Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... Rhodium (Rh), a transition metal, which often has a red-pink colour,1 was named after rhodon, the Greek term for rose. It is one of the least abundant metals in the earth’s crust and was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (1803-04) in crude platinum ore from South America. Rhodium is often used as ...
... Rhodium (Rh), a transition metal, which often has a red-pink colour,1 was named after rhodon, the Greek term for rose. It is one of the least abundant metals in the earth’s crust and was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (1803-04) in crude platinum ore from South America. Rhodium is often used as ...
4 Expressing and Measuring Chemical Change
... time, most equations can eventually be balanced this way. However, the job can be made much easier if you follow a good plan of attack. Keep the following hints in mind when attempting to balance an equation: • Begin by balancing atoms that appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Atom ...
... time, most equations can eventually be balanced this way. However, the job can be made much easier if you follow a good plan of attack. Keep the following hints in mind when attempting to balance an equation: • Begin by balancing atoms that appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Atom ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... (Other concepts introduced in this framework are reviewed in [39, 40]) In this way it is shown that DFT gave the possibility to sharply define concepts known for a long time in chemistry, but to which inadequate precision could be given to use them with confidence in quantitative studies. The last 1 ...
... (Other concepts introduced in this framework are reviewed in [39, 40]) In this way it is shown that DFT gave the possibility to sharply define concepts known for a long time in chemistry, but to which inadequate precision could be given to use them with confidence in quantitative studies. The last 1 ...
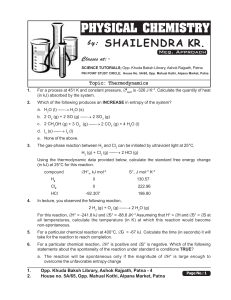
Thermodynamics - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... For particular chemical reaction, both ∆H° and ∆S° are negative. Which of the following statements about the spontaneity of the reaction under standard conditions is TRUE? a. The reaction will be spontaneous only if the magnitude of ∆H° is large enough to overcome the unfavorable entropy change. b. ...
... For particular chemical reaction, both ∆H° and ∆S° are negative. Which of the following statements about the spontaneity of the reaction under standard conditions is TRUE? a. The reaction will be spontaneous only if the magnitude of ∆H° is large enough to overcome the unfavorable entropy change. b. ...
Solution Definition and Speciation Calculations
... pe = 16.9Eh, Eh platinum electrode measurement ...
... pe = 16.9Eh, Eh platinum electrode measurement ...
Chemical Equations
... In the method of half-reactions, you first break down the reaction into the unbalanced oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Then you balance each half-reaction separately by the following procedure: First do steps 1-4 to each half-reaction: 1. Balance the elements other than O and H. 2. Balance t ...
... In the method of half-reactions, you first break down the reaction into the unbalanced oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Then you balance each half-reaction separately by the following procedure: First do steps 1-4 to each half-reaction: 1. Balance the elements other than O and H. 2. Balance t ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... 8. In an electrochemical cell, electrons travel in which direction? A. from the anode to the cathode through the external circuit B. from the anode to the cathode through the porous cup C. from the cathode to the anode through the external circuit D. from the cathode to the anode through the porous ...
... 8. In an electrochemical cell, electrons travel in which direction? A. from the anode to the cathode through the external circuit B. from the anode to the cathode through the porous cup C. from the cathode to the anode through the external circuit D. from the cathode to the anode through the porous ...
chemical kinetics - Berkeley City College
... k1 Step-1: NO2 + NO2 > NO3 + NO; [slow; rate-determining] Step-2: NO3 + CO > CO2 + NO; [fast] The rate law for the rate-determining step: Rate = k1[NO2]2, which is identical in form to the rate law obtained experimentally, in which k1 = k. The second step, which occurs very fast, does not influe ...
... k1 Step-1: NO2 + NO2 > NO3 + NO; [slow; rate-determining] Step-2: NO3 + CO > CO2 + NO; [fast] The rate law for the rate-determining step: Rate = k1[NO2]2, which is identical in form to the rate law obtained experimentally, in which k1 = k. The second step, which occurs very fast, does not influe ...
Document
... Enthalpy of neutralization can be expressed per mole of either base or acid consumed. ...
... Enthalpy of neutralization can be expressed per mole of either base or acid consumed. ...
Photosynthesis in Hydrogen-Dominated Atmospheres
... where Sa is the actual number of hydrogen atoms bonded to an atom and Sh is the number that could be bonded if the atom were fully reduced with hydrogen. This is a simple measure of reduction that is suited to comparing molecules’ redox state in a hydrogen-dominated environment. We note that this do ...
... where Sa is the actual number of hydrogen atoms bonded to an atom and Sh is the number that could be bonded if the atom were fully reduced with hydrogen. This is a simple measure of reduction that is suited to comparing molecules’ redox state in a hydrogen-dominated environment. We note that this do ...
Assessing the Potential for the Reactions of
... Since the water concentration itself depends extremely weakly on pH in this pH region, this mechanism is consistent with kinetics data shown in Figure 2. Water as a Catalyst for Amine−Epoxide Systems. In a previous study, Azizi and Saidi synthesized various β-amino alcohols by reaction of epoxides i ...
... Since the water concentration itself depends extremely weakly on pH in this pH region, this mechanism is consistent with kinetics data shown in Figure 2. Water as a Catalyst for Amine−Epoxide Systems. In a previous study, Azizi and Saidi synthesized various β-amino alcohols by reaction of epoxides i ...
Basic Organic Chemistry Laboratory Course
... Aliphatic compounds burn in air with a yellow, nearly smokeless flame, while aromatic compounds show a yellow, strongly sooting flame. In general one can say that the larger the degree of unsaturation of a certain compound, the sootier its flame. The test is carried out by burning a small amount o ...
... Aliphatic compounds burn in air with a yellow, nearly smokeless flame, while aromatic compounds show a yellow, strongly sooting flame. In general one can say that the larger the degree of unsaturation of a certain compound, the sootier its flame. The test is carried out by burning a small amount o ...
BSc/MSci Course Unit Examination - QMplus
... (n) An electrical current flows through a wire and does 333 J of work every second causing the temperature of the wire to increase. After some time, the temperature of the wire stops increasing. The current is then switched off and the wire cools. Calculate q, w and ΔU per second at the following ti ...
... (n) An electrical current flows through a wire and does 333 J of work every second causing the temperature of the wire to increase. After some time, the temperature of the wire stops increasing. The current is then switched off and the wire cools. Calculate q, w and ΔU per second at the following ti ...
electrochemistry
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
Chem 12 Prov Exam PLO Review
... • reactions are the result of collisions between reactant particles • not all collisions are successful • sufficient kinetic energy (KE) and favourable geometry are required • to increase the rate of a reaction one must increase the frequency of successful collisions • energy changes are involved in ...
... • reactions are the result of collisions between reactant particles • not all collisions are successful • sufficient kinetic energy (KE) and favourable geometry are required • to increase the rate of a reaction one must increase the frequency of successful collisions • energy changes are involved in ...
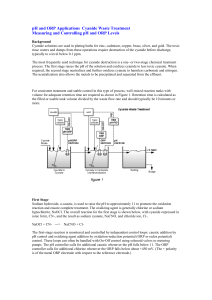
pH and ORP Applications Cyanide Waste Treatment
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
3/23/2014 1 8 Chemical Equations Chapter Outline Chemical
... produced during the reaction. Reactants: substances consumed during the reaction. Products: substances formed during the reaction. ...
... produced during the reaction. Reactants: substances consumed during the reaction. Products: substances formed during the reaction. ...
advanced chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... (b) Explain why a solution of HCl in water conducts electricity but a solution of the compound in hexane does not. In water, HCl reacts to form ions {H+(aq) = H3O+(aq)} and Cl- and these are responsible for the conductivity of the solution. (1) In hexane, since the solvent cannot accept protons (no ...
... (b) Explain why a solution of HCl in water conducts electricity but a solution of the compound in hexane does not. In water, HCl reacts to form ions {H+(aq) = H3O+(aq)} and Cl- and these are responsible for the conductivity of the solution. (1) In hexane, since the solvent cannot accept protons (no ...
View
... as evidenced by its relatively accessible one-electron reduction potential,5 possesses electron-acceptor properties, which can be tuned by the substituents,6 and also luminescence properties in some derivatives.7 The large majority of the coordinating units attached to the 2,4,6 positions of the 1,3 ...
... as evidenced by its relatively accessible one-electron reduction potential,5 possesses electron-acceptor properties, which can be tuned by the substituents,6 and also luminescence properties in some derivatives.7 The large majority of the coordinating units attached to the 2,4,6 positions of the 1,3 ...
Lectures on Chapter 4, Part 2 Powerpoint 97 Document
... SO32-(aq) SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen fro ...
... SO32-(aq) SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen fro ...
Molecular geometry
... that is slightly altered or perturbed by some additional force or interaction (such as the interaction between the two atoms). Variational method (used in molecular orbital theory): The energy of a trial function (educated function) within the Schrodinger equation is minimized. ...
... that is slightly altered or perturbed by some additional force or interaction (such as the interaction between the two atoms). Variational method (used in molecular orbital theory): The energy of a trial function (educated function) within the Schrodinger equation is minimized. ...
Chemical Reactions
... we know that, in chemical reactions, atoms are never destroyed or created; they merely shift from one substance to another. Thus all the atoms present at the start of the reaction (on the left side of the equation) must still be present at the end (on the right side of the equation). In the equation ...
... we know that, in chemical reactions, atoms are never destroyed or created; they merely shift from one substance to another. Thus all the atoms present at the start of the reaction (on the left side of the equation) must still be present at the end (on the right side of the equation). In the equation ...
General Chemistry Discretes Test
... For question 3, the correct choice is A . One is asked in this question to determine which of the choices contains a false description of the gas. Under conditions of high pressure and low temperature, the gas is not behaving ideally and corrections must be made for the volume of the gas molecules a ...
... For question 3, the correct choice is A . One is asked in this question to determine which of the choices contains a false description of the gas. Under conditions of high pressure and low temperature, the gas is not behaving ideally and corrections must be made for the volume of the gas molecules a ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.