File - Hondorf Physics
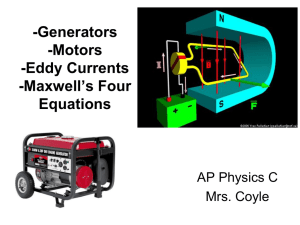
... magnetic field and the magnetic force causes the loop to rotate. • Remember, Lenz’s law says that the induced EMF must act to reduce the current. • This is known as “back EMF” • Faster rotations cause more back EMF and less current. ...
... magnetic field and the magnetic force causes the loop to rotate. • Remember, Lenz’s law says that the induced EMF must act to reduce the current. • This is known as “back EMF” • Faster rotations cause more back EMF and less current. ...
1 - tamta
... Magnetic flux is the amount of magnetic field threading or “flowing through” a certain area A, such as the area inside a flat coil of wire. This is represented diagrammatically by the total number of magnetic flux lines that pass through area A. ...
... Magnetic flux is the amount of magnetic field threading or “flowing through” a certain area A, such as the area inside a flat coil of wire. This is represented diagrammatically by the total number of magnetic flux lines that pass through area A. ...
Electromagnetism_Notes
... tightness of the coil and the speed that the magnet moves affect the strength of the electromagnet. The tighter the coil and the faster the magnet moves both make the electric current stronger. ...
... tightness of the coil and the speed that the magnet moves affect the strength of the electromagnet. The tighter the coil and the faster the magnet moves both make the electric current stronger. ...
PowerPoint - science
... smaller electricity energy current 2 Copy Figure 2 on Page 260 – label the parts and voltages. 5 of 33 ...
... smaller electricity energy current 2 Copy Figure 2 on Page 260 – label the parts and voltages. 5 of 33 ...
Electro-magnetics Electro
... t Added Commutator - Based On Ampere’s Work t Converted Oscillating Current To Unidirectional Current ...
... t Added Commutator - Based On Ampere’s Work t Converted Oscillating Current To Unidirectional Current ...