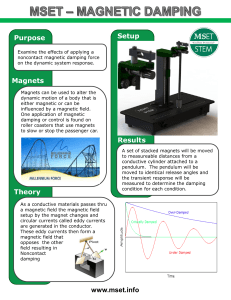
Imaging of local magnetic structure by polarized neutron holography
... hologram. A model of a magnetic hologram is hereby presented taking into account the magnetic interaction between neutrons and magnetic atoms. Particular features of the hologram are discussed and a method to reconstruct the components of the magnetic moments in the sample is provided. The proposed ...
... hologram. A model of a magnetic hologram is hereby presented taking into account the magnetic interaction between neutrons and magnetic atoms. Particular features of the hologram are discussed and a method to reconstruct the components of the magnetic moments in the sample is provided. The proposed ...
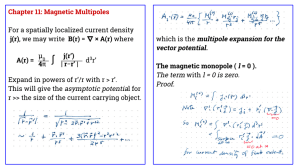
magnets ch.18
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
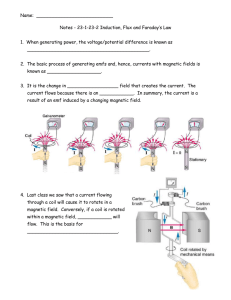
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
Magnetism - jfindlay.ca
... MAGNETIC FIELD LINES 1. Open the interactive simulation titled “Magnetic Field Lines Surrounding a Bar Magnet”. 2. The activity above shows the direction of the magnetic field around each bar magnet. Using this activity, draw at least six magnetic field lines on either side of the magnet and decide ...
... MAGNETIC FIELD LINES 1. Open the interactive simulation titled “Magnetic Field Lines Surrounding a Bar Magnet”. 2. The activity above shows the direction of the magnetic field around each bar magnet. Using this activity, draw at least six magnetic field lines on either side of the magnet and decide ...
bar magnets - jfindlay.ca
... MAGNETIC FIELD LINES 1. Open the interactive simulation titled “Magnetic Field Lines Surrounding a Bar Magnet”. 2. The activity above shows the direction of the magnetic field around each bar magnet. Using this activity, draw at least six magnetic field lines on either side of the magnet and decide ...
... MAGNETIC FIELD LINES 1. Open the interactive simulation titled “Magnetic Field Lines Surrounding a Bar Magnet”. 2. The activity above shows the direction of the magnetic field around each bar magnet. Using this activity, draw at least six magnetic field lines on either side of the magnet and decide ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms
... Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms Solenoid|A long, helically wound coil of insulated wire. Magnetic domain|A group of atoms whose magnetic fields are aligned in the same direction. Magnetic field|A region in which a magnetic force can be detected. Electromagnetic induction|The process of crea ...
... Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms Solenoid|A long, helically wound coil of insulated wire. Magnetic domain|A group of atoms whose magnetic fields are aligned in the same direction. Magnetic field|A region in which a magnetic force can be detected. Electromagnetic induction|The process of crea ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.