Physiology Ch 58 p711-720 [4-25
... causes decreases in arterial pressure/heart rate transmitted through reticular regions Regulation of Body Temperature – anterior portion of hypothalamus (preoptic area) regulates body temperature; increase in blood temperature activates temp-sensitive neurons, whereas a decrease in blood temp decr ...
... causes decreases in arterial pressure/heart rate transmitted through reticular regions Regulation of Body Temperature – anterior portion of hypothalamus (preoptic area) regulates body temperature; increase in blood temperature activates temp-sensitive neurons, whereas a decrease in blood temp decr ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... Reinforcement Learning: Theoretical Comment on O’Reilly et al. (2007) James C. Houk Northwestern University The ability to survive in the world depends critically on the brain’s capacity to detect earlier and earlier predictors of reward or punishment. The dominant theoretical perspective for unders ...
... Reinforcement Learning: Theoretical Comment on O’Reilly et al. (2007) James C. Houk Northwestern University The ability to survive in the world depends critically on the brain’s capacity to detect earlier and earlier predictors of reward or punishment. The dominant theoretical perspective for unders ...
Clinical and Neuropathological Features of
... severe loss of Purkinje cells and neurons of the granular layer, accompanied by reactive Bergmann gliosis (Fig. 2a, b). Staining with CHIP antibody showed mainly cytoplasmic diffuse reactivity in neurons, often extending to dendrites and axons (Fig. 2c, d), and also in astrocytes. Some swollen axona ...
... severe loss of Purkinje cells and neurons of the granular layer, accompanied by reactive Bergmann gliosis (Fig. 2a, b). Staining with CHIP antibody showed mainly cytoplasmic diffuse reactivity in neurons, often extending to dendrites and axons (Fig. 2c, d), and also in astrocytes. Some swollen axona ...
How do Human Sensors Work?
... receptor on your finger that senses it and relays it to the nervous system (spinal cord and brain), which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of how to react, and then commands the hand muscles (the effector) to jerk back quickly. In summary: We go from stimulus (touch) to respons ...
... receptor on your finger that senses it and relays it to the nervous system (spinal cord and brain), which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of how to react, and then commands the hand muscles (the effector) to jerk back quickly. In summary: We go from stimulus (touch) to respons ...
Neurotransmitter Test Assessment
... oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be a contributor to anxiousness. Also, brain norepinephrine turnover is increased in conditions of str ...
... oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be a contributor to anxiousness. Also, brain norepinephrine turnover is increased in conditions of str ...
OCULAR HEMORRHAGE IN CHILDREN
... cells undergo mitoses to produce neurons and glia. After mitoses, some of the newly generated cells will remain in the germinal zone and undergo further divisions, while others will migrate outward to their final destinations. At 8 gw, the first young neurons begin to migrate outward. Initially, sim ...
... cells undergo mitoses to produce neurons and glia. After mitoses, some of the newly generated cells will remain in the germinal zone and undergo further divisions, while others will migrate outward to their final destinations. At 8 gw, the first young neurons begin to migrate outward. Initially, sim ...
Chapter 48 Nervous System
... Biogenic amines mostly function within the CNS. Dopamine and serotonin affect mood and have been linked to depression, attention deficit disorder; Parkinson's and schizophrenia result from lack of dopamine. ...
... Biogenic amines mostly function within the CNS. Dopamine and serotonin affect mood and have been linked to depression, attention deficit disorder; Parkinson's and schizophrenia result from lack of dopamine. ...
Document
... the cortex and basal ganglia control motor and cognitive programs, whereas connections between the cortex and the medial temporal region and amygdala mediate emotional behavior. Abnormalities in the development of the cerebral cortex and associated structures have been suggested to occur in several ...
... the cortex and basal ganglia control motor and cognitive programs, whereas connections between the cortex and the medial temporal region and amygdala mediate emotional behavior. Abnormalities in the development of the cerebral cortex and associated structures have been suggested to occur in several ...
Neural Substrate Expansion for the Restoration of Brain
... clinical translation of this concept could transform the prospects of patients suffering from congenital brain defects or acquired brain damage. In recent years, both biological (Arvidsson et al., 2002; Gaillard et al., 2007; Niu et al., 2013; Michelsen et al., 2015) and electronic (Berger et al., 2 ...
... clinical translation of this concept could transform the prospects of patients suffering from congenital brain defects or acquired brain damage. In recent years, both biological (Arvidsson et al., 2002; Gaillard et al., 2007; Niu et al., 2013; Michelsen et al., 2015) and electronic (Berger et al., 2 ...
Nervous
... Part of the auditory pathways and visual reflexes Also involved in regulating muscle tone/activity and coordination ...
... Part of the auditory pathways and visual reflexes Also involved in regulating muscle tone/activity and coordination ...
Resources: - Real Science
... First they show that the network of brain cells used in future thought is not isolated in the brain's frontal cortex, as some researchers suggest. The frontal cortex plays a well-known role in activities focused on the future, such as anticipation, planning and monitoring. But the spark for these, a ...
... First they show that the network of brain cells used in future thought is not isolated in the brain's frontal cortex, as some researchers suggest. The frontal cortex plays a well-known role in activities focused on the future, such as anticipation, planning and monitoring. But the spark for these, a ...
Nervous System - AP Psychology: 2(A)
... LO 2.7 Structures controlling emotion, learning, memory, and motivation AP Subdivisions & functions ...
... LO 2.7 Structures controlling emotion, learning, memory, and motivation AP Subdivisions & functions ...
Neurology
... Cerebral Cortex- Over evolutionary time, gray matter developed over the cerebrum. This is the cerebral cortex and it is an information-processing center. It increased in size more rapidly than the skull so that it has become folded (convoluted) in order to fit in the skull. Intelligence, emotion, cr ...
... Cerebral Cortex- Over evolutionary time, gray matter developed over the cerebrum. This is the cerebral cortex and it is an information-processing center. It increased in size more rapidly than the skull so that it has become folded (convoluted) in order to fit in the skull. Intelligence, emotion, cr ...
Selective loss of 20S proteasome a-subunits in the substantia nigra
... 20S proteasomal b- and a-subunits and were quantified by densitometry (Fig. 1A) [11,19]. In control brains, the content of b-subunits were similar in the various brain regions studied and these levels did not change significantly in PD (Fig. 1B). The content of a-subunits were different in the vario ...
... 20S proteasomal b- and a-subunits and were quantified by densitometry (Fig. 1A) [11,19]. In control brains, the content of b-subunits were similar in the various brain regions studied and these levels did not change significantly in PD (Fig. 1B). The content of a-subunits were different in the vario ...
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 1. The Neuroendocrine System: Sum
... Non-regulatory Behaviors: behaviors that are not controlled by homeostatic mechanisms - all behaviors excluding those regulated by homeostatic processes Examples: sexual behavior, parental behavior, aggression, playing sports, watching TV, etc The hypothalamus is particularly important for the contr ...
... Non-regulatory Behaviors: behaviors that are not controlled by homeostatic mechanisms - all behaviors excluding those regulated by homeostatic processes Examples: sexual behavior, parental behavior, aggression, playing sports, watching TV, etc The hypothalamus is particularly important for the contr ...
Analysis of Functional MRI Data Using Mutual Information?
... Functional magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful new imaging modality with the ability to noninvasively generate images of the brain that re ect brain tissue hemodynamics. Brain tissue hemodynamics are spatially related to the metabolic demands of the brain tissue caused by neuronal activity. The ...
... Functional magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful new imaging modality with the ability to noninvasively generate images of the brain that re ect brain tissue hemodynamics. Brain tissue hemodynamics are spatially related to the metabolic demands of the brain tissue caused by neuronal activity. The ...
8th Grade Information Processing
... the nervous systems, including structure, function, and disorders. • Neuroscience is a relatively new field. New information is always being discovered and there are still many unexplained mysteries of the brain. ...
... the nervous systems, including structure, function, and disorders. • Neuroscience is a relatively new field. New information is always being discovered and there are still many unexplained mysteries of the brain. ...
Mike Webster the king of the NFL comes in with all his brute force
... are seen in almost any sport. People get killed in sports that they love, mostly by just playing the game. In this text, concussions and CTE information will be shown and also how CTE and concussions affects these sports, how to get these cases, what is the NFL doing about this, how can you die f ...
... are seen in almost any sport. People get killed in sports that they love, mostly by just playing the game. In this text, concussions and CTE information will be shown and also how CTE and concussions affects these sports, how to get these cases, what is the NFL doing about this, how can you die f ...
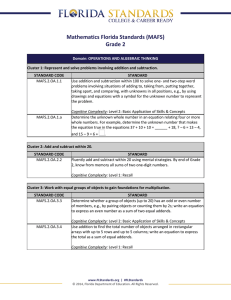
Grade 2 - MAFS - Florida Department Of Education
... Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object. Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole-number units. Cognitive Complexity: Level 2: Basic Applic ...
... Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object. Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole-number units. Cognitive Complexity: Level 2: Basic Applic ...
CHAPTER 4 How do neurons transmit information?
... electrons = positive pole) Electrical potential: difference in electrical charge between negative and positive poles (measured in Volts) ...
... electrons = positive pole) Electrical potential: difference in electrical charge between negative and positive poles (measured in Volts) ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.