Hybridization and MO Theory PPT
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom. hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized. If the molecule has four single bonds, it is sp3 hybridized. This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal ...
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom. hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized. If the molecule has four single bonds, it is sp3 hybridized. This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal ...
Unit 9
... *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has 3) *Note: Resonance structures with pi bonds usually indicates delocalized pi bonds *Note: Be weary ...
... *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has 3) *Note: Resonance structures with pi bonds usually indicates delocalized pi bonds *Note: Be weary ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... 2. Based on the activity series, which one of the reactions below will occur? (A) Zn (s) + MnI2 (aq) ZnI2 (aq) + Mn (s) (B) SnCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Sn (s) + CuCl2 (aq) (C) 2AgNO3 (aq) + Pb (s) 2Ag (s) + Pb(NO3 )2 (aq) (D) 3Hg (l) + 2Cr(NO3 )3 (aq) 3Hg(NO3 )2 + 2Cr (s) (E) 3FeBr2 (aq) + 2Au (s) ...
... 2. Based on the activity series, which one of the reactions below will occur? (A) Zn (s) + MnI2 (aq) ZnI2 (aq) + Mn (s) (B) SnCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Sn (s) + CuCl2 (aq) (C) 2AgNO3 (aq) + Pb (s) 2Ag (s) + Pb(NO3 )2 (aq) (D) 3Hg (l) + 2Cr(NO3 )3 (aq) 3Hg(NO3 )2 + 2Cr (s) (E) 3FeBr2 (aq) + 2Au (s) ...
apchapt9
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules because one of the sp3 lobes holds the lone p ...
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules because one of the sp3 lobes holds the lone p ...
Orbitals and Covalen..
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules because one of the sp3 lobes holds the lone p ...
... We know the geometry from experiment. We know the orbitals of the atom hybridizing atomic orbitals can explain the geometry. So if the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized This includes bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules because one of the sp3 lobes holds the lone p ...
Chapter1011
... • Double bond -- combination of one s bond and one p bond • Triple bond -- combination of one s bond and two p bonds ...
... • Double bond -- combination of one s bond and one p bond • Triple bond -- combination of one s bond and two p bonds ...
Exam 3 Key
... f. What is the name of the electron group geometry around the left O? tetrahedral g. What is the name of the electron group geometry around the nitrogen? trigonal planar h. Draw a sketch with bond angles. ...
... f. What is the name of the electron group geometry around the left O? tetrahedral g. What is the name of the electron group geometry around the nitrogen? trigonal planar h. Draw a sketch with bond angles. ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
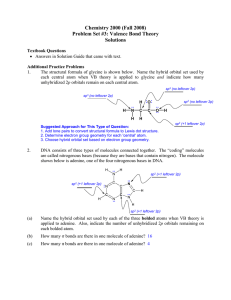
... The structural formula of glycine is shown below. Name the hybrid orbital set used by each central atom when VB theory is applied to glycine and indicate how many unhybridized 2p orbitals remain on each central atom. sp3 (no leftover 2p) sp3 (no leftover 2p) ...
... The structural formula of glycine is shown below. Name the hybrid orbital set used by each central atom when VB theory is applied to glycine and indicate how many unhybridized 2p orbitals remain on each central atom. sp3 (no leftover 2p) sp3 (no leftover 2p) ...
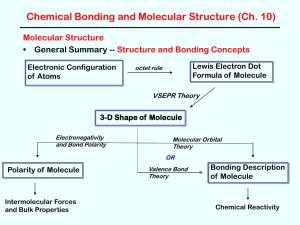
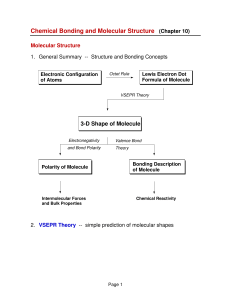
3-D Shape of Molecule
... In less symmetrical structures (e.g., SO2 and SF4), the bond dipoles do not cancel and there is a net dipole moment which makes the molecule polar. ...
... In less symmetrical structures (e.g., SO2 and SF4), the bond dipoles do not cancel and there is a net dipole moment which makes the molecule polar. ...
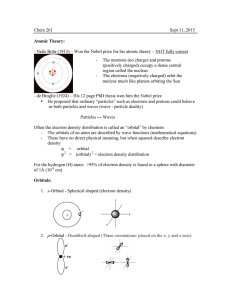
Chem 261 Sept 11, 2015 Atomic Theory:
... - Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract each other - Atoms want to have an inert gas electron configuration (isoelectronic with inert gas, such as He, Ne, Ar. Helium is the inert gas that hydrogen can be isoelectronic with) Atoms H He Li ...
... - Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract each other - Atoms want to have an inert gas electron configuration (isoelectronic with inert gas, such as He, Ne, Ar. Helium is the inert gas that hydrogen can be isoelectronic with) Atoms H He Li ...
Bonding II
... takes place between atoms when their atomic or hybrid orbitals interact – “overlap” • To interact, the orbitals must either be aligned along the axis between the atoms, or • The orbitals must be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the interatomic axis ...
... takes place between atoms when their atomic or hybrid orbitals interact – “overlap” • To interact, the orbitals must either be aligned along the axis between the atoms, or • The orbitals must be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the interatomic axis ...
AP LAb 8
... A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Each atom can provide one of the electrons of the pair (though there are exceptions). A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. Molecules can be either polar or nonpolar. If the bonds are nonpolar ...
... A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Each atom can provide one of the electrons of the pair (though there are exceptions). A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. Molecules can be either polar or nonpolar. If the bonds are nonpolar ...
Ch 6 PART (B) List the seven diatomic compounds What is the
... Ch 6 PART (B) List the seven diatomic compounds What is the hybridization of NH3 ? Is it a polar molecule? What is its ideal bond angle and geometry Sp3, yes, tetrahedral, 109 (actual is pyramidal at 107) ...
... Ch 6 PART (B) List the seven diatomic compounds What is the hybridization of NH3 ? Is it a polar molecule? What is its ideal bond angle and geometry Sp3, yes, tetrahedral, 109 (actual is pyramidal at 107) ...
chemical bonding
... H2O. They also explain the formation of multiple bonds in molecules like C2H2 and C2H4. ...
... H2O. They also explain the formation of multiple bonds in molecules like C2H2 and C2H4. ...
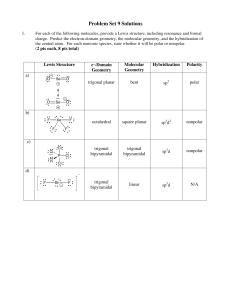
Problem Set 9 Solutions
... There are three σ bonds made between left C sp3 hybrid orbitals and H s-orbitals. There is one σ bond made between left C sp3 hybrid orbital and right C sp hybrid orbital. There is one σ bond made between right C sp hybrid orbital and N sp hybrid orbital. There are two π bonds made between right C u ...
... There are three σ bonds made between left C sp3 hybrid orbitals and H s-orbitals. There is one σ bond made between left C sp3 hybrid orbital and right C sp hybrid orbital. There is one σ bond made between right C sp hybrid orbital and N sp hybrid orbital. There are two π bonds made between right C u ...
AP HYBRIDIZATION
... orbitals for bonding; a new set of atomic orbitals might better serve the carbon atom. To account for the known structure of methane, it makes sense to assume that the carbon atom has four equivalent energy atomic orbitals, arranged tetrahedrally – since that’s what experiments reveal. Such a set of ...
... orbitals for bonding; a new set of atomic orbitals might better serve the carbon atom. To account for the known structure of methane, it makes sense to assume that the carbon atom has four equivalent energy atomic orbitals, arranged tetrahedrally – since that’s what experiments reveal. Such a set of ...
Polarity of Molecules
... Valence bond (VB) model Combines the notion of electron-pair bonding (Lewis valence) with the idea of atomic orbitals Review atomic orbitals from Ch 6! ...
... Valence bond (VB) model Combines the notion of electron-pair bonding (Lewis valence) with the idea of atomic orbitals Review atomic orbitals from Ch 6! ...
Chem 102A
... 2. Which of the following statements is false concerning bonding? a) In a C-O bond, electron density on the average is greater near the O atom. b) A C-O bond is an example of a polar covalent bond. c) Elements with extremely different electronegativity values tend to form ionic bonds with each other ...
... 2. Which of the following statements is false concerning bonding? a) In a C-O bond, electron density on the average is greater near the O atom. b) A C-O bond is an example of a polar covalent bond. c) Elements with extremely different electronegativity values tend to form ionic bonds with each other ...
Chemistry 235 Semester 04-2008 Homework for Submission #3
... 3) What are meant by the terms valence state and hybridization of atomic orbitals? (4) The valence state of an atom is a state which is obtained by promoting an s-electron to an empty p-orbital in the same shell. This increases the number of bonds that the atom can form. Hybridisation of atomic orbi ...
... 3) What are meant by the terms valence state and hybridization of atomic orbitals? (4) The valence state of an atom is a state which is obtained by promoting an s-electron to an empty p-orbital in the same shell. This increases the number of bonds that the atom can form. Hybridisation of atomic orbi ...
Tying some loose ends and introducing some new ones.
... orbitals combine to form three sp2 hybrids that are 120 degrees apart. The remaining p orbital on each carbon atom is perpendicular to this plane and may be used to make a double bond. ...
... orbitals combine to form three sp2 hybrids that are 120 degrees apart. The remaining p orbital on each carbon atom is perpendicular to this plane and may be used to make a double bond. ...
Bent's rule

Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the isovalent hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry Bent as follows: ""Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents"".The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as spn, where n is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the n+1 spn orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing hybridised orbitals with noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to how these hybridised orbitals should be constructed. Bent's rule is that in a molecule, a central atom bonded to multiple groups will hybridise so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards electropositive groups, while orbitals with more p character will be directed towards groups that are more electronegative. By removing the assumption that all hybrid orbitals are equivalent spn orbitals, better predictions and explanations of properties such as molecular geometry and bond strength can be obtained.Bent's rule can be generalized to d-block elements as well. The hybridisation of a metal center is arranged so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards ligands that form bonds with more covalent character. Equivalently, orbitals with more d character are directed towards groups that form bonds of greater ionic character.