Today: Finish Ch 23: Electric Current Chapter 24: Magnetism
... • Next simplest: a compass in a coil of wires, so that magnetic field sensed by compass is increased: So can detect very small currents – called a ...
... • Next simplest: a compass in a coil of wires, so that magnetic field sensed by compass is increased: So can detect very small currents – called a ...
Homework Set #3
... uniform magnetic field pointing directly up is slowly turned on, such that the strength of the magnetic field can be expressed as a function of time as: B(t) = 0.02(T /s2) × t2. What is the total EMF in the coil as a function of time? In which direction does the current flow? Question 3 (3 points) A ...
... uniform magnetic field pointing directly up is slowly turned on, such that the strength of the magnetic field can be expressed as a function of time as: B(t) = 0.02(T /s2) × t2. What is the total EMF in the coil as a function of time? In which direction does the current flow? Question 3 (3 points) A ...
Lesson 11. Topic “ Magnetism” Grammar material: The Present
... In studying the electric current, we observe the following relation between magnetism and the electric current: on the one hand magnetism is produced by the current and on the other hand the current is produced from the magnetism. Magnetism is mentioned in the oldest writings of man. Romans, for exa ...
... In studying the electric current, we observe the following relation between magnetism and the electric current: on the one hand magnetism is produced by the current and on the other hand the current is produced from the magnetism. Magnetism is mentioned in the oldest writings of man. Romans, for exa ...
Magnetic Forces Practice
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
Flux or flux linkage? - Institute of Physics
... Magnetic field lines start and finish at poles. Physicists picture this as a ‘flow’ in magnetic circuit. • magnetic flux (phi), unit Weber • magnetic flux density B, unit Weber m-2 or Tesla ...
... Magnetic field lines start and finish at poles. Physicists picture this as a ‘flow’ in magnetic circuit. • magnetic flux (phi), unit Weber • magnetic flux density B, unit Weber m-2 or Tesla ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
... Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
Make a Magnet - Discovery Education
... 1. Is the nail magnetic? See if you can use it to pick up the paper clips. Write your observations on the attached worksheet. 2. Wrap the center portion of the wire around the nail 10 times so that it forms a coil. You should have extra wire at both ends. 3. Attach one end of the wire to the (+) ter ...
... 1. Is the nail magnetic? See if you can use it to pick up the paper clips. Write your observations on the attached worksheet. 2. Wrap the center portion of the wire around the nail 10 times so that it forms a coil. You should have extra wire at both ends. 3. Attach one end of the wire to the (+) ter ...
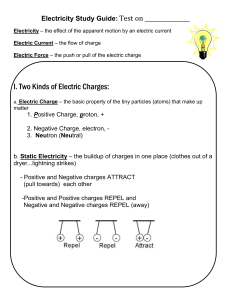
Electric Charge
... All magnets have a north pole and a south pole. b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a battery The electric current flows through the c ...
... All magnets have a north pole and a south pole. b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a battery The electric current flows through the c ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.