood supply and consumes 20% of the body’s oxy ...
Brain
... planning, mood, smell and social judgement • Parietal contains areas for sensory reception & integration of sensory information • Occipital is visual center of brain • Temporal contains areas for hearing, smell, learning, memory, emotional behavior • Insula is still little known ...
... planning, mood, smell and social judgement • Parietal contains areas for sensory reception & integration of sensory information • Occipital is visual center of brain • Temporal contains areas for hearing, smell, learning, memory, emotional behavior • Insula is still little known ...
A New Mathematics-Inspired Understanding of Breathing and the
... the two sides of the body). Synchronization is key to the network’s operation. Other mathematicians—David Terman, Jon Rubin, and colleagues—joined the modeling effort [3,6], and several remarkable network properties were deduced. The same cellular burst-generating mechanism involving persistent sodi ...
... the two sides of the body). Synchronization is key to the network’s operation. Other mathematicians—David Terman, Jon Rubin, and colleagues—joined the modeling effort [3,6], and several remarkable network properties were deduced. The same cellular burst-generating mechanism involving persistent sodi ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... Neuron: Nerve cell. The basic units of the central nervous system, neurons are responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. ...
... Neuron: Nerve cell. The basic units of the central nervous system, neurons are responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. ...
PoNS Fact Sheet - Helius Medical Technologies
... and cerebellum – the main control centers for many life functions including sensory perception and movement. From the brain stem, these impulses travel throughout the brain and activate or reactivate neurons and structures involved in human function – the cortex, spinal cord and potentially the enti ...
... and cerebellum – the main control centers for many life functions including sensory perception and movement. From the brain stem, these impulses travel throughout the brain and activate or reactivate neurons and structures involved in human function – the cortex, spinal cord and potentially the enti ...
Slide ()
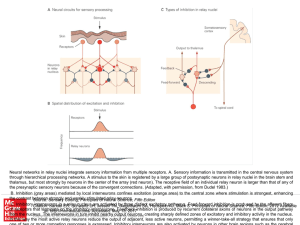
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.