Fundamentals of magnetic field
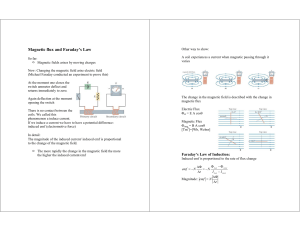
... The flux change occurs either because the magnetic field is changing with time (transformer inductance) or because the wire loop is moving relative to a magnetic field (motional inductance). The Faraday's induction law describes both phenomena. a) If a wire loop is fixed and the flux is varying with ...
... The flux change occurs either because the magnetic field is changing with time (transformer inductance) or because the wire loop is moving relative to a magnetic field (motional inductance). The Faraday's induction law describes both phenomena. a) If a wire loop is fixed and the flux is varying with ...
chapter20
... • Self-inductance occurs when the changing flux through a circuit arises from the circuit itself. – As the current increases, the magnetic flux through a loop due to this current also increases. – The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux. – As the magnitude of the ...
... • Self-inductance occurs when the changing flux through a circuit arises from the circuit itself. – As the current increases, the magnetic flux through a loop due to this current also increases. – The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux. – As the magnitude of the ...
B - LSU Physics
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
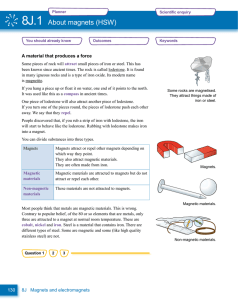
8J.1 About magnets (HSW)
... A strong magnet held on one side of your hand can move a magnetic object on the other side. The magnetic force passes through non-magnetic materials like paper, plastic, paint, skin and bone. The force between a magnet and another magnet or some magnetic material works through many other materials. ...
... A strong magnet held on one side of your hand can move a magnetic object on the other side. The magnetic force passes through non-magnetic materials like paper, plastic, paint, skin and bone. The force between a magnet and another magnet or some magnetic material works through many other materials. ...
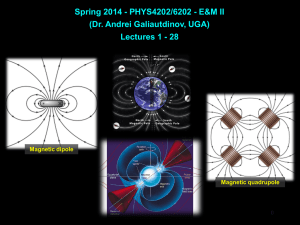
Spring 2014 - PHYS4202/6202 - E&M II (Dr. Andrei Galiautdinov, UGA) 0
... change its magnetization. To select a memory location, one of the X and one of the Y lines are driven with half the current ("halfselect") required to cause this change. Only the combined B-field generated where the X and Y lines cross is sufficient to change the state; other cores will see only hal ...
... change its magnetization. To select a memory location, one of the X and one of the Y lines are driven with half the current ("halfselect") required to cause this change. Only the combined B-field generated where the X and Y lines cross is sufficient to change the state; other cores will see only hal ...
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION • So far we have
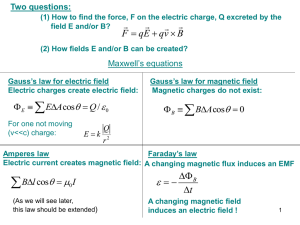
... law relates the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed loop to the current passing thru that loop, while Faraday’s law relates the line integral of the electric field around a closed loop to the rate of change of the magnetic flux thru that loop. Both give fields that encircle their res ...
... law relates the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed loop to the current passing thru that loop, while Faraday’s law relates the line integral of the electric field around a closed loop to the rate of change of the magnetic flux thru that loop. Both give fields that encircle their res ...
Maxwell`s Equations, Part I: History
... to be stored for long periods of time, letting researchers experiment with electricity and see its effects more clearly. Advances were quick, given the ready source of what we now know as static electricity. Among other discoveries was the demonstration by Alessandro Volta that materials could be e ...
... to be stored for long periods of time, letting researchers experiment with electricity and see its effects more clearly. Advances were quick, given the ready source of what we now know as static electricity. Among other discoveries was the demonstration by Alessandro Volta that materials could be e ...
• How does the neutron interact with magnetism? • The fundamental
... It arises from the spatial distribution of unpaired electrons around a magnetic atom INSTITUT MAX VON LAUE - PAUL LANGEVIN ...
... It arises from the spatial distribution of unpaired electrons around a magnetic atom INSTITUT MAX VON LAUE - PAUL LANGEVIN ...