Problem
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml are fixed. – If we want to put more than one ...
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml are fixed. – If we want to put more than one ...
2nd Semester Chemistry Terms - Glancy 4TH PERIOD PHYSICAL
... 37. Critical mass- the minimum mass of fissionable material in a reactor or nuclear bomb that will sustain a chain reaction 38. Nuclear fusion- the combining of nuclei of light atoms to form heavier nuclei, with the release of much energy ...
... 37. Critical mass- the minimum mass of fissionable material in a reactor or nuclear bomb that will sustain a chain reaction 38. Nuclear fusion- the combining of nuclei of light atoms to form heavier nuclei, with the release of much energy ...
ABSTRACT: Prediction of hybridization state is
... added one d orbital gradually as follows5σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 01 additional σ bond = sp3d hrbridization. 6σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 02 additional σ bonds = sp3d2 hrbridization. 7σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 03 additional σ bonds = sp3d3 hrbridization. Eg:- ...
... added one d orbital gradually as follows5σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 01 additional σ bond = sp3d hrbridization. 6σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 02 additional σ bonds = sp3d2 hrbridization. 7σ bonds = 4σ bonds + 03 additional σ bonds = sp3d3 hrbridization. Eg:- ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... Covalent bonds come in several varieties. A single bond forms between two atoms that share one pair of electrons. Consider the element carbon. It has four valence electrons. Carbon requires four additional electrons to reach a stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combin ...
... Covalent bonds come in several varieties. A single bond forms between two atoms that share one pair of electrons. Consider the element carbon. It has four valence electrons. Carbon requires four additional electrons to reach a stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combin ...
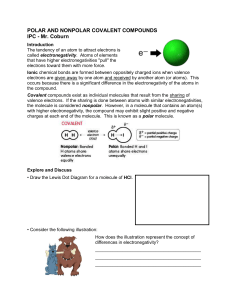
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories
... • But: Lewis structures are two dimensional and molecules are 3 dimensional objects. • The 3D structure is absolutely critical for understanding molecules. • Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions of the atomic nuclei ...
... • But: Lewis structures are two dimensional and molecules are 3 dimensional objects. • The 3D structure is absolutely critical for understanding molecules. • Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions of the atomic nuclei ...
02-Atoms-Molecules
... The Octet Rule Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell ...
... The Octet Rule Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell ...
Molecular Geometry
... • NOTE: If there are only two atoms in the molecule, the molecule will be linear no matter what the electron domain is. ...
... • NOTE: If there are only two atoms in the molecule, the molecule will be linear no matter what the electron domain is. ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... from the nucleus as you go down the group. Ionization energy decreases as you move down through a group. ...
... from the nucleus as you go down the group. Ionization energy decreases as you move down through a group. ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint
... Scientists show the composition of compounds by a kind of shorthand known as a chemical formula. Water, which contains two atoms of hydrogen for each atom of oxygen, has the chemical formula =H2O. The formula for table salt, NaCl, indicates that the elements that make up table salt—sodium and chlori ...
... Scientists show the composition of compounds by a kind of shorthand known as a chemical formula. Water, which contains two atoms of hydrogen for each atom of oxygen, has the chemical formula =H2O. The formula for table salt, NaCl, indicates that the elements that make up table salt—sodium and chlori ...
Chemistry - Delhi Public School, Faridabad
... An element A combines with element B. An atom of A contains two electrons in its outermost shell whereas that of B has six electrons in its outermost shell. Two electrons are transferred from the atom A to the atom B. a. What is the nature of bond between A and B? b. What is the electronic structure ...
... An element A combines with element B. An atom of A contains two electrons in its outermost shell whereas that of B has six electrons in its outermost shell. Two electrons are transferred from the atom A to the atom B. a. What is the nature of bond between A and B? b. What is the electronic structure ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... Figure 2.7 Net bonding force curve for a Na+−Cl− pair showing an equilibrium bond length of a0 = 0.28 nm. ...
... Figure 2.7 Net bonding force curve for a Na+−Cl− pair showing an equilibrium bond length of a0 = 0.28 nm. ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... If it could as easily lose or gain e-, then it will probably share them. It will form a covalent bond. ...
... If it could as easily lose or gain e-, then it will probably share them. It will form a covalent bond. ...
makeup2
... is discharging and producing an electric current must be (A) positive (B) negative (C) zero (D) unpredictable 51. The average distance of an electron in a hydrogen atom from the nucleus is indicated by the quantum number (A) n (B) ml (C) l (D) ms 52. "Wood alcohol" (methyl alcohol or methanol), CH4O ...
... is discharging and producing an electric current must be (A) positive (B) negative (C) zero (D) unpredictable 51. The average distance of an electron in a hydrogen atom from the nucleus is indicated by the quantum number (A) n (B) ml (C) l (D) ms 52. "Wood alcohol" (methyl alcohol or methanol), CH4O ...
Chapter 9 - VSEPR - River Dell Regional School District
... For a molecule that consists of more than two atoms (a polyatomic molecule), the dipole moment depends upon both the individual bond polarities and the molecular geometry. • Bond dipoles and dipole moments are vector quantities; that is they have both a magnitude and a direction. • The overall dipol ...
... For a molecule that consists of more than two atoms (a polyatomic molecule), the dipole moment depends upon both the individual bond polarities and the molecular geometry. • Bond dipoles and dipole moments are vector quantities; that is they have both a magnitude and a direction. • The overall dipol ...
Exam 3B - TAMU Chemistry
... (3) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decide between two answers, put your best answer down for the first (odd) question and the other answer down for the se ...
... (3) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decide between two answers, put your best answer down for the first (odd) question and the other answer down for the se ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... Adapted from Fig. 2.7, Callister 7e. (Fig. 2.7 is adapted from Linus Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd edition, Copyright 1939 and 1940, 3rd edition. Copyright 1960 by Cornell University. ...
... Adapted from Fig. 2.7, Callister 7e. (Fig. 2.7 is adapted from Linus Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd edition, Copyright 1939 and 1940, 3rd edition. Copyright 1960 by Cornell University. ...
Bent's rule

Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the isovalent hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry Bent as follows: ""Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents"".The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as spn, where n is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the n+1 spn orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing hybridised orbitals with noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to how these hybridised orbitals should be constructed. Bent's rule is that in a molecule, a central atom bonded to multiple groups will hybridise so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards electropositive groups, while orbitals with more p character will be directed towards groups that are more electronegative. By removing the assumption that all hybrid orbitals are equivalent spn orbitals, better predictions and explanations of properties such as molecular geometry and bond strength can be obtained.Bent's rule can be generalized to d-block elements as well. The hybridisation of a metal center is arranged so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards ligands that form bonds with more covalent character. Equivalently, orbitals with more d character are directed towards groups that form bonds of greater ionic character.