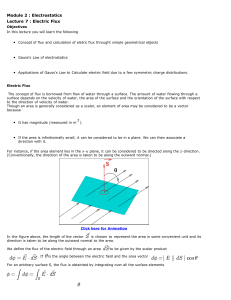
Module 2 : Electrostatics Lecture 7 : Electric Flux
... The outward normals to the triangular faces AED, BFC, as well as the normal to the base are perpendicular to . Hence the flux through each of these faces is zero. The vertical rectangular face ABFE has an area 0.06 m . The outward normal to this face is perpendicular to the electric field. The flux ...
... The outward normals to the triangular faces AED, BFC, as well as the normal to the base are perpendicular to . Hence the flux through each of these faces is zero. The vertical rectangular face ABFE has an area 0.06 m . The outward normal to this face is perpendicular to the electric field. The flux ...
Magnetism ppt
... • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconductors are materials that have a zero resistance to a current flowing through ...
... • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconductors are materials that have a zero resistance to a current flowing through ...
4 Fields2 - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Example 2 • Find the electric field intensity midway between a +5.0 μC charge and a -3.5 μC charge. Assume they are 5.0cm apart. • ***NOTE: Since these charges are attractive we call this COMPLIMENTARY FIELDS. To find the NET electric field, we ADD the field intensities together (use magnitudes- ig ...
... Example 2 • Find the electric field intensity midway between a +5.0 μC charge and a -3.5 μC charge. Assume they are 5.0cm apart. • ***NOTE: Since these charges are attractive we call this COMPLIMENTARY FIELDS. To find the NET electric field, we ADD the field intensities together (use magnitudes- ig ...
Activity: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
... beneath the container. The needle-shaped iron filings should align themselves along the magnetic field lines so you can visualize the magnetic field around the magnet. (Note: The magnetic field itself is smooth, not made of “field lines”. The lines you see are simply the result of the iron filings a ...
... beneath the container. The needle-shaped iron filings should align themselves along the magnetic field lines so you can visualize the magnetic field around the magnet. (Note: The magnetic field itself is smooth, not made of “field lines”. The lines you see are simply the result of the iron filings a ...
Voltage/Current PowerPoint
... Q is doing something to the “space” around it…the force on q depends on where you put it in this “space”. If we know what a point in “space” is like, we can describe the force on some charge q in that space. As q is moved further away, what happens to the force? ...
... Q is doing something to the “space” around it…the force on q depends on where you put it in this “space”. If we know what a point in “space” is like, we can describe the force on some charge q in that space. As q is moved further away, what happens to the force? ...
Electric Field: Sheet of Charge
... a sphere at radius r, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the sphere and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the sphere. ...
... a sphere at radius r, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the sphere and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the sphere. ...
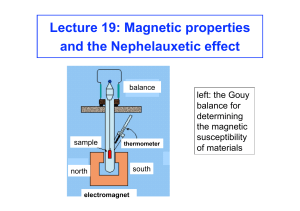
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... have only one or two unpaired electrons, but even so, the value of µeff is much lower than expected from the spinonly formula. (Note: the only high-spin complex from the 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements is [PdF6]4- and PdF2). ...
... have only one or two unpaired electrons, but even so, the value of µeff is much lower than expected from the spinonly formula. (Note: the only high-spin complex from the 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements is [PdF6]4- and PdF2). ...
Read Chapter 1 in the textbook (pages 4 – 21)
... d. velocity _____6. When an electron is moved near a negatively charged sphere, its potential energy increases. The reason this happens is because _____. a. opposite charges attract c. work is done against an electric field b. like charges repel d. all of the above _____7. If two protons are held cl ...
... d. velocity _____6. When an electron is moved near a negatively charged sphere, its potential energy increases. The reason this happens is because _____. a. opposite charges attract c. work is done against an electric field b. like charges repel d. all of the above _____7. If two protons are held cl ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.