chapter 23 the transition elements and their
... a) While transition elements commonly show multiple oxidation states, main-group elements show multiple oxidation states less frequently. Since the outermost s and d electrons in transition elements are so close in energy, all of these electrons can become involved in the bonding. b) The +2 oxidatio ...
... a) While transition elements commonly show multiple oxidation states, main-group elements show multiple oxidation states less frequently. Since the outermost s and d electrons in transition elements are so close in energy, all of these electrons can become involved in the bonding. b) The +2 oxidatio ...
Syllabus of Medical / Dental Colleges Entrance Test 2016
... h) Describe intermolecular forces (Van der Waal’s forces), based on permanent and induced dipoles, as in CHCl3, Br2 and in liquid noble gases i) ...
... h) Describe intermolecular forces (Van der Waal’s forces), based on permanent and induced dipoles, as in CHCl3, Br2 and in liquid noble gases i) ...
Hadronic Chemistry and Binding Energies
... Note that equation (9) still does not admit the attractive forces between the pair of singlet electrons and is not bound to any nuclei. These two aspects have been well attended by introducing conventional nonunitary form that reads as, ...
... Note that equation (9) still does not admit the attractive forces between the pair of singlet electrons and is not bound to any nuclei. These two aspects have been well attended by introducing conventional nonunitary form that reads as, ...
C:\usb key\sch3u\unit 1\chapter 2 test answers.wpd
... London forces; dipole/dipole forces; Hydrogen bonds; Covalent and Ionic 11) Which compound in each of the following pairs of compounds will have the higher melting point? Give the deciding factor in each case. a) NH3 and PH3 b) LiBr and SBr2 c) BCl3 and BCl2F d) C4H10 and C12H26 ...
... London forces; dipole/dipole forces; Hydrogen bonds; Covalent and Ionic 11) Which compound in each of the following pairs of compounds will have the higher melting point? Give the deciding factor in each case. a) NH3 and PH3 b) LiBr and SBr2 c) BCl3 and BCl2F d) C4H10 and C12H26 ...
Part A
... • Attractive force between electropositive hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule • Common between dipoles such as water • Also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecule in a three-dimensional shape ...
... • Attractive force between electropositive hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule • Common between dipoles such as water • Also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecule in a three-dimensional shape ...
AP Chemistry: Total Notes Review
... 4: use double and triple bonds as necessary o Formal charges: subtract the amount of electrons on the periodic table (for that element) from the electrons you drew in ~ 0 means right on ~ the negative charge should be on the most electronegative atom o Resonance: when one Lewis structure can’t accur ...
... 4: use double and triple bonds as necessary o Formal charges: subtract the amount of electrons on the periodic table (for that element) from the electrons you drew in ~ 0 means right on ~ the negative charge should be on the most electronegative atom o Resonance: when one Lewis structure can’t accur ...
covalent - Typepad
... 52. In which of these compounds is the bond between the atoms NOT a nonpolar covalent bond? a. Cl2 c. HCl b. H2 d. O2 53. To draw a Lewis structure, it is NOT necessary to know a. bond energies. b. the types of atoms in the molecule. c. the number of valence electrons for each atom. d. the number of ...
... 52. In which of these compounds is the bond between the atoms NOT a nonpolar covalent bond? a. Cl2 c. HCl b. H2 d. O2 53. To draw a Lewis structure, it is NOT necessary to know a. bond energies. b. the types of atoms in the molecule. c. the number of valence electrons for each atom. d. the number of ...
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
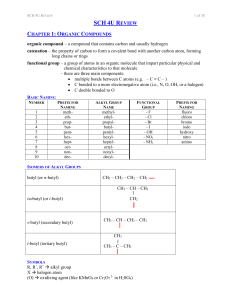
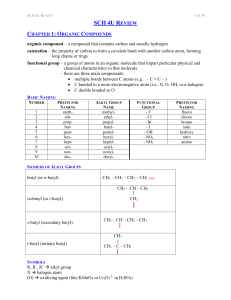
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
Chapter 2 - San Joaquin Memorial High School
... The Greeks were the first to try to explain why chemical changes occur. By about 400 B.C. they had proposed that all matter was composed of four fundamental substances: fire, earth, water, and air. The Greeks also considered the question of whether matter is continuous, and thus infinitely divisible ...
... The Greeks were the first to try to explain why chemical changes occur. By about 400 B.C. they had proposed that all matter was composed of four fundamental substances: fire, earth, water, and air. The Greeks also considered the question of whether matter is continuous, and thus infinitely divisible ...
CHAPTER 20 METALLURGY AND THE CHEMISTRY OF METALS
... formation. Then, we can calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, from the standard free energy change. ...
... formation. Then, we can calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, from the standard free energy change. ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... the organism – right now, a protein called hemoglobin is picking up oxygen from your lungs and will soon deliver it to the rest of your body. But EAL, the protein I work with, is an enzyme, which means it is a protein that serves as a catalyst for a chemical reaction. Specifically, EAL is the cataly ...
... the organism – right now, a protein called hemoglobin is picking up oxygen from your lungs and will soon deliver it to the rest of your body. But EAL, the protein I work with, is an enzyme, which means it is a protein that serves as a catalyst for a chemical reaction. Specifically, EAL is the cataly ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element “X” to 3 decimal places. ...
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element “X” to 3 decimal places. ...
sch4ureview
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
12 U Chem Review
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
Materials and Processes
... What do you understand by Miller indices of a crystal plane? Show that in a cubic crystal the spacing between two consecutive parallel planes of Miller indices (hkℓ) is given by a ...
... What do you understand by Miller indices of a crystal plane? Show that in a cubic crystal the spacing between two consecutive parallel planes of Miller indices (hkℓ) is given by a ...
ism ismismismismismrapidrevisionquestionsismismismismismism
... electrons for covalent bond formation while the fifth electron is extra and conducts electricity. These are called n-type semiconductors. When silicon is doped with group 13 impurities, they form three covalent bonds and electron holes. These are called p-type semiconductors. Explain the following w ...
... electrons for covalent bond formation while the fifth electron is extra and conducts electricity. These are called n-type semiconductors. When silicon is doped with group 13 impurities, they form three covalent bonds and electron holes. These are called p-type semiconductors. Explain the following w ...
handout 4
... Lecture Example: Baking soda (NaHCO3) is used as an antacid. It neutralizes HCl in the stomach. How many grams of HCl are neutralized per 1.00 gram of baking soda? If all the baking soda reacts, how many grams of water is produced? ...
... Lecture Example: Baking soda (NaHCO3) is used as an antacid. It neutralizes HCl in the stomach. How many grams of HCl are neutralized per 1.00 gram of baking soda? If all the baking soda reacts, how many grams of water is produced? ...
click here.
... protons is Oxygen. A non-metal in group 16. 20. Element 117 will fall in group 17 -- the halogens. Groups are also known as families because the elements in that family share characteristics. Since element 117 will be a Halogen, it will likely have halogen characteristics -- a colored gas at room te ...
... protons is Oxygen. A non-metal in group 16. 20. Element 117 will fall in group 17 -- the halogens. Groups are also known as families because the elements in that family share characteristics. Since element 117 will be a Halogen, it will likely have halogen characteristics -- a colored gas at room te ...
Document
... Cl0 it is more negative), due to a gain of 1 electron. The “gained” electron is the same electron, as that lost by the sodium. Thus, 1 electron was lost… 1 was gained… illustrating the Law of the Conservation of Charge. ...
... Cl0 it is more negative), due to a gain of 1 electron. The “gained” electron is the same electron, as that lost by the sodium. Thus, 1 electron was lost… 1 was gained… illustrating the Law of the Conservation of Charge. ...
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... * each atom gets one of the bonding electrons; each atom has now an unpaired electron and is therefore unstable and reactive; such a particle with an unpaired electron is called a free radical * free radicals have a strong tendency to react and usually have a short existence; tend to be intermediate ...
... * each atom gets one of the bonding electrons; each atom has now an unpaired electron and is therefore unstable and reactive; such a particle with an unpaired electron is called a free radical * free radicals have a strong tendency to react and usually have a short existence; tend to be intermediate ...
X PS EM - deo kadapa
... 3. Name and state the law which is kept in mind while we balance a chemical equation. Ans:- Law of conservation of mass is applied here. Accordingly matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Thus during a chemical reaction the total mass of the reactants and products remains same. Therefore for a ...
... 3. Name and state the law which is kept in mind while we balance a chemical equation. Ans:- Law of conservation of mass is applied here. Accordingly matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Thus during a chemical reaction the total mass of the reactants and products remains same. Therefore for a ...
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... their atoms have the same number of electron shells. their atoms have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells. their atoms have the same electronic arrangement. ...
... their atoms have the same number of electron shells. their atoms have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells. their atoms have the same electronic arrangement. ...
Metalloid Al- and Ga-clusters: a novel dimension in organometallic
... this process of the formation and breaking of metal–metal bonds (MM) are mostly unknown. This fundamental process and molecular intermediates exhibiting MM bonding are therefore central to this contribution. These molecular intermediates are mostly addressed as metal atom clusters.1 However, since t ...
... this process of the formation and breaking of metal–metal bonds (MM) are mostly unknown. This fundamental process and molecular intermediates exhibiting MM bonding are therefore central to this contribution. These molecular intermediates are mostly addressed as metal atom clusters.1 However, since t ...
Chapter -13 Principles of Metallurgy
... VI group was known as chalcogens, Justify? VI group was known as chalcogens, Since, most of the ores are in the form of oxides (or) sulphides and so on. These are called as chalcogens which means ore forming elements. ...
... VI group was known as chalcogens, Justify? VI group was known as chalcogens, Since, most of the ores are in the form of oxides (or) sulphides and so on. These are called as chalcogens which means ore forming elements. ...
Ch 2 Sample Exercises PPT
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...