Chem101 - Lecture 2 Elements Elements
... • Atoms are the limit of chemical subdivision in matter. • Each element has a different type of atom. ...
... • Atoms are the limit of chemical subdivision in matter. • Each element has a different type of atom. ...
Nonlocal optical response in metallic nanostructures
... from the bound electrons εcore (ω) can be determined from the measured bulk dielectric functions εexp (ω) using the recipe εcore (ω) = εexp (ω) + ωp2 /(ω2 + iγ ω) [138]. Comparing the hydrodynamic wave equation (equation (16)) with the wave equation from the phenomenological nonlocal model (equation ...
... from the bound electrons εcore (ω) can be determined from the measured bulk dielectric functions εexp (ω) using the recipe εcore (ω) = εexp (ω) + ωp2 /(ω2 + iγ ω) [138]. Comparing the hydrodynamic wave equation (equation (16)) with the wave equation from the phenomenological nonlocal model (equation ...
Curriculum Vitae - Université Paris-Sud
... latent image or the effects of radiation were at that time unexplained. Progressively, the complexity of the specific absorption of high-energy radiation by matter, including the non-homogeneous spatial distribution of initial ions and radicals, was better understood, at least in aqueous solutions. ...
... latent image or the effects of radiation were at that time unexplained. Progressively, the complexity of the specific absorption of high-energy radiation by matter, including the non-homogeneous spatial distribution of initial ions and radicals, was better understood, at least in aqueous solutions. ...
chemistry - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... paints peel off and firewoods burn. We grow up, we grow old. Living plants and animals undergo ceaseless change, and even dead animals and plants continue to change as they decay. Such changes fascinated people and inspired them to look more closely at nature’s way of working. Understanding change i ...
... paints peel off and firewoods burn. We grow up, we grow old. Living plants and animals undergo ceaseless change, and even dead animals and plants continue to change as they decay. Such changes fascinated people and inspired them to look more closely at nature’s way of working. Understanding change i ...
EXAM IR - Academics
... 2. Draw the Lewis dot structure of the phosphate ion. Include resonance structures if appropriate. Predict the 3-D shape of the ion. 3PO4 5 + 4(6) + 3 = 32 e- ...
... 2. Draw the Lewis dot structure of the phosphate ion. Include resonance structures if appropriate. Predict the 3-D shape of the ion. 3PO4 5 + 4(6) + 3 = 32 e- ...
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
... while the highly branched alkane C8H18 causes little knocking and is assigned an octane rating of 100. A gasoline with an octane rating of 87 causes the same knocking as a mixture that is 87% in the branched alkane and 13% of the straight chain alkane. Alkenes are organic compounds that contain carb ...
... while the highly branched alkane C8H18 causes little knocking and is assigned an octane rating of 100. A gasoline with an octane rating of 87 causes the same knocking as a mixture that is 87% in the branched alkane and 13% of the straight chain alkane. Alkenes are organic compounds that contain carb ...
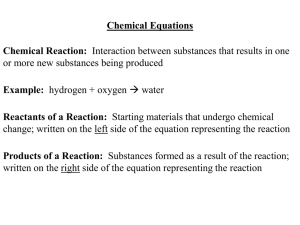
Chemical Equations Chemical Reaction: Interaction between
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
Chapter 5 ppt
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
PDF - mockies – Mockiesgateacademy
... Where has chemistry come from ? Throughout the history of the human race, people have struggled to make sense of the world around them. Through the branch of science we call chemistry we have gained an understanding of the matter which makes up our world and of the interactions between particles on ...
... Where has chemistry come from ? Throughout the history of the human race, people have struggled to make sense of the world around them. Through the branch of science we call chemistry we have gained an understanding of the matter which makes up our world and of the interactions between particles on ...
Photocatalysis on TiOn Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and
... since the electron exchange process requires simultaneous overlap of two orbital pairs, whereas only one such overlap is necessary for electron t r a n ~ f e r . ~ Dipole-dipole coupling occurs by a Coulombic resonance interaction in which the oscillating dipole of an excited state molecule is coupl ...
... since the electron exchange process requires simultaneous overlap of two orbital pairs, whereas only one such overlap is necessary for electron t r a n ~ f e r . ~ Dipole-dipole coupling occurs by a Coulombic resonance interaction in which the oscillating dipole of an excited state molecule is coupl ...
Unit 12: Electrochemistry
... Why study electricity in chemistry? Isn’t that a physics topic? Well, yes it is, as I have taught Regents physics as well. But to understand what you can DO with electricity in physics, you need to understand how electricity is created in the chemical world. In today’s (2015) world, electricity and ...
... Why study electricity in chemistry? Isn’t that a physics topic? Well, yes it is, as I have taught Regents physics as well. But to understand what you can DO with electricity in physics, you need to understand how electricity is created in the chemical world. In today’s (2015) world, electricity and ...
Concept Development Studies in Chemistry
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
File
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
Chapter 22 - 2012 Book Archive
... are all relatively electropositive; that is, they tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions rather than gain them. Although group 13 includes aluminum, the most abundant metal on Earth, none of these elements was known until the early 19th century because they are never found in nature in their f ...
... are all relatively electropositive; that is, they tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions rather than gain them. Although group 13 includes aluminum, the most abundant metal on Earth, none of these elements was known until the early 19th century because they are never found in nature in their f ...
sec chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
Answers - Pearson
... 14 Phosphorus exists as molecules with four atoms: P4. Sulfur exists as molecules with eight atoms: S8. There are stronger London dispersion forces between the larger S8 molecules as there are more electrons. ...
... 14 Phosphorus exists as molecules with four atoms: P4. Sulfur exists as molecules with eight atoms: S8. There are stronger London dispersion forces between the larger S8 molecules as there are more electrons. ...
chemistry writing team
... Pauli’s Exclusion Principle : ‘‘No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.’’ Two electrons can have same values for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). An orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opporite spins. Hund’s Rule ...
... Pauli’s Exclusion Principle : ‘‘No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.’’ Two electrons can have same values for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). An orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opporite spins. Hund’s Rule ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy. Light, x-rays, radio signals and microwaves are all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light is only a small part of the range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Figure 1.1: The electromagnetic spectrum ...
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy. Light, x-rays, radio signals and microwaves are all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light is only a small part of the range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Figure 1.1: The electromagnetic spectrum ...
Summer Assignment: Some Review / Basic Prep
... moving electrolytes (+ and -) allow for the conductance of an electrical current Yes: The fused compound (melted or liquefied phase) has had the ionic bond(s) broken and thus electrolytes have been produced. No: There are no free moving electrolytes. Really, only metals conduct electricity as a soli ...
... moving electrolytes (+ and -) allow for the conductance of an electrical current Yes: The fused compound (melted or liquefied phase) has had the ionic bond(s) broken and thus electrolytes have been produced. No: There are no free moving electrolytes. Really, only metals conduct electricity as a soli ...
SELECTED ANSWERS
... The Lewis structure shows the two O–H covalent bonds and the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The space-filling model provides the most accurate representation of the electron charge clouds for the atoms and the bonding electrons. The ball-and-stick model emphasizes the molecule’s correct molecula ...
... The Lewis structure shows the two O–H covalent bonds and the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The space-filling model provides the most accurate representation of the electron charge clouds for the atoms and the bonding electrons. The ball-and-stick model emphasizes the molecule’s correct molecula ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... Some hydrated magnesium sulfate (MgSO4.7H2O) was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The following reaction had occurred: MgSO4.7H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + 7H2O(l) (a) Why was it heated until there was no further change in mass? (1 mark) (b) When some drops of water were put ont ...
... Some hydrated magnesium sulfate (MgSO4.7H2O) was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The following reaction had occurred: MgSO4.7H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + 7H2O(l) (a) Why was it heated until there was no further change in mass? (1 mark) (b) When some drops of water were put ont ...
as a PDF
... lead systematically to core-shell particles. For example, Au(core)/Pd(shell) clusters were synthesized by reduction of the mixed ion aqueous17 or alcoholic solutions.18 Gold/palladium bimetallic particles having a palladium-rich shell were synthesized by Liu et al.19 Two-step alcoholic reduction giv ...
... lead systematically to core-shell particles. For example, Au(core)/Pd(shell) clusters were synthesized by reduction of the mixed ion aqueous17 or alcoholic solutions.18 Gold/palladium bimetallic particles having a palladium-rich shell were synthesized by Liu et al.19 Two-step alcoholic reduction giv ...
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...