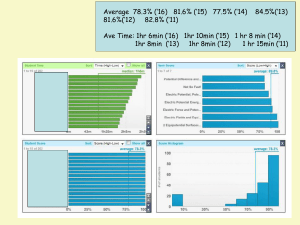
PHYS_2326_042109
... When magnet is turned on – momentarily current appears as B increases. When B reaches steady value – current disappears no matter how strong B field is. If we squeeze the coil as to change its area – current appears but only while we are deforming the coil. If we rotate the coil, current appears but ...
... When magnet is turned on – momentarily current appears as B increases. When B reaches steady value – current disappears no matter how strong B field is. If we squeeze the coil as to change its area – current appears but only while we are deforming the coil. If we rotate the coil, current appears but ...
1. Course Name : Electromagnetism
... This course builds on the Electricity and Magnetism course offered at Level 1. It covers eelectrostatics, stationary electric fields in conducting media, magneto-static field laws, Maxwell’s equations and their applications. 5. Course Objectives At the end of the course, the student will be able to: ...
... This course builds on the Electricity and Magnetism course offered at Level 1. It covers eelectrostatics, stationary electric fields in conducting media, magneto-static field laws, Maxwell’s equations and their applications. 5. Course Objectives At the end of the course, the student will be able to: ...
magnetic field - Rosehill
... cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typica ...
... cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typica ...
Announcements
... The force on a negative charge is opposite the force on a positive charge The force is proportional to the velocity v The magnitude and direction of F depends on the angle between v and B ...
... The force on a negative charge is opposite the force on a positive charge The force is proportional to the velocity v The magnitude and direction of F depends on the angle between v and B ...
magnetism - University of South Alabama
... Magnetic Force: y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron ...
... Magnetic Force: y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron ...
magnetism lesson - Red Hook Central Schools
... Direction of mag force on q perpendicular to v vector & to B field. For +q place right hand fingers into field, thumb points to v, palm points to mag force. For – q use left hand. ...
... Direction of mag force on q perpendicular to v vector & to B field. For +q place right hand fingers into field, thumb points to v, palm points to mag force. For – q use left hand. ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.