No Slide Title
... Formation of the cerebellum or cerebrum involves formation of multiple neuronal layers in the cortex There is a second wave of proliferation fron the inner ventricular layer-->Germinal layer and give rise to cerebellar cortex ...
... Formation of the cerebellum or cerebrum involves formation of multiple neuronal layers in the cortex There is a second wave of proliferation fron the inner ventricular layer-->Germinal layer and give rise to cerebellar cortex ...
Document
... Introduced as being scientific but its use was exploited by quacks on gullible individuals ...
... Introduced as being scientific but its use was exploited by quacks on gullible individuals ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... NMDA channels are activated rise in Ca2+ triggers calcium-dependent kinases and the tyrosine kinase that together induce LTP. The Ca2+/calmodulin kinase phosphorylates channels and increases their sensitivity to glumate. Once LTP is induced, the postsynaptic cell release a set of retrograde messe ...
... NMDA channels are activated rise in Ca2+ triggers calcium-dependent kinases and the tyrosine kinase that together induce LTP. The Ca2+/calmodulin kinase phosphorylates channels and increases their sensitivity to glumate. Once LTP is induced, the postsynaptic cell release a set of retrograde messe ...
BUILDING AN ARTIFICIAL BRAIN
... "Simulation and Evolution of the Motions of a Life Sized Kitten Robot "Robokoneko" as Controlled by a 32000 Neural Net Module Artificial Brain", Hugo de Garis, Nikolai Petroff, Michael Korkin, Gary Fehr, Eiji Nawa, (Invitation by Editor to the Computational Geometry Journal (CGJ), Special Issue on C ...
... "Simulation and Evolution of the Motions of a Life Sized Kitten Robot "Robokoneko" as Controlled by a 32000 Neural Net Module Artificial Brain", Hugo de Garis, Nikolai Petroff, Michael Korkin, Gary Fehr, Eiji Nawa, (Invitation by Editor to the Computational Geometry Journal (CGJ), Special Issue on C ...
Unit 2 bio-behavior review guide
... Use your book to answer these questions. This will help be your study guide for your test. 1. The right hemisphere, in most people, is primarily responsible for a. counting b. sensation c. emotions d. speech 2. If a person's left hemisphere is dominant, they will probably be a. left-handed b. right- ...
... Use your book to answer these questions. This will help be your study guide for your test. 1. The right hemisphere, in most people, is primarily responsible for a. counting b. sensation c. emotions d. speech 2. If a person's left hemisphere is dominant, they will probably be a. left-handed b. right- ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... • Neurons: nerve cells • Dendrites: branch-like end of neuron which receives messages • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
... • Neurons: nerve cells • Dendrites: branch-like end of neuron which receives messages • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
... synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptive field, with parallel regions where illumination eit ...
... synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptive field, with parallel regions where illumination eit ...
File
... • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and personality. • The brain stem is in charge of keeping the automatic systems of your body working. ...
... • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and personality. • The brain stem is in charge of keeping the automatic systems of your body working. ...
Autism And Mirror Neurons
... • Mirror neurons in the posterior parietal cortex interpret the movement • Mirror neurons in the inferior frontal cortex infer the goal or intent of the action • Parts of the insula, which receive input from all three cortical areas, project to the limbic system ...
... • Mirror neurons in the posterior parietal cortex interpret the movement • Mirror neurons in the inferior frontal cortex infer the goal or intent of the action • Parts of the insula, which receive input from all three cortical areas, project to the limbic system ...
FIRST BRAIN-TO-BRAIN INTERFACE ALLOWS TRANSMISSION
... "neurophysiology of social interaction." "To understand social interaction, we could record from animals' brains while they are socializing and analyze how their brains adapt—for example when a new member of the colony is introduced," he said. Such complex experiments will be enabled by the laborato ...
... "neurophysiology of social interaction." "To understand social interaction, we could record from animals' brains while they are socializing and analyze how their brains adapt—for example when a new member of the colony is introduced," he said. Such complex experiments will be enabled by the laborato ...
Culturing the adolescent brain: what can
... that show considerable cultural variation in the transition from childhood to adulthood and, first of all, unpack the very category of ‘adolescence’ as we commonly know it in cognitive neuroscience. THE CULTURAL CONSTRUCTION OF ADOLESCENCE AS A CATEGORY In searching for biologically based explanatio ...
... that show considerable cultural variation in the transition from childhood to adulthood and, first of all, unpack the very category of ‘adolescence’ as we commonly know it in cognitive neuroscience. THE CULTURAL CONSTRUCTION OF ADOLESCENCE AS A CATEGORY In searching for biologically based explanatio ...
Central nervous system practical block
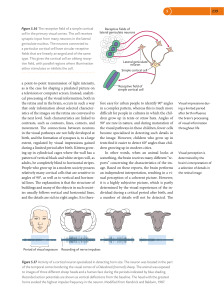
... demyelinated area. The lesion is centered around a small vein (arrow) which is surrounded by inflammatory cells . ...
... demyelinated area. The lesion is centered around a small vein (arrow) which is surrounded by inflammatory cells . ...
feel like doing. Brain-Based Principles 1-6
... “Our brains stay mostly the same—except we lose brain cells every day.” (This is old and mostly wrong.) ...
... “Our brains stay mostly the same—except we lose brain cells every day.” (This is old and mostly wrong.) ...
Local integration 2
... between blood flow and cognitive activity to an understanding of how cognitive activity takes place • We want to know not just where cognitive activity is happening, but how it is happening • Requires calibrating imaging data with data about neural activity Cognitive Science José Luis Bermúdez / C ...
... between blood flow and cognitive activity to an understanding of how cognitive activity takes place • We want to know not just where cognitive activity is happening, but how it is happening • Requires calibrating imaging data with data about neural activity Cognitive Science José Luis Bermúdez / C ...
Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Document
... D. The solution of saliva and food molecules wash over your taste buds and an impulse is sent to the brain E. The brain interprets the impulse and you can taste the food. F. Four basic areas of taste buds: sweet, salty, sour, and bitter G. When you are sick, you have trouble tasting food because the ...
... D. The solution of saliva and food molecules wash over your taste buds and an impulse is sent to the brain E. The brain interprets the impulse and you can taste the food. F. Four basic areas of taste buds: sweet, salty, sour, and bitter G. When you are sick, you have trouble tasting food because the ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Impulse Impulse is an electrical or chemical message that is carried by nerve cells. ...
... Impulse Impulse is an electrical or chemical message that is carried by nerve cells. ...
PowerPoint Chapter 29
... 1. Nervous system- fast acting and “hard wired” a. Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal cordinterprets messages and stores some messages for later use ...
... 1. Nervous system- fast acting and “hard wired” a. Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal cordinterprets messages and stores some messages for later use ...
Gluck_OutlinePPT_Ch02
... Early study of the brain: Phrenology: relate personality/mental abilities to size and shape of skull. Study brain anatomy by examining post-mortem healthy or abnormal brains after death. ...
... Early study of the brain: Phrenology: relate personality/mental abilities to size and shape of skull. Study brain anatomy by examining post-mortem healthy or abnormal brains after death. ...
Communication Breakdown KEY
... You have explored electrical communication from the basic flow of ions in the membrane to the communication of nerve cells via chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Unfortunately, at many points along the communication pathway, this system can fail. And when this system fails, the effects are d ...
... You have explored electrical communication from the basic flow of ions in the membrane to the communication of nerve cells via chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Unfortunately, at many points along the communication pathway, this system can fail. And when this system fails, the effects are d ...
Focus on Vocabulary Chapter 02
... into the association areas of the brain has shown that they do not have specific functions; rather, they are involved in many different operations such as interpreting, integrating, and acting on sensory information and linking it with stored memories. The incorrect notion that we use only 10 percen ...
... into the association areas of the brain has shown that they do not have specific functions; rather, they are involved in many different operations such as interpreting, integrating, and acting on sensory information and linking it with stored memories. The incorrect notion that we use only 10 percen ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... system (or CNS) includes the brain and the spinal cord. The brain is, of course, located within the skull and the spinal cord is encased in the bony spinal column which runs down the center of the back. The peripheral nervous system (PNS), on the other hand, consists of nerve fibers which run from t ...
... system (or CNS) includes the brain and the spinal cord. The brain is, of course, located within the skull and the spinal cord is encased in the bony spinal column which runs down the center of the back. The peripheral nervous system (PNS), on the other hand, consists of nerve fibers which run from t ...
Modeling Neuromodulation as a Framework to Integrate - HAL
... discuss here and will be only considered in the remaining of the paper. In order to introduce the influence of neuromodulators on the normal functioning of the cerebral structures, let us first rapidly define what we call a ’normal’ (or nominal) functioning of the cognitive architecture. In short, a ...
... discuss here and will be only considered in the remaining of the paper. In order to introduce the influence of neuromodulators on the normal functioning of the cerebral structures, let us first rapidly define what we call a ’normal’ (or nominal) functioning of the cognitive architecture. In short, a ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.