9278654 PS/Chemistry Ja03 - Dolgeville Central School
... When cola, a type of soda pop, is manufactured, CO2(g) is dissolved in it. 65 A capped bottle of cola contains CO2(g) under high pressure. When the cap is removed, how does pressure affect the solubility of the dissolved CO2(g)? [1] 66 A glass of cold cola is left to stand 5 minutes at room temperat ...
... When cola, a type of soda pop, is manufactured, CO2(g) is dissolved in it. 65 A capped bottle of cola contains CO2(g) under high pressure. When the cap is removed, how does pressure affect the solubility of the dissolved CO2(g)? [1] 66 A glass of cold cola is left to stand 5 minutes at room temperat ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Potentiometric
... values compatible with CN2= 0.60 ppm and CN8'= 0.30 ppm reported for linear amines8 (Table 11). No shielding constants could be obtained for the H3L3+ form because at p H 0.4 this species is not fully formed. The pH dependence of the proton chemical shifts of the ethylene protons and the methyl prot ...
... values compatible with CN2= 0.60 ppm and CN8'= 0.30 ppm reported for linear amines8 (Table 11). No shielding constants could be obtained for the H3L3+ form because at p H 0.4 this species is not fully formed. The pH dependence of the proton chemical shifts of the ethylene protons and the methyl prot ...
Amines - ncert
... present at different positions in the parent chain, their positions are specified by giving numbers to the carbon atoms bearing –NH2 groups and suitable prefix such as di, tri, etc. is attached to the amine. The letter ‘e’ of the suffix of the hydrocarbon part is retained. For example, H2N–CH2–CH2–N ...
... present at different positions in the parent chain, their positions are specified by giving numbers to the carbon atoms bearing –NH2 groups and suitable prefix such as di, tri, etc. is attached to the amine. The letter ‘e’ of the suffix of the hydrocarbon part is retained. For example, H2N–CH2–CH2–N ...
Objectives - hartman
... • Calculate the amount in moles or mass in grams of a product, given the amounts in moles or masses in grams of two reactants, one of which is in excess. • Distinguish between theoretical yield, actual yield, and percentage yield. • Calculate percentage yield, given the actual yield and quantity of ...
... • Calculate the amount in moles or mass in grams of a product, given the amounts in moles or masses in grams of two reactants, one of which is in excess. • Distinguish between theoretical yield, actual yield, and percentage yield. • Calculate percentage yield, given the actual yield and quantity of ...
Some generalization of Langmuir adsorption isotherm
... isotherms. Gregg and Sing 3 have given a detailed discussion of the various models used to interpret each type of the isotherms. The derivation of a scientifically based adsorption isotherm was first achieved by Langmuir (1918). The Langmuir isotherm model assumes monolayer adsorption on a homogeneo ...
... isotherms. Gregg and Sing 3 have given a detailed discussion of the various models used to interpret each type of the isotherms. The derivation of a scientifically based adsorption isotherm was first achieved by Langmuir (1918). The Langmuir isotherm model assumes monolayer adsorption on a homogeneo ...
Physical Sciences Grade 10 Term 2
... tube and fills the test tube up to the ¾ mark with water. The contents of the test tube are then shaken vigorously to dissolve the chemicals, use a rubber stopper to close the test tube before shaking it. If possible measure the mass of all the test tubes with their contents and record this mass. To ...
... tube and fills the test tube up to the ¾ mark with water. The contents of the test tube are then shaken vigorously to dissolve the chemicals, use a rubber stopper to close the test tube before shaking it. If possible measure the mass of all the test tubes with their contents and record this mass. To ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... ____ 87. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 88. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
... ____ 87. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 88. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1st Ed. Nivaldo Tro ...
... Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1st Ed. Nivaldo Tro ...
RUMPLE-DISSERTATION-2014 - SMARTech Home
... To my family and friends, especially my parents, JoAnne and Paul, and my brother, Bryan, without whom I would not be the person I am today. ...
... To my family and friends, especially my parents, JoAnne and Paul, and my brother, Bryan, without whom I would not be the person I am today. ...
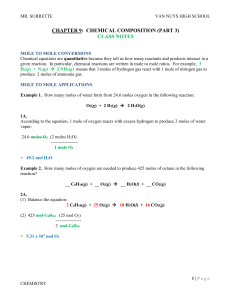
Stoichiometry
... done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to discuss the number of atoms in moles than it is as individual items - 0.10 mol H2O is a mu ...
... done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to discuss the number of atoms in moles than it is as individual items - 0.10 mol H2O is a mu ...
grafted chitosan - Repositorio Académico
... reaction temperature (50, 60, 70, and/or 80 8C). Polymerization was started and continued for a predetermined period, between 30 and 150 min. The reaction was stopped by rapidly cooling down the reactor, then the product was precipitated by pouring the polymerization mixture into a large amount of a ...
... reaction temperature (50, 60, 70, and/or 80 8C). Polymerization was started and continued for a predetermined period, between 30 and 150 min. The reaction was stopped by rapidly cooling down the reactor, then the product was precipitated by pouring the polymerization mixture into a large amount of a ...
electrical energy and capacitance
... = 7.96 x 106 g 8.0 x 103 kg H2SO4 LIMITING REACTANT Limiting reactants are compounds completely consumed in chemical reactions. THEORETICAL YIELD Theoretical yield is the amount of product that can be made in a chemical reaction. It is based on the amount of limiting reagent. ...
... = 7.96 x 106 g 8.0 x 103 kg H2SO4 LIMITING REACTANT Limiting reactants are compounds completely consumed in chemical reactions. THEORETICAL YIELD Theoretical yield is the amount of product that can be made in a chemical reaction. It is based on the amount of limiting reagent. ...
The polydentate ligands include polyaminopolycarbonic acids, such
... Properties of complex compounds allow for their application in medicine and pharmacy. Many complex compounds have biological activity (Co2+ -ion is complexing agent in a molecule of vitamin B12, compound of platinum - cis[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] has antineoplastic effect). Currently available new drugs from pl ...
... Properties of complex compounds allow for their application in medicine and pharmacy. Many complex compounds have biological activity (Co2+ -ion is complexing agent in a molecule of vitamin B12, compound of platinum - cis[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] has antineoplastic effect). Currently available new drugs from pl ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.