Zeeman Effect
... done over a state with a given value of the total angular momentum. If the interaction term VM is small (less than the fine structure), it can be treated as a perturbation; this is the Zeeman effect proper. In the Paschen-Back effect, described below, VM exceeds the LS coupling significantly (but is ...
... done over a state with a given value of the total angular momentum. If the interaction term VM is small (less than the fine structure), it can be treated as a perturbation; this is the Zeeman effect proper. In the Paschen-Back effect, described below, VM exceeds the LS coupling significantly (but is ...
Electric Potential
... Electrical power generation is the foundation by which electricity is supplied to homes and businesses around the world. Electricity is generated in many ways hydroelectric, nuclear, coal, gas, oil fired, wind solar, geothermal. ...
... Electrical power generation is the foundation by which electricity is supplied to homes and businesses around the world. Electricity is generated in many ways hydroelectric, nuclear, coal, gas, oil fired, wind solar, geothermal. ...
Electric Field
... A. The strength of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is given by B = onI B. The magnetic field is constant everywhere inside the solenoid. C. The magnetic field can be increased by _____________ the number of turns per unit length or by _____________ the current. D. Label the north and south p ...
... A. The strength of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is given by B = onI B. The magnetic field is constant everywhere inside the solenoid. C. The magnetic field can be increased by _____________ the number of turns per unit length or by _____________ the current. D. Label the north and south p ...
Magnetism Vocabulary Terms
... Compasses are designed to use this magnetic attraction in the south to point toward north. ...
... Compasses are designed to use this magnetic attraction in the south to point toward north. ...
Electricity and Magnetism Notes and buzzer
... wire to a distant location. When you’re done winding, both ends of your wire coil should have free ends that are at least 4-5” in length. c. Use about 7m of wire and wrap it as many times as you can. The more coils, the stronger the magnetic field. d. When you’re done, leave 4-5” hanging free on the ...
... wire to a distant location. When you’re done winding, both ends of your wire coil should have free ends that are at least 4-5” in length. c. Use about 7m of wire and wrap it as many times as you can. The more coils, the stronger the magnetic field. d. When you’re done, leave 4-5” hanging free on the ...
Magnetism - Physics: 1(AE) 2(B,D)
... This is how an electric motor works… An electric motor utilizes the property of electromagnetic induction to convert electricity into mechanical energy to make things move. The conductor itself, a coiled wire, will move to oppose the magnetic field. Just when it gets into position the current is re ...
... This is how an electric motor works… An electric motor utilizes the property of electromagnetic induction to convert electricity into mechanical energy to make things move. The conductor itself, a coiled wire, will move to oppose the magnetic field. Just when it gets into position the current is re ...
Ferromagnetic Materials : Curie
... Above a critical temperature Tc, the Curie temperature, all ferromagnetic materials become paramagnetic. This is because thermal energy is large enough to overcome the cooperative ordering of the magnetic moments. The susceptibility of a material, χ, indicates how dramatically a material responds to ...
... Above a critical temperature Tc, the Curie temperature, all ferromagnetic materials become paramagnetic. This is because thermal energy is large enough to overcome the cooperative ordering of the magnetic moments. The susceptibility of a material, χ, indicates how dramatically a material responds to ...
Magnetism - BAschools.org
... magnetism – the properties and interactions between magnets based on the alignment of particles in a substance ...
... magnetism – the properties and interactions between magnets based on the alignment of particles in a substance ...
Right-hand rule
... magnetic field the resulting force on the charge points outwards from the palm. The force on a negatively charged particle is in the opposite direction. If both the speed and the charge are reversed then the direction of the force remains the same. For that reason a magnetic field measurement (by it ...
... magnetic field the resulting force on the charge points outwards from the palm. The force on a negatively charged particle is in the opposite direction. If both the speed and the charge are reversed then the direction of the force remains the same. For that reason a magnetic field measurement (by it ...
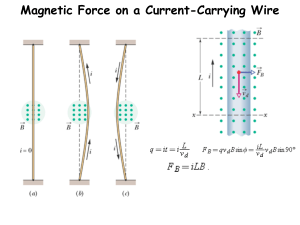
Magnetic Force Exerted on a Current Carrying Wire Magnetic force
... Magnetic force exerted on a current: The magnitude of the magnetic force FB on W that a magnetic field B exerts on a current I passing through a wire of length L is F B on W = ILBsinθ where θ is the angle between the directions of the B-field and the direction the Length of the wire points(which is ...
... Magnetic force exerted on a current: The magnitude of the magnetic force FB on W that a magnetic field B exerts on a current I passing through a wire of length L is F B on W = ILBsinθ where θ is the angle between the directions of the B-field and the direction the Length of the wire points(which is ...
Magnetism - District 196
... Atomic Theory of Magnetism We now know today that magneic fields are produced by the motion of electric charges. The charges can spin or orbit. Electrons have two magnetic fields, one due to the spin and one due to its orbit about the nucleus. The field due to the spin is stronger. In most material ...
... Atomic Theory of Magnetism We now know today that magneic fields are produced by the motion of electric charges. The charges can spin or orbit. Electrons have two magnetic fields, one due to the spin and one due to its orbit about the nucleus. The field due to the spin is stronger. In most material ...
marcelo.loewe
... • By the time the quarks and gluon thermalize the temperature becomes the largest of the energy scales. This means that the weak magnetic field approximation seems to be appropriate (eB <
... • By the time the quarks and gluon thermalize the temperature becomes the largest of the energy scales. This means that the weak magnetic field approximation seems to be appropriate (eB <
Electricity from Magnetism
... that electricity became practical for use in technology. His efforts created the “ancestor” of the electric motor and generators. • Discovered electromagnetic induction (1831) ….which was a turning point in physics ...
... that electricity became practical for use in technology. His efforts created the “ancestor” of the electric motor and generators. • Discovered electromagnetic induction (1831) ….which was a turning point in physics ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.