Neurosteroids: Expression of Steroidogenic Enzymes and
... human of two isoforms of the enzyme: type I 3b-HSD which is mainly expressed in the placenta (Luu-The et al., 1989) and type II 3b-HSD which is predominantly expressed in the adrenal gland and gonads (Rhéaume et al., 1991). Four types of 3b-HSD cDNAs (types I-IV) have been characterized in the rat ...
... human of two isoforms of the enzyme: type I 3b-HSD which is mainly expressed in the placenta (Luu-The et al., 1989) and type II 3b-HSD which is predominantly expressed in the adrenal gland and gonads (Rhéaume et al., 1991). Four types of 3b-HSD cDNAs (types I-IV) have been characterized in the rat ...
the nervous system i
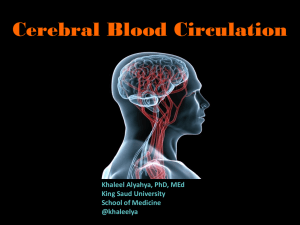
... Describe arterial & venous vascular disorders and their clinical manifestations. ...
... Describe arterial & venous vascular disorders and their clinical manifestations. ...
US Copyright Law
... describe similar relations in the body as a whole; therefore, the brain's orientation with respect to the body determines the coordinate frame of reference that is used to describe anatomical relationships in the brain. But some confusing aspects of the terminology arise from differences in how the ...
... describe similar relations in the body as a whole; therefore, the brain's orientation with respect to the body determines the coordinate frame of reference that is used to describe anatomical relationships in the brain. But some confusing aspects of the terminology arise from differences in how the ...
Sample
... Correct. The dendrite receives a message, the cell body processes it, the axon takes a message to the terminal buttons, and the terminal buttons release neurotransmitters. b) terminal buttons, dendrites, cell body, axon c) cell body, dendrites, terminal buttons, axon Incorrect. Every part of this an ...
... Correct. The dendrite receives a message, the cell body processes it, the axon takes a message to the terminal buttons, and the terminal buttons release neurotransmitters. b) terminal buttons, dendrites, cell body, axon c) cell body, dendrites, terminal buttons, axon Incorrect. Every part of this an ...
Chapter 8 The Nervous System
... and gray matter Acts as the major center for controlling the ANS; therefore, it helps control the functioning of most internal organs Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands; therefore, it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contain ...
... and gray matter Acts as the major center for controlling the ANS; therefore, it helps control the functioning of most internal organs Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands; therefore, it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contain ...
The Neural Architecture Underlying Habit Learning: An Evolving
... When I began to study the brain, as a student in the late 1960's, there was enormous excitement about work on the neocortex. Surely this was the organ of thought and creativity, the organ underlying our ability to see and hear and feel, our ability to act deliberatively, to do mathematics. And, buil ...
... When I began to study the brain, as a student in the late 1960's, there was enormous excitement about work on the neocortex. Surely this was the organ of thought and creativity, the organ underlying our ability to see and hear and feel, our ability to act deliberatively, to do mathematics. And, buil ...
Full Text
... and empty space in the background of the target stimulus can predict both the Muller-Lyer and Titchener (and some others) illusions based on the same computational processes From the author’s point of view, formation of the same perceptual outcome is not inconceivable based on a continues mode (28, ...
... and empty space in the background of the target stimulus can predict both the Muller-Lyer and Titchener (and some others) illusions based on the same computational processes From the author’s point of view, formation of the same perceptual outcome is not inconceivable based on a continues mode (28, ...
Neuroscience, Fifth Edition
... Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Body: The Dorsal Column–Medial Lemniscal System 198 Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Face: The Trigeminothalamic System 200 Central Pathways Conveying Proprioceptive Information from the Body 200 Central Pathways Conveyin ...
... Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Body: The Dorsal Column–Medial Lemniscal System 198 Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Face: The Trigeminothalamic System 200 Central Pathways Conveying Proprioceptive Information from the Body 200 Central Pathways Conveyin ...
Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Activity in
... input resistance, and these effects were blocked by bicuculline. Application of SP depolarized hamster rNST neurons. Thus, GABA and SP have similar membrane effects in both the rat and hamster rNST. A Tiumber of investigators have demonstrated that glutamate is the putative neurotransmitter involved ...
... input resistance, and these effects were blocked by bicuculline. Application of SP depolarized hamster rNST neurons. Thus, GABA and SP have similar membrane effects in both the rat and hamster rNST. A Tiumber of investigators have demonstrated that glutamate is the putative neurotransmitter involved ...
nervous system part 6 EEG, walkfulness and sleep
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
EEG - pressthebar
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
... nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds before and during REM sleep. ...
Acetylcholinesterase in central vocal control nuclei of the zebra finch
... and memory processes. The vocal repertoire in each case needs to be acquired. Once acquired it is either retained throughout life in a stereotyped manner, or can built upon. It may be lost in one season when not in use, and needs to be acquired anew in the next when required. The vocal control pathw ...
... and memory processes. The vocal repertoire in each case needs to be acquired. Once acquired it is either retained throughout life in a stereotyped manner, or can built upon. It may be lost in one season when not in use, and needs to be acquired anew in the next when required. The vocal control pathw ...
Effect of deep brain stimulation on substantia nigra neurons in a
... DBS is a surgical treatment method developed in the last decade, and is recognized as a new milestone for treatment of PD since the introduction of levodopa. Through continuous high-frequency stimulation regulating neural network function, DBS realigns the balance in basal ganglia motor circuits, wh ...
... DBS is a surgical treatment method developed in the last decade, and is recognized as a new milestone for treatment of PD since the introduction of levodopa. Through continuous high-frequency stimulation regulating neural network function, DBS realigns the balance in basal ganglia motor circuits, wh ...
5-28-2007
... ‘sublenticular extended amygdala’, a continuum between the centromedial amygdala and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (Heimer and Van Hoesen, 2006). It remains an open question whether or not activations related to the basal forebrain corticopetal system can be segregated from those cell grou ...
... ‘sublenticular extended amygdala’, a continuum between the centromedial amygdala and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (Heimer and Van Hoesen, 2006). It remains an open question whether or not activations related to the basal forebrain corticopetal system can be segregated from those cell grou ...
ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Dopaminergic Neurons
... other neurons? and 2) is there differential vulnerability to CXI inhibition within the dopaminergic midbrain population, and is this correlated with the pattern of neurodegeneration? In this context, a new neurotoxicological PD model, developed by Bertabet et al. (4), is of high relevance. Chronic b ...
... other neurons? and 2) is there differential vulnerability to CXI inhibition within the dopaminergic midbrain population, and is this correlated with the pattern of neurodegeneration? In this context, a new neurotoxicological PD model, developed by Bertabet et al. (4), is of high relevance. Chronic b ...
States of Consciousness Ch. 5
... synthesizes neural signals generated from activity in the lower part of the brain – dreams brain’s attempts to find logic in random brain activity (internally generated stimuli) that occurs during sleep • primary motor and sensory areas of forebrain stimulated (create sensation of running/feeling ...
... synthesizes neural signals generated from activity in the lower part of the brain – dreams brain’s attempts to find logic in random brain activity (internally generated stimuli) that occurs during sleep • primary motor and sensory areas of forebrain stimulated (create sensation of running/feeling ...
The Isotropic Fractionator: A Fast, Reliable Method to Determine
... of isolated nuclei in which cytoarchitectural heterogeneities have been literally dissolved. Because this suspension has a known, defined volume and can be made homogeneous by agitation, the total number of nuclei therein (and, therefore, the total number of cells in the original tissue) can be esti ...
... of isolated nuclei in which cytoarchitectural heterogeneities have been literally dissolved. Because this suspension has a known, defined volume and can be made homogeneous by agitation, the total number of nuclei therein (and, therefore, the total number of cells in the original tissue) can be esti ...
cp_kellermann_launay_17092010
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
Ontogeny, Compartmentation, and Turnover of Spectrin lsoforms in
... across brain regions develops during the third postnatal week. In this compartment, both spectrin forms may be metabolized in viva, at least in part, by calcium-activated proteolysis. The presence in mammalian neurons of 2 spectrin isoforms and their compattmentation into distinct domains suggests m ...
... across brain regions develops during the third postnatal week. In this compartment, both spectrin forms may be metabolized in viva, at least in part, by calcium-activated proteolysis. The presence in mammalian neurons of 2 spectrin isoforms and their compattmentation into distinct domains suggests m ...
Communication as an emergent metaphor for neuronal operation
... from statistics. Moreover, as in fact classical neural nets offer the same explanatory power as regression, they can be therefore regarded as its non-linear counterparts. It is however doubtful whether non-linear regression constitutes a satisfactory (or the most general) model of fundamental inform ...
... from statistics. Moreover, as in fact classical neural nets offer the same explanatory power as regression, they can be therefore regarded as its non-linear counterparts. It is however doubtful whether non-linear regression constitutes a satisfactory (or the most general) model of fundamental inform ...
29.2 Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Makes decisions on what needs to be done • Sends messages/instructions to motor neurons • Located in CNS ...
... • Makes decisions on what needs to be done • Sends messages/instructions to motor neurons • Located in CNS ...
Chapter 13
... C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses are located in which part of the brain? A.midbrain B.corpus callosum C.cerebrum D.medulla oblongata E.cerebellum ...
... C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses are located in which part of the brain? A.midbrain B.corpus callosum C.cerebrum D.medulla oblongata E.cerebellum ...
the nervous system i
... Review: THE BRAIN Large mass of nervous tissue located in cranial cavity. Has four major regions. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) ...
... Review: THE BRAIN Large mass of nervous tissue located in cranial cavity. Has four major regions. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) ...
Lecture Guide - TestbankCart.com
... life-sustaining functions such as breathing and swallowing. The nerves from each side of the body also cross over in this structure to opposite sides. 2. The pons is above the medulla and acts as a bridge between the lower part of the brain and the upper part. It influences sleep, dreaming, arousal, ...
... life-sustaining functions such as breathing and swallowing. The nerves from each side of the body also cross over in this structure to opposite sides. 2. The pons is above the medulla and acts as a bridge between the lower part of the brain and the upper part. It influences sleep, dreaming, arousal, ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.