Vocabulary Terms
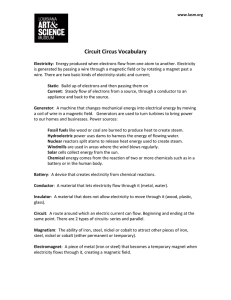
... Circuit Circus Vocabulary Electricity: Energy produced when electrons flow from one atom to another. Electricity is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and ...
... Circuit Circus Vocabulary Electricity: Energy produced when electrons flow from one atom to another. Electricity is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and ...
Interactions between Electricity and Magnetism
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
magnet
... magnetic field that is opposite to its own • Increasing the temperature of a magnet (in higher temperatures, atoms vibrate faster so they may no longer line up) ...
... magnetic field that is opposite to its own • Increasing the temperature of a magnet (in higher temperatures, atoms vibrate faster so they may no longer line up) ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... behaves like a magnet (since it can exert a force on another magnet… like a permanent magnet would) Let’s use field theory to understand what’s happening ...
... behaves like a magnet (since it can exert a force on another magnet… like a permanent magnet would) Let’s use field theory to understand what’s happening ...
SUPERCONDUCTING MATERIALS
... reason the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches a speed that can sustain levitation. Propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forwards. The propulsion coils that exert a f ...
... reason the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches a speed that can sustain levitation. Propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forwards. The propulsion coils that exert a f ...
Magnets
... • The first magnets used were made of heavy natural material called a lodestone, which is a mineral magnetite. • A compass today uses a lightweight magnetic needle that is free to turn. • A compass needle points along an imaginary line connecting the North and South poles. This is because earth is ...
... • The first magnets used were made of heavy natural material called a lodestone, which is a mineral magnetite. • A compass today uses a lightweight magnetic needle that is free to turn. • A compass needle points along an imaginary line connecting the North and South poles. This is because earth is ...
Magnets and electricity - Rm. E
... Complete a quick lab on electromagnetic and answer each question using complete sentences. ...
... Complete a quick lab on electromagnetic and answer each question using complete sentences. ...
Name: #_____ Test on:______ Magnetism Study Guide What are
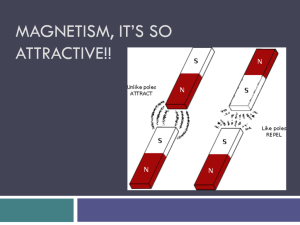
... Magnets will have the strongest magnetic pull when opposite poles are placed near each other. When a north pole end and a south pole end are placed near each other, the magnets will attract each other or stick together. When two bar magnets are placed together, if a north pole bar magnet repels an u ...
... Magnets will have the strongest magnetic pull when opposite poles are placed near each other. When a north pole end and a south pole end are placed near each other, the magnets will attract each other or stick together. When two bar magnets are placed together, if a north pole bar magnet repels an u ...
class number
... 2) True False Like magnetic poles will repel one another, but unlike poles will attract. 3) True False The magnetic force is found everywhere around a magnet; not just at the poles. 4) Define “ferromagnetic” _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________ ...
... 2) True False Like magnetic poles will repel one another, but unlike poles will attract. 3) True False The magnetic force is found everywhere around a magnet; not just at the poles. 4) Define “ferromagnetic” _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________ ...
Phet Exploration: Magnets, Transformers, and Generators
... Hint: Go back to part 2, with the Pickup Coil, and describe what created a voltage in the coil. c) Can you still get the light to work somehow if you use a battery? 5. Generator a) Turn on the water to get the generator to work. What combination of variable settings gives the greatest amount of ligh ...
... Hint: Go back to part 2, with the Pickup Coil, and describe what created a voltage in the coil. c) Can you still get the light to work somehow if you use a battery? 5. Generator a) Turn on the water to get the generator to work. What combination of variable settings gives the greatest amount of ligh ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller ...
... A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.