File
... Supporting cells in the CNS Support, insulate, and protect neurons Not able to transmit impulses Never lose ability to divide so most brain tumors are gliomas. Tumors are formed by neuroglia ...
... Supporting cells in the CNS Support, insulate, and protect neurons Not able to transmit impulses Never lose ability to divide so most brain tumors are gliomas. Tumors are formed by neuroglia ...
PNS Study Guide
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
5. Electrical Signals
... transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body) • Neurons: (a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses) • Nerve cells: (cell which is part of the nervous system, neuron) • Spinal cord: (the cylindrical bundle of nerve fibres which is enclosed in the spine and connected to the brain, with whi ...
... transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body) • Neurons: (a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses) • Nerve cells: (cell which is part of the nervous system, neuron) • Spinal cord: (the cylindrical bundle of nerve fibres which is enclosed in the spine and connected to the brain, with whi ...
Artificial Eye.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... contact with the nerve fiber layer retinal ganglion cells. The information in this approach must be captured by a camera system before transmitting data and energy to the implant. The "Sub retinal" approach involves the electrical stimulation of the inner retina from the sub retinal space by implant ...
... contact with the nerve fiber layer retinal ganglion cells. The information in this approach must be captured by a camera system before transmitting data and energy to the implant. The "Sub retinal" approach involves the electrical stimulation of the inner retina from the sub retinal space by implant ...
Slide ()
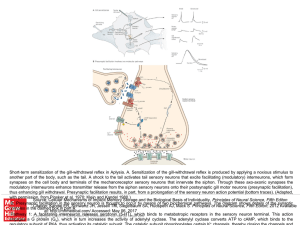
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Information Processing SG
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
MOTILITY-FLOW AND GROWTH CONE NAVIGATION ANALYSIS
... Incubator-Imaging system Image enhancement and processing results ...
... Incubator-Imaging system Image enhancement and processing results ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... are sent around the body on a minute to minute and often a second to second basis. We also know that all body functions depend on these messages to keep us at homeostasis both physiologically and psychologically. We know a lot, but many mysteries of the brain still have to be solved before we can ef ...
... are sent around the body on a minute to minute and often a second to second basis. We also know that all body functions depend on these messages to keep us at homeostasis both physiologically and psychologically. We know a lot, but many mysteries of the brain still have to be solved before we can ef ...
The Nervous System
... environment and monitors the status of the internal environment Central Nervous System -Spinal cord : receives information from the PNS and sends out motor commands for movement, -Brain: integrates various functions of the entire body -both are covered with protective layers called meninges and are ...
... environment and monitors the status of the internal environment Central Nervous System -Spinal cord : receives information from the PNS and sends out motor commands for movement, -Brain: integrates various functions of the entire body -both are covered with protective layers called meninges and are ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
Early Brain Development
... planned actions by the baby. Neurons1: a nerve cell Neural Pathways2: the link between neurons ...
... planned actions by the baby. Neurons1: a nerve cell Neural Pathways2: the link between neurons ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... • Nerve = A long, tough strand of nervous tissue typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
... • Nerve = A long, tough strand of nervous tissue typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
The Nervous System
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
Exam 5 Objectives Bio241
... released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mechanism of action of cocaine? SSRIs? 8. Be familiar (do not memorize chemical structures) with the ...
... released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mechanism of action of cocaine? SSRIs? 8. Be familiar (do not memorize chemical structures) with the ...
Neural-Ville
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
Lecture
... Neural representation: cells, networks, modules Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features ...
... Neural representation: cells, networks, modules Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features ...
The Emerging Nervous System
... connections between neurons • Usually occurs after time of first birthday ...
... connections between neurons • Usually occurs after time of first birthday ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate along the entire length of an axon (1 ...
... – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate along the entire length of an axon (1 ...
Nervous System Notes File
... 1. Caused by injury to the upper part of the spinal cord 2. Causes paralysis of both upper and lower limbs iv. Paraplegia 1. Caused by injury that occurs at the lower part of the spinal cord 2. Causes paralysis of both lower limbs Degenerative Diseases – diseases that cause cells and tissues to dete ...
... 1. Caused by injury to the upper part of the spinal cord 2. Causes paralysis of both upper and lower limbs iv. Paraplegia 1. Caused by injury that occurs at the lower part of the spinal cord 2. Causes paralysis of both lower limbs Degenerative Diseases – diseases that cause cells and tissues to dete ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... gyrus leaves the person able to speak and understand but unable to read. Damage to Wernicke’s area disrupts understanding. Damage to Broca’s area disrupts speaking ...
... gyrus leaves the person able to speak and understand but unable to read. Damage to Wernicke’s area disrupts understanding. Damage to Broca’s area disrupts speaking ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
I. Introduction to class
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
The Nervous System
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
Neural Nets
... History of neural networks research The Perceptron Examples Training algorithm Fundamental training theorem Two-level perceptrons ...
... History of neural networks research The Perceptron Examples Training algorithm Fundamental training theorem Two-level perceptrons ...