Physics Form 5 Syllabus
... As from September 2009, the unit ‘The Earth and the Universe’ was removed from the Form 5 syllabus. The section ‘Alternating Current’ was also removed from the Form 5 syllabus. ...
... As from September 2009, the unit ‘The Earth and the Universe’ was removed from the Form 5 syllabus. The section ‘Alternating Current’ was also removed from the Form 5 syllabus. ...
magnetism ppt
... • Temporary magnets • Magnetism can be turned on and off • Made by wrapping wire around a piece of iron and sending a current through the wire • Magnetic field is in the same direction as the electric current ...
... • Temporary magnets • Magnetism can be turned on and off • Made by wrapping wire around a piece of iron and sending a current through the wire • Magnetic field is in the same direction as the electric current ...
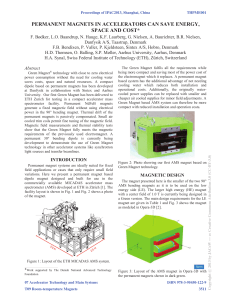
permanent magnets in accelerators can save energy
... the fringe fields. The entrance and exit angles were 28.42° and 28.47°, respectively, and thus within the stringent specification. The transverse variation of the effective field boundary was found to be straight within ±0.1 mm and this result is about a factor of three better than the original AMS ...
... the fringe fields. The entrance and exit angles were 28.42° and 28.47°, respectively, and thus within the stringent specification. The transverse variation of the effective field boundary was found to be straight within ±0.1 mm and this result is about a factor of three better than the original AMS ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • A solenoid has a north (incoming current) and south (outgoing current) pole. • The strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid depends on the number of loops of wire and the amount of current in the wire. • An electromagnet is a strong magnet created when an iron core is inserted into the center ...
... • A solenoid has a north (incoming current) and south (outgoing current) pole. • The strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid depends on the number of loops of wire and the amount of current in the wire. • An electromagnet is a strong magnet created when an iron core is inserted into the center ...
Magnetism - Physics: 1(AE) 2(B,D)
... The direction of the magnetic field is determined by using a compass. ...
... The direction of the magnetic field is determined by using a compass. ...
Faraday`s Experiment
... number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict what you think will happen if a magnet approaches a wire loop. Will the movement of elect ...
... number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict what you think will happen if a magnet approaches a wire loop. Will the movement of elect ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Consider a simple transformer that has a 100-turn primary coil and a 1000-turn secondary coil. The primary is connected to a 120 volt AC source and the secondary is connected to an electrical device with a resistance of 1000 ohms. 1) What will be the voltage output of the secondary? 2) What current ...
... Consider a simple transformer that has a 100-turn primary coil and a 1000-turn secondary coil. The primary is connected to a 120 volt AC source and the secondary is connected to an electrical device with a resistance of 1000 ohms. 1) What will be the voltage output of the secondary? 2) What current ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.