bar magnets - jfindlay.ca
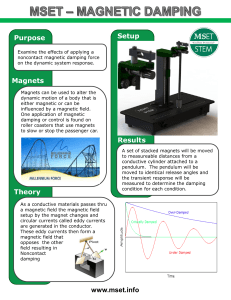
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics & Astronomy Outreach
... • The instantaneous energy density associated with the magnetic field of an EM wave equals the instantaneous energy density associated with the electric field – In a given volume, the energy is shared equally by the two fields ...
... • The instantaneous energy density associated with the magnetic field of an EM wave equals the instantaneous energy density associated with the electric field – In a given volume, the energy is shared equally by the two fields ...
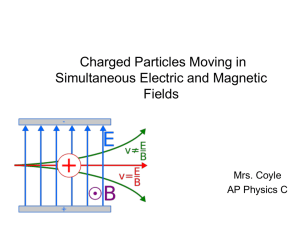
3 Simultaneous Magnetic and Electric Fields
... F = qE + qv x B =0 qE = qv x B v=E/B An entering particle of this speed will continue moving straight across the plates. If the particle has a different speed, then the magnetic force will be different and the net force will not be zero. ...
... F = qE + qv x B =0 qE = qv x B v=E/B An entering particle of this speed will continue moving straight across the plates. If the particle has a different speed, then the magnetic force will be different and the net force will not be zero. ...
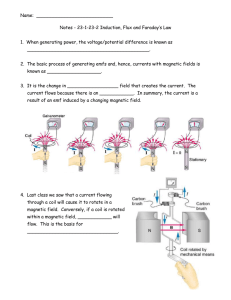
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
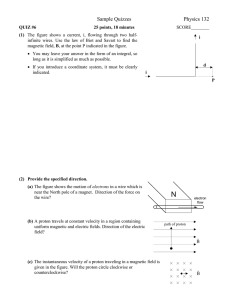
Sample Quizzes Physics 132
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
Chapter 5 Crystal field theory
... The ligand- field splitting parameter, Δo varies with the identity of the ligand. In the series of complexes [CoX(NH3)5]n+ with X = I-, Br-, Cl- H20 and NH3, the colours range from purple (for X = I-) through pink (X = Cl-) to yellow (with NH3). Ligand that give rise to high energy transition (such ...
... The ligand- field splitting parameter, Δo varies with the identity of the ligand. In the series of complexes [CoX(NH3)5]n+ with X = I-, Br-, Cl- H20 and NH3, the colours range from purple (for X = I-) through pink (X = Cl-) to yellow (with NH3). Ligand that give rise to high energy transition (such ...
notes13-- Interactions of electrons with an electromagnetic field
... This is the magnetic flux quantization-- a direct consequence of Gauge invariant. Example: Consider a magnet having the shape of a donut. At normal temperature the magnet is a normal metal and the magnetic flux lines can penetrate the hole as well as the metal. At low temperature where the metal bec ...
... This is the magnetic flux quantization-- a direct consequence of Gauge invariant. Example: Consider a magnet having the shape of a donut. At normal temperature the magnet is a normal metal and the magnetic flux lines can penetrate the hole as well as the metal. At low temperature where the metal bec ...
Magnetism and spintransport in the heterostructure of Ferroelectric/ferromagnetic films
... magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant energy dissipation, thus consuming power and producing heat due to the large current required. In this collaborative program, we aim to develop a new generation of magne ...
... magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant energy dissipation, thus consuming power and producing heat due to the large current required. In this collaborative program, we aim to develop a new generation of magne ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.




















![The electronic configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010079862_1-7325b22ef907f6eb15733a24a4dfe50f-300x300.png)