Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics point of view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics point of view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
Chapter 18 Review 18.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation
... Corrosion- process of returning metals to their natural state Cathodic Protection- the connection of an active metal to another to prevent corrosion - corrosion involves the oxidation of metals - this process creates great economic lose - most metals produce a thin oxide coating, which protect their ...
... Corrosion- process of returning metals to their natural state Cathodic Protection- the connection of an active metal to another to prevent corrosion - corrosion involves the oxidation of metals - this process creates great economic lose - most metals produce a thin oxide coating, which protect their ...
Chapter 22-Newest-CD
... Color and Magnetism Magnetism • Many transition metal complexes are paramagnetic (i.e. they have unpaired electrons). • There are some interesting observations. Consider a d6 metal ion: – [Co(NH3)6]3+ has no unpaired electrons, but [CoF6]3has four unpaired electrons per ion. ...
... Color and Magnetism Magnetism • Many transition metal complexes are paramagnetic (i.e. they have unpaired electrons). • There are some interesting observations. Consider a d6 metal ion: – [Co(NH3)6]3+ has no unpaired electrons, but [CoF6]3has four unpaired electrons per ion. ...
Common Chemical Formula List
... has remained intact, then that can often be balanced first, as it is acts as a single species. The ions NO3- and CO32- are examples of a complex ion. A VERY useful rule is to leave balancing oxygen and hydrogen to the last steps as these elements are often in more than one chemical on each side , an ...
... has remained intact, then that can often be balanced first, as it is acts as a single species. The ions NO3- and CO32- are examples of a complex ion. A VERY useful rule is to leave balancing oxygen and hydrogen to the last steps as these elements are often in more than one chemical on each side , an ...
Chapter 3 : Simple Bonding Theory Why do they make chemical
... The bond energy E(AB) in a molecule AB is always greater than the mean of the bond energies E(AA) + E(BB) in the homonuclear species AA and BB. Pauling argued that in an "ideal" covalent bond E(AB) should equal this mean, and that the "excess" bond energy is caused by electrostatic attraction betwee ...
... The bond energy E(AB) in a molecule AB is always greater than the mean of the bond energies E(AA) + E(BB) in the homonuclear species AA and BB. Pauling argued that in an "ideal" covalent bond E(AB) should equal this mean, and that the "excess" bond energy is caused by electrostatic attraction betwee ...
NM Strand
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...
biol 1406 chapter 3: water
... neutrons. How many protons and neutrons does boron-11 have? Explain. ...
... neutrons. How many protons and neutrons does boron-11 have? Explain. ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... c) Which term in the equation do you think is most important in any difference between them? Z+Zd. What is the purpose of the Madelung constant? The Madelung constant accounts for all the extended attractive and repulsive interactions in the extended structure. ...
... c) Which term in the equation do you think is most important in any difference between them? Z+Zd. What is the purpose of the Madelung constant? The Madelung constant accounts for all the extended attractive and repulsive interactions in the extended structure. ...
Final Exam
... heard, but as the train gets closer, the whistle gets louder. This is an example of _______. A. a sonic boom B. interference C. refraction D. the Doppler effect ...
... heard, but as the train gets closer, the whistle gets louder. This is an example of _______. A. a sonic boom B. interference C. refraction D. the Doppler effect ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese ...
... * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese ...
Chapter 9 Notes - UIC Department of Chemistry
... (originating in their charges.) Lewis structures for ionic compounds are written by putting two Lewis ionic symbols together. F− Lewis structures for ions: Mg2+ Ionic compounds-put the ions together as in a formula: MgF2 Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds 1) Nonmetals tend to share electrons in ...
... (originating in their charges.) Lewis structures for ionic compounds are written by putting two Lewis ionic symbols together. F− Lewis structures for ions: Mg2+ Ionic compounds-put the ions together as in a formula: MgF2 Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds 1) Nonmetals tend to share electrons in ...
Exam Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Key concepts of chemistry from high school chemistry
... number of particles represents a mole of the particle. So, there is a mole of carbon atoms (i.e. an Avogadro’s number of atoms) in the exact 12-‐gram sample of pure carbon-‐12 AND there is a ...
... number of particles represents a mole of the particle. So, there is a mole of carbon atoms (i.e. an Avogadro’s number of atoms) in the exact 12-‐gram sample of pure carbon-‐12 AND there is a ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
Chapter 7
... • Set of four numbers that completely specify each electron 1. Prinicipal quantum number, n, corresponds to the energy level 2. Second quantum number, l, corresponds to the sublevel within the energy level. It provides information about the shape of the electron cloud 3. Third quantum number, m, is ...
... • Set of four numbers that completely specify each electron 1. Prinicipal quantum number, n, corresponds to the energy level 2. Second quantum number, l, corresponds to the sublevel within the energy level. It provides information about the shape of the electron cloud 3. Third quantum number, m, is ...
Adv review key
... Determine if the following is a chemical or physical properties: _P_1. Oxygen is odorless and colorless _C_2. Copper turns green when exposed to the environment _P_3. The piece of metal is magnetic _P_4. The density of water is 1.0 gram per cubic centimeter _P_5. Diamonds are a very hard substance ...
... Determine if the following is a chemical or physical properties: _P_1. Oxygen is odorless and colorless _C_2. Copper turns green when exposed to the environment _P_3. The piece of metal is magnetic _P_4. The density of water is 1.0 gram per cubic centimeter _P_5. Diamonds are a very hard substance ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... Determine if the following is a chemical or physical properties: _P_1. Oxygen is odorless and colorless _C_2. Copper turns green when exposed to the environment _P_3. The piece of metal is magnetic _P_4. The density of water is 1.0 gram per cubic centimeter _P_5. Diamonds are a very hard substance ...
... Determine if the following is a chemical or physical properties: _P_1. Oxygen is odorless and colorless _C_2. Copper turns green when exposed to the environment _P_3. The piece of metal is magnetic _P_4. The density of water is 1.0 gram per cubic centimeter _P_5. Diamonds are a very hard substance ...
File
... • Periodic Table of Elements-originally developed by Dimitri Mendeleev and ordered by the cycle of the element’s properties. Now there are 118 elements that have been discovered and they ordered by their atomic number. ...
... • Periodic Table of Elements-originally developed by Dimitri Mendeleev and ordered by the cycle of the element’s properties. Now there are 118 elements that have been discovered and they ordered by their atomic number. ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... Read This! The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory helps predict the shapes of molecules and is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of ...
... Read This! The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory helps predict the shapes of molecules and is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of ...
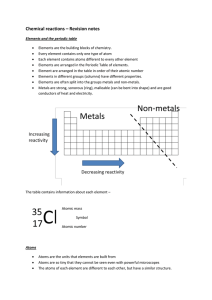
Chemical reactions revision
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Slide 1
... IUPAC names for a carboxylic acid are derived from the name of the parent hydrocarbon. – The final -e is dropped from the name of the parent hydrocarbon – The suffix -oic is added followed by the word acid. Many organic acids are called by their common (trivial) names which are derived from Greek or ...
... IUPAC names for a carboxylic acid are derived from the name of the parent hydrocarbon. – The final -e is dropped from the name of the parent hydrocarbon – The suffix -oic is added followed by the word acid. Many organic acids are called by their common (trivial) names which are derived from Greek or ...
Elements and Atoms
... • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
... • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
Semiconductors: Electrons and holes
... present. In that case, the dopant with the higher concentration “wins”. For example, consider a piece of silicon that has a donor concentration ND = 5x1017 cm–3 and an acceptor concentration of NA = 2x1017 cm–3. The empty bonding spots of the acceptor atoms will take up 2x1017 cm–3 of the electrons ...
... present. In that case, the dopant with the higher concentration “wins”. For example, consider a piece of silicon that has a donor concentration ND = 5x1017 cm–3 and an acceptor concentration of NA = 2x1017 cm–3. The empty bonding spots of the acceptor atoms will take up 2x1017 cm–3 of the electrons ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... Making ionic bond in NaCl • YouTube - ?Ionic and covalent bonding example?? • YouTube - ?Reaction of Sodium & Chlorine (with subtitles)?? ...
... Making ionic bond in NaCl • YouTube - ?Ionic and covalent bonding example?? • YouTube - ?Reaction of Sodium & Chlorine (with subtitles)?? ...
Midterm Review File
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...