Dissociation of H in the energy region at the n state
... observed time-dependent Balmer-a intensity. In these experiments, states of ungerade symmetry are excited, while in the present experiments gerade states are accessed. These experimental results are therefore not directly applicable, but we can conclude that the observed Hq signal mainly results fro ...
... observed time-dependent Balmer-a intensity. In these experiments, states of ungerade symmetry are excited, while in the present experiments gerade states are accessed. These experimental results are therefore not directly applicable, but we can conclude that the observed Hq signal mainly results fro ...
PHYS2042 Quantum Mechanics (Part II)
... In the first half of this course, you have been introduced to the formal structure of quantum mechanics. This included the concepts of quantum states, operators, wave functions, and measurements. You have seen some of the consequences of this formalism. For example, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principl ...
... In the first half of this course, you have been introduced to the formal structure of quantum mechanics. This included the concepts of quantum states, operators, wave functions, and measurements. You have seen some of the consequences of this formalism. For example, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principl ...
Chapter 2
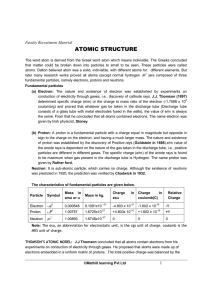
... behavior of an element • Each element consists of unique atoms. • _____ -smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. • -composed of smaller parts, called subatomic particles. • Two of these, _______ and ________, form a dense core, the atomic nucleus, at the center of an ...
... behavior of an element • Each element consists of unique atoms. • _____ -smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. • -composed of smaller parts, called subatomic particles. • Two of these, _______ and ________, form a dense core, the atomic nucleus, at the center of an ...
Measurements of Photoionization Cross Sections of Positive and
... & Iglesias 1994), The OPACITY Project (1995) and The Iron Project (Nahar & Pradhan 1994, Hummer et al 1993) have put considerable effort into the calculations of photoionization cross sections for all elements up to iron, and substantial theoretical work has also been performed for negative ions (Iv ...
... & Iglesias 1994), The OPACITY Project (1995) and The Iron Project (Nahar & Pradhan 1994, Hummer et al 1993) have put considerable effort into the calculations of photoionization cross sections for all elements up to iron, and substantial theoretical work has also been performed for negative ions (Iv ...
Bose-Einstein Condensation
... • The fastest moving atoms move furthest from the minimum, to a position of highest energy (see the upper atom shown in the figure). • Magnetic resonance is used to reverse the moments of the most energetic atoms, causing them to leave the trap, which is now an energy maximum. • Slowly reducing the ...
... • The fastest moving atoms move furthest from the minimum, to a position of highest energy (see the upper atom shown in the figure). • Magnetic resonance is used to reverse the moments of the most energetic atoms, causing them to leave the trap, which is now an energy maximum. • Slowly reducing the ...
Atom Smallest particle of an element having the same chemical
... the electron does not lose or gain energy. The radii of the spherical orbits are well defined. (only certain radii can exist). Electron in an orbit has a well defined specific energy. i.e. energy quantized. (Orbit - a place in which electron can exist/reside, is called an “allowed” energy state.) ...
... the electron does not lose or gain energy. The radii of the spherical orbits are well defined. (only certain radii can exist). Electron in an orbit has a well defined specific energy. i.e. energy quantized. (Orbit - a place in which electron can exist/reside, is called an “allowed” energy state.) ...
`Cutoff Frequency` of Quantum-Dot Single-Electron Pump - e-SI-Amp
... However, the authors [5] reported nonadiabatic excitations in localized quasibound states on QD. We presume that the nonadiabatic excitations could lead to influence the pumping accuracy, which was neglected in the model [1]. Focusing on the nonadiabatic effects on the quasibound state, we searched ...
... However, the authors [5] reported nonadiabatic excitations in localized quasibound states on QD. We presume that the nonadiabatic excitations could lead to influence the pumping accuracy, which was neglected in the model [1]. Focusing on the nonadiabatic effects on the quasibound state, we searched ...
CHEM_S1CourseReview_2011
... What is an atom? What are the early models of the atom and how has scientific exploration lead to the current model? What is a theory? How do you identify the relative mass, relative charge, and location of the three smaller subatomic particles of an atom? What is the overall charge of an ...
... What is an atom? What are the early models of the atom and how has scientific exploration lead to the current model? What is a theory? How do you identify the relative mass, relative charge, and location of the three smaller subatomic particles of an atom? What is the overall charge of an ...
Preparation of Papers in Two-Column Format for
... Précis-Insights into analysis of an experimental semiconductor laser with external optical feedback system gained from simulation with theoretical models. Over the years, theoretical semiconductor laser equation models have enabled the research community to map out semiconductor laser behavior and s ...
... Précis-Insights into analysis of an experimental semiconductor laser with external optical feedback system gained from simulation with theoretical models. Over the years, theoretical semiconductor laser equation models have enabled the research community to map out semiconductor laser behavior and s ...
Recent Development in Density Functional Theory in the
... density, kinetic effects, and electron correlations due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Coulomb repulsion. The ‘Newtonian’ description is: (a) tangible, (b) leads to further insights into the electronic structure, (c) knowledge of classical physics can be made to bear on this understanding. ...
... density, kinetic effects, and electron correlations due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Coulomb repulsion. The ‘Newtonian’ description is: (a) tangible, (b) leads to further insights into the electronic structure, (c) knowledge of classical physics can be made to bear on this understanding. ...
Quantum Mechanics Unit Review AP Physics
... 7. Why is the quantum mechanical model of the atom different from Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom? The quantum mechanical model of the atom makes two major changes to Bohr’s model. First it does away with Bohr’s orbits because the uncertainty principle won’t allow enough precision in an electron’ ...
... 7. Why is the quantum mechanical model of the atom different from Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom? The quantum mechanical model of the atom makes two major changes to Bohr’s model. First it does away with Bohr’s orbits because the uncertainty principle won’t allow enough precision in an electron’ ...
Chapter 1 Glossary The Nature of Chemistry
... Dipole-dipole attraction The intermolecular attraction between the partial negative end of one polar molecule and the partial positive end of another polar molecule. Hydrogen bond The intermolecular attraction between a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom of one molecule and a hydrogen atom bonded to ...
... Dipole-dipole attraction The intermolecular attraction between the partial negative end of one polar molecule and the partial positive end of another polar molecule. Hydrogen bond The intermolecular attraction between a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom of one molecule and a hydrogen atom bonded to ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.