PDF - Molecular Brain
... products and maintain energy homeostasis. The above hypothesis was further confirmed by a widespread decrease in levels of Suc, which is an important intermediate product of TCA cycle, thereby indicating the inhibition of TCA cycle. Metabolic changes in Lac and Suc suggest that altered energy metabo ...
... products and maintain energy homeostasis. The above hypothesis was further confirmed by a widespread decrease in levels of Suc, which is an important intermediate product of TCA cycle, thereby indicating the inhibition of TCA cycle. Metabolic changes in Lac and Suc suggest that altered energy metabo ...
module 6 - sandrablake
... meet, there is a tiny fluid filled gap called a synapse that action potentials cannot jump. In this gap, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters travel across the synapse to carry the information from one neuron to the next. The neurotransmitters can come to rest only in receptor sites design ...
... meet, there is a tiny fluid filled gap called a synapse that action potentials cannot jump. In this gap, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters travel across the synapse to carry the information from one neuron to the next. The neurotransmitters can come to rest only in receptor sites design ...
doc neuro chap 13, 14, 15, 16, 18
... nonhuman subjects; evolutionary continuity; interest in animals for their own sake; provide experimental control. Experimental approaches to understanding behaviour 1- Invasive physiological research methods 2- Behavioural paradigm that assess constituent cognitive processes 3- Pharmacological resea ...
... nonhuman subjects; evolutionary continuity; interest in animals for their own sake; provide experimental control. Experimental approaches to understanding behaviour 1- Invasive physiological research methods 2- Behavioural paradigm that assess constituent cognitive processes 3- Pharmacological resea ...
discintro
... individual cognizers. Turing’s criterion for cognition was individual, autonomous input/output capacity. It is not clear that distributed cognition could pass the Turing Test. Cognition is what cognizers do: What are cognizers? They are autonomous systems with certain I/O (input/output) performance ...
... individual cognizers. Turing’s criterion for cognition was individual, autonomous input/output capacity. It is not clear that distributed cognition could pass the Turing Test. Cognition is what cognizers do: What are cognizers? They are autonomous systems with certain I/O (input/output) performance ...
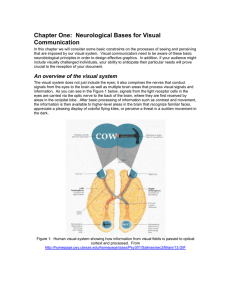
Chapter One: Neurological Bases for Visual Communication
... The visual cortices The “mixed” signals from the optic chiasmus travel all the way to the back of your brain first, to a region known as the primary visual cortex, or V1. This low-level vision area is responsible for recognizing orientation of lines, contrast, and some motion. You are not consciousl ...
... The visual cortices The “mixed” signals from the optic chiasmus travel all the way to the back of your brain first, to a region known as the primary visual cortex, or V1. This low-level vision area is responsible for recognizing orientation of lines, contrast, and some motion. You are not consciousl ...
What Do Mirror Neurons Mean?
... other individuals to learn how to cope with the world. This is an important difference between humans and other species that may play a major role in bootstrapping more sophisticated cognitive social skills (we are back to the nature/nurture debate). At present we can only make hypotheses about the ...
... other individuals to learn how to cope with the world. This is an important difference between humans and other species that may play a major role in bootstrapping more sophisticated cognitive social skills (we are back to the nature/nurture debate). At present we can only make hypotheses about the ...
Barlow, Horace (2001) - Cambridge Neuroscience
... Statistical regularities of the environment are important for learning, memory, intelligence, inductive inference, and in fact for any area of cognitive science where an informationprocessing brain promotes survival by exploiting them. This has been recognised by many of those interested in cognitiv ...
... Statistical regularities of the environment are important for learning, memory, intelligence, inductive inference, and in fact for any area of cognitive science where an informationprocessing brain promotes survival by exploiting them. This has been recognised by many of those interested in cognitiv ...
Sleep imaging and the neuro- psychological assessment of dreams
... The study of human sleep has recently benefited from the contribution of functional imaging techniques, such as PET [1–6] and fMRI [7], which provide maps of changes in regional neural activity during distinct sleep stages. Meaningful information is obtained when the neuroimaging data are explained ...
... The study of human sleep has recently benefited from the contribution of functional imaging techniques, such as PET [1–6] and fMRI [7], which provide maps of changes in regional neural activity during distinct sleep stages. Meaningful information is obtained when the neuroimaging data are explained ...
Di (n)-Butyl Phthalate Induced Neuronal Perturbations in Rat Brain
... mammals over the generations. While DBP found to be environmental endocrine disruptor (EED) acts as estrogenic or anti-androgenic which impedes the generation of gonadal hormones found essential for the development of CNS during the critical period of development [16]. Markey et al. (2003) [17] find ...
... mammals over the generations. While DBP found to be environmental endocrine disruptor (EED) acts as estrogenic or anti-androgenic which impedes the generation of gonadal hormones found essential for the development of CNS during the critical period of development [16]. Markey et al. (2003) [17] find ...
The Nervous System - Blackwell Publishing
... (see chapter 6). Some of those hormones not only influence your heart and muscles, but also modify what is happening in your brain. Your elation at winning reflects activity in your brain’s reward systems. And throughout the sequence, your memory systems (see chapter 11) were laying down records of ...
... (see chapter 6). Some of those hormones not only influence your heart and muscles, but also modify what is happening in your brain. Your elation at winning reflects activity in your brain’s reward systems. And throughout the sequence, your memory systems (see chapter 11) were laying down records of ...
chapt14_HumanBiology14e_lecture
... What are the two parts of the nervous system? What three things protect the CNS? What are the four parts of the brain and their functions? What is the reticular activating system and the limbic system? What are some higher mental functions of the brain? What are the two parts of the peripheral nervo ...
... What are the two parts of the nervous system? What three things protect the CNS? What are the four parts of the brain and their functions? What is the reticular activating system and the limbic system? What are some higher mental functions of the brain? What are the two parts of the peripheral nervo ...
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM. (2009). Targeted electrode
... pathways linking these regions in humans can result in disturbances in emotion regulation typical of MDD, namely negative mood coupled with sustained changes in motivation, motor performance, cognition, and circadian functions. Studies of regional brain dysfunction with functional imaging further su ...
... pathways linking these regions in humans can result in disturbances in emotion regulation typical of MDD, namely negative mood coupled with sustained changes in motivation, motor performance, cognition, and circadian functions. Studies of regional brain dysfunction with functional imaging further su ...
Cells in human postmortem brain tissue slices remain alive for
... During the first few days, the green cells (containing active esterases) became brighter and the number of red nuclei (dead cells) did not appear to alter. This indicates that the tissue needed to recover from the postmortem situation and the transfer to the culture medium. After recovery, viable ce ...
... During the first few days, the green cells (containing active esterases) became brighter and the number of red nuclei (dead cells) did not appear to alter. This indicates that the tissue needed to recover from the postmortem situation and the transfer to the culture medium. After recovery, viable ce ...
The Nervous System
... the understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system, and to the understanding of biological, psychological and social factors that influence learning and memory. Use these tables as checklists when revising. Tick off each dot point when you are satisfied that you have thoroughly co ...
... the understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system, and to the understanding of biological, psychological and social factors that influence learning and memory. Use these tables as checklists when revising. Tick off each dot point when you are satisfied that you have thoroughly co ...
Modeling cortical maps with Topographica
... input pathway, but larger scale models will be crucial for understanding phenomena such as object perception, scene segmentation, speech processing, and motor control. Topographica is intended to support the development of such models. To make it practical to model topographic maps at this large sca ...
... input pathway, but larger scale models will be crucial for understanding phenomena such as object perception, scene segmentation, speech processing, and motor control. Topographica is intended to support the development of such models. To make it practical to model topographic maps at this large sca ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is composed of those nerves that branch from ...
... system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is composed of those nerves that branch from ...
Chapter 12: The Central Nervous System
... production Recently shown to “light up” as we prepare to think or even think about voluntary activities other than speech ...
... production Recently shown to “light up” as we prepare to think or even think about voluntary activities other than speech ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is composed of those nerves that branch from ...
... system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is composed of those nerves that branch from ...
How Does the Brain Develop?
... In the course of development, changes take place both in the brain and in behavior. Scientists assume that these two lines of development are closely linked. As the brain develops, neurons become more and more intricately connected, and these increasingly complex interconnections underlie increased ...
... In the course of development, changes take place both in the brain and in behavior. Scientists assume that these two lines of development are closely linked. As the brain develops, neurons become more and more intricately connected, and these increasingly complex interconnections underlie increased ...
Decision Making: Hitting an uncertain target | eLife
... decisions), while the primary motor cortex is responsible for executing the decision. (B) In a target estimation situation there is an infinite number of options (six of which are indicated by red arrows), and the probability of success can be plotted as a distribution with two peaks (yellow line). ...
... decisions), while the primary motor cortex is responsible for executing the decision. (B) In a target estimation situation there is an infinite number of options (six of which are indicated by red arrows), and the probability of success can be plotted as a distribution with two peaks (yellow line). ...
Outline for CNS, PNS, and ANS
... O. corpus callosum – largest commissure (connection) between the hemispheres. Allows them to communicate. P. primary motor area – controls voluntary muscle movements - located in the precentral gyrus Q. primary sensory area – receives information from voluntary muscles. Located in the postcentral gy ...
... O. corpus callosum – largest commissure (connection) between the hemispheres. Allows them to communicate. P. primary motor area – controls voluntary muscle movements - located in the precentral gyrus Q. primary sensory area – receives information from voluntary muscles. Located in the postcentral gy ...
Cognition with Neurons: A Large-Scale, Biologically Realistic Model of the... Task
... human performance on the Wason task. Since the early 1990s, there have been a series of suggestions as to how to incorporate structure-sensitive processing in models employing distributed representations (including Spatter Codes (Kanerva 1994); Holographic Reduced Representations (HRRs; Plate 1991); ...
... human performance on the Wason task. Since the early 1990s, there have been a series of suggestions as to how to incorporate structure-sensitive processing in models employing distributed representations (including Spatter Codes (Kanerva 1994); Holographic Reduced Representations (HRRs; Plate 1991); ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.