Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... targets of these neurons express NGF mRNA and protein (Korsching et al., 1985; Shelton and Reichardt, 1986; AyerLeLievre et al., 1988).At target fields, NGF is taken up by highaffinity NGF receptors (NGF-R) on nerve terminals (Greene and Shooter, 1980; Taniuchi et al., 1986; Stach and Perez-Polo, 19 ...
... targets of these neurons express NGF mRNA and protein (Korsching et al., 1985; Shelton and Reichardt, 1986; AyerLeLievre et al., 1988).At target fields, NGF is taken up by highaffinity NGF receptors (NGF-R) on nerve terminals (Greene and Shooter, 1980; Taniuchi et al., 1986; Stach and Perez-Polo, 19 ...
llllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll
... cardiovascular system. It is clear that thrombin aids in the formation of blood clots by catalyzing the conversion of ?brinogen to ?brin. which is an integral part of most clots. In addition. thrombin is known to act directly on cells in the blood and in the interior blood vessel wall. and speci?cal ...
... cardiovascular system. It is clear that thrombin aids in the formation of blood clots by catalyzing the conversion of ?brinogen to ?brin. which is an integral part of most clots. In addition. thrombin is known to act directly on cells in the blood and in the interior blood vessel wall. and speci?cal ...
Amo, Neuron, 2014
... is often more effective for animal survival than panic behavior alone. A candidate site responsible for active avoidance is the lateral habenula (LHb). In mammals, LHb neurons are phasically activated to negative or aversive emotional events or by situations where the outcome does not match the init ...
... is often more effective for animal survival than panic behavior alone. A candidate site responsible for active avoidance is the lateral habenula (LHb). In mammals, LHb neurons are phasically activated to negative or aversive emotional events or by situations where the outcome does not match the init ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... in animals (Woolf et al., 1977) and humans (Wall and CronlyDillon, 1960), and pathological pain in patients (Wall and Sweet, 1967; Meyer and Fields, 1972), the underlying mechanisms of this inhibition are still largely unknown. Notably, whether such an inhibition of nociception occurs at the cortica ...
... in animals (Woolf et al., 1977) and humans (Wall and CronlyDillon, 1960), and pathological pain in patients (Wall and Sweet, 1967; Meyer and Fields, 1972), the underlying mechanisms of this inhibition are still largely unknown. Notably, whether such an inhibition of nociception occurs at the cortica ...
Downloadable Full Text - DSpace@MIT
... (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc), which play important roles in a broad range of motivated behaviors and neuropsychiatric disorders1-3. Although DA neuron activity often correlates with a reward prediction error (i.e. the difference between expected and actual rewards) these cells also can signal ...
... (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc), which play important roles in a broad range of motivated behaviors and neuropsychiatric disorders1-3. Although DA neuron activity often correlates with a reward prediction error (i.e. the difference between expected and actual rewards) these cells also can signal ...
The neuronal structure of the substantia nigra in the guinea pig
... and Pfister [7] distinguished polygonal (spiny or aspiny), fusiform and triangular neurons. These neurons are considered to be nigral projection cells, whereas small spherical, spindle-shaped and neuroglioform neurons are reported to be interneurons [7]. The fusiform, triangular and multipolar neuro ...
... and Pfister [7] distinguished polygonal (spiny or aspiny), fusiform and triangular neurons. These neurons are considered to be nigral projection cells, whereas small spherical, spindle-shaped and neuroglioform neurons are reported to be interneurons [7]. The fusiform, triangular and multipolar neuro ...
Differences in postingestive metabolism of glutamate and glycine
... 6ByJ (B6) inbred strain drink more MSG and Gly solutions than mice from the 129P3/J (129) inbred strain. Like many free amino acids, Glu and Gly have distinct tastes to humans and other animals. Glu salts, including MSG, have umami (savory meaty) taste, whereas Gly has sweet taste (Refs. 15, 22, 26; ...
... 6ByJ (B6) inbred strain drink more MSG and Gly solutions than mice from the 129P3/J (129) inbred strain. Like many free amino acids, Glu and Gly have distinct tastes to humans and other animals. Glu salts, including MSG, have umami (savory meaty) taste, whereas Gly has sweet taste (Refs. 15, 22, 26; ...
doc PHGY311
... projections reaching other brain regions as well as ending in other hypothalamic nuclei. This intricate system of neuronal connections allows continuous communication between the hypothalamic neurons and other brain regions. The hypothalamic nuclei can be classified on the basis of their anatomic lo ...
... projections reaching other brain regions as well as ending in other hypothalamic nuclei. This intricate system of neuronal connections allows continuous communication between the hypothalamic neurons and other brain regions. The hypothalamic nuclei can be classified on the basis of their anatomic lo ...
Heading: Sensory Deprivation in Humans, Mice, and History Caleb B. Carson Running Head: Sensory Deprivation
... blocked, but it is still unknown as to how this perceptual disorder occurs. There is a theory that this is caused by receptor hypersensitivity. “This could be explained by examining the effective mechanisms of hallucinogens and atypical antipsychotics. Hallucinogens and serotonin-dopamine antagon ...
... blocked, but it is still unknown as to how this perceptual disorder occurs. There is a theory that this is caused by receptor hypersensitivity. “This could be explained by examining the effective mechanisms of hallucinogens and atypical antipsychotics. Hallucinogens and serotonin-dopamine antagon ...
Differences in postingestive metabolism of glutamate and glycine
... 6ByJ (B6) inbred strain drink more MSG and Gly solutions than mice from the 129P3/J (129) inbred strain. Like many free amino acids, Glu and Gly have distinct tastes to humans and other animals. Glu salts, including MSG, have umami (savory meaty) taste, whereas Gly has sweet taste (Refs. 15, 22, 26; ...
... 6ByJ (B6) inbred strain drink more MSG and Gly solutions than mice from the 129P3/J (129) inbred strain. Like many free amino acids, Glu and Gly have distinct tastes to humans and other animals. Glu salts, including MSG, have umami (savory meaty) taste, whereas Gly has sweet taste (Refs. 15, 22, 26; ...
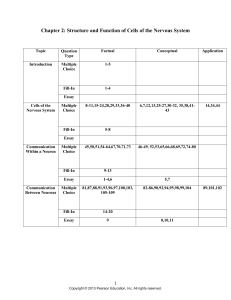
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... A. Adenosine levels increase. B. Dopamine levels decrease. C. The central nervous system slows down. D. Action potentials in neurons become stronger. ...
... A. Adenosine levels increase. B. Dopamine levels decrease. C. The central nervous system slows down. D. Action potentials in neurons become stronger. ...
High acetylcholine sets circuit dynamics for attention and
... The direct depolarization of interneurons is consistent with the fact that nicotinic receptor activation causes an increase in GABA currents in hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons (Alkondon and Albuquerque, 2001). Similarly, in the neocortex, there is a selective nicotinic depolarization of ...
... The direct depolarization of interneurons is consistent with the fact that nicotinic receptor activation causes an increase in GABA currents in hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons (Alkondon and Albuquerque, 2001). Similarly, in the neocortex, there is a selective nicotinic depolarization of ...
13-1 CHAPTER 13 SYNAPSES The nervous system consists of
... norepinephrine effects on sympathetic postsynaptic structures have been explained by invoking a second messenger, in this case, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The model proposed for this kind of transmission, called metabotropic transmission, is shown schematically in Figure 13-4B. According ...
... norepinephrine effects on sympathetic postsynaptic structures have been explained by invoking a second messenger, in this case, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The model proposed for this kind of transmission, called metabotropic transmission, is shown schematically in Figure 13-4B. According ...
The sacral autonomic outflow is sympathetic
... Cranial parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (or visceromotor (VM) neurons) are born in the pMNv domain progenitor domain of the hindbrain5 that expresses the homeogene Phox2b and produces, in addition to VM neurons, branchiomotor (BM) ones6. The postmitotic precursors migrate dorsally 7 to form nu ...
... Cranial parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (or visceromotor (VM) neurons) are born in the pMNv domain progenitor domain of the hindbrain5 that expresses the homeogene Phox2b and produces, in addition to VM neurons, branchiomotor (BM) ones6. The postmitotic precursors migrate dorsally 7 to form nu ...
Feedforward and feedback inhibition in neostriatal GABAergic spiny
... afterhyperpolarization and fired rebound spikes following the offset of a hyperpolarizing current pulse delivered when the cell was depolarized (Fig. 4B), characteristics different from those of either PV+ or LTS neurons. Depolarization from rest sometimes evoked a plateau-like potential that did no ...
... afterhyperpolarization and fired rebound spikes following the offset of a hyperpolarizing current pulse delivered when the cell was depolarized (Fig. 4B), characteristics different from those of either PV+ or LTS neurons. Depolarization from rest sometimes evoked a plateau-like potential that did no ...
Sample
... a. The dynein molecule is involved in anterograde axoplasmic transport. b. Retrograde axoplasmic transport involves moving substances from the soma to the axon terminals. c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde ax ...
... a. The dynein molecule is involved in anterograde axoplasmic transport. b. Retrograde axoplasmic transport involves moving substances from the soma to the axon terminals. c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde ax ...
button - TestbankEbook
... a. The dynein molecule is involved in anterograde axoplasmic transport. b. Retrograde axoplasmic transport involves moving substances from the soma to the axon terminals. c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde ax ...
... a. The dynein molecule is involved in anterograde axoplasmic transport. b. Retrograde axoplasmic transport involves moving substances from the soma to the axon terminals. c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde ax ...
Analysis of Firing Correlations Between Sympathetic Premotor
... activity of premotor neurons might be synchronized by common inputs from those driving sources, especially if they are rhythmic, as suggested by Gebber, Barman and colleagues (see Gebber 1980, 1990). Alternatively the driving inputs might come from multiple, asynchronous sources, causing little sync ...
... activity of premotor neurons might be synchronized by common inputs from those driving sources, especially if they are rhythmic, as suggested by Gebber, Barman and colleagues (see Gebber 1980, 1990). Alternatively the driving inputs might come from multiple, asynchronous sources, causing little sync ...
Neurotransmitter Transporters
... movement of Cl 2 into the cell, while excitatory amino acid transporters are dependent on external H 1 and internal K 1 levels, but not that of Cl 2 . The movement of ions and transmitter during uptake occurs in a defined ratio, with one to several ions coupled to the movement of one molecule of tran ...
... movement of Cl 2 into the cell, while excitatory amino acid transporters are dependent on external H 1 and internal K 1 levels, but not that of Cl 2 . The movement of ions and transmitter during uptake occurs in a defined ratio, with one to several ions coupled to the movement of one molecule of tran ...
Arctigenin Efficiently Enhanced Sedentary Mice Treadmill
... Physical inactivity is considered as one of the potential risk factors for the development of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic diseases, while endurance exercise training could enhance fat oxidation that is associated with insulin sensitivity improvement in obesity. AMP-activated protein kinase ( ...
... Physical inactivity is considered as one of the potential risk factors for the development of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic diseases, while endurance exercise training could enhance fat oxidation that is associated with insulin sensitivity improvement in obesity. AMP-activated protein kinase ( ...
stretch reflex 2
... 5) Reciprocal innervation: • In which stretch of a ms results in reflex contraction of the stretched ms and relaxation of the antagonistic ms. ...
... 5) Reciprocal innervation: • In which stretch of a ms results in reflex contraction of the stretched ms and relaxation of the antagonistic ms. ...
Neuronal and microglial cathepsins in aging and age
... after leakage from lysosomes, whereas others such as cathepsins D, E, and S are stable even at neutral pH (Bednarski and Lynch, 1996; Turk et al., 2000). Therefore, these enzymes are capable of degrading cytoskeletal proteins and bioactive peptides in the cytoplasm of neurons. Furthermore, there is ...
... after leakage from lysosomes, whereas others such as cathepsins D, E, and S are stable even at neutral pH (Bednarski and Lynch, 1996; Turk et al., 2000). Therefore, these enzymes are capable of degrading cytoskeletal proteins and bioactive peptides in the cytoplasm of neurons. Furthermore, there is ...
full text pdf
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
Get PDF - IOS Press
... and was sustained even after several weeks. Increases in BDNF mRNA were also detected in the lumbar spinal cord [36], the cerebellum and the cortex, but was not in the striatum [37]. Voluntary exercise also enhances the process of learning. Indeed, running enhances LTP in the DG and improves spatial ...
... and was sustained even after several weeks. Increases in BDNF mRNA were also detected in the lumbar spinal cord [36], the cerebellum and the cortex, but was not in the striatum [37]. Voluntary exercise also enhances the process of learning. Indeed, running enhances LTP in the DG and improves spatial ...
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Inflammatory and Degenerative Brain
... Indirect evidence of COX-2 involvement in synaptic plasticity has been obtained in the recent years by using COX inhibitors in in vivo and in vitro models of synaptic plasticity. COX-2 inhibitors, but not COX-1 selective inhibitors, administered systemically shortly after training in the Morris wate ...
... Indirect evidence of COX-2 involvement in synaptic plasticity has been obtained in the recent years by using COX inhibitors in in vivo and in vitro models of synaptic plasticity. COX-2 inhibitors, but not COX-1 selective inhibitors, administered systemically shortly after training in the Morris wate ...