Forces (magnets) Study guide
... Target 2: I can conduct and evaluate an investigation that proves that non-contact force fields exist. 13. An object can have an electric charge by either gaining or losing _________________________. 14. Name two real world examples of static electricity. a. _________________________________________ ...
... Target 2: I can conduct and evaluate an investigation that proves that non-contact force fields exist. 13. An object can have an electric charge by either gaining or losing _________________________. 14. Name two real world examples of static electricity. a. _________________________________________ ...
L15 Electromagnetic induction and inductance
... L15.8 : Electromagnetic induction Electric motors: The inverse of generators, current leads to motion. If the torque is constant, why doesn’t the loop get faster and faster? The rotating loop produces an induced EMF which opposes the original current, and the torque is reduced (a back EMF). So we ge ...
... L15.8 : Electromagnetic induction Electric motors: The inverse of generators, current leads to motion. If the torque is constant, why doesn’t the loop get faster and faster? The rotating loop produces an induced EMF which opposes the original current, and the torque is reduced (a back EMF). So we ge ...
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics
... wires [Ampère expt with 2 wires] - a current can magnetize an iron bar - permanent magnets must be made of molecules with tiny circulating currents that line up. • Earth is a permanent magnet due to circulating charged currents in its core ...
... wires [Ampère expt with 2 wires] - a current can magnetize an iron bar - permanent magnets must be made of molecules with tiny circulating currents that line up. • Earth is a permanent magnet due to circulating charged currents in its core ...
Define and Explain Electromagnetic Induction
... Note that this induced emf is indistinguishable from that of a battery and that the current is still just the rate of the motion of charges; therefore, Ohm's law and other relationships for currents in wires are still valid. Lenz's law The direction of the induced current can be found from Lenz's l ...
... Note that this induced emf is indistinguishable from that of a battery and that the current is still just the rate of the motion of charges; therefore, Ohm's law and other relationships for currents in wires are still valid. Lenz's law The direction of the induced current can be found from Lenz's l ...
EM Induction 2
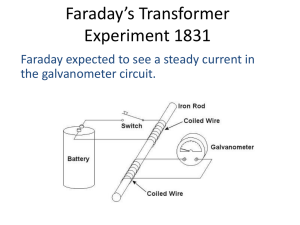
... Experiment 1831 Faraday expected to see a steady current in the galvanometer circuit. ...
... Experiment 1831 Faraday expected to see a steady current in the galvanometer circuit. ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.