1. Define the following term: system. A) The part of the universe that
... A) State functions: P,V; Not: work, energy B) State functions: energy, P; Not: T, heat C) State functions: energy, V; Not: work, heat D) State functions: energy, work; Not: T, heat ...
... A) State functions: P,V; Not: work, energy B) State functions: energy, P; Not: T, heat C) State functions: energy, V; Not: work, heat D) State functions: energy, work; Not: T, heat ...
Chemistry Higher Level Chapter 5 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electron transfer can lead to the formation of stable ionic compounds. The questi ...
... dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electron transfer can lead to the formation of stable ionic compounds. The questi ...
AP `94 Multiple Choice
... If the temperature decreases from 110_C to 40_C at a constant pressure of 1.1 atmospheres, which of the processes occurs? If the pressure Increases from 0.5 to 1.5 atmospheres at a constant temperature of 50_C, which of the processes occurs? ...
... If the temperature decreases from 110_C to 40_C at a constant pressure of 1.1 atmospheres, which of the processes occurs? If the pressure Increases from 0.5 to 1.5 atmospheres at a constant temperature of 50_C, which of the processes occurs? ...
Describe properties of particles and thermochemical - Mr
... special characteristics of transition metals (variable oxidation state, colour) related to electron configuration. Transition metals will be limited to iron, vanadium, chromium, manganese, copper and zinc periodic trends in atomic radius, ionisation energy, and electronegativity, and comparison ...
... special characteristics of transition metals (variable oxidation state, colour) related to electron configuration. Transition metals will be limited to iron, vanadium, chromium, manganese, copper and zinc periodic trends in atomic radius, ionisation energy, and electronegativity, and comparison ...
Energetics of adsorption of neutral and charged molecules at the air
... water. The corrections due to water background were of minor importance for the various molecules studied. In all cases, the adsorption was found to obey the Langmuir isotherm” (see below) over all ranges of concentrations. As an example, the experimental points along with the Langmuir fit are shown ...
... water. The corrections due to water background were of minor importance for the various molecules studied. In all cases, the adsorption was found to obey the Langmuir isotherm” (see below) over all ranges of concentrations. As an example, the experimental points along with the Langmuir fit are shown ...
File
... Award [3] for correct final answer. Award [2] for (+)540. If old Data Booklet is used accept answer: –535 (kJ mol–1) or award [2] for (+)535. ...
... Award [3] for correct final answer. Award [2] for (+)540. If old Data Booklet is used accept answer: –535 (kJ mol–1) or award [2] for (+)535. ...
Current Density Distribution for a Full Scale Industrial Alluminization
... (11) leads to an overestimation of the charge deposited by a 2%. Boundary conditions (12-13) give a tremendous drop of the charge deposited by a factor of 102 (Figure 2c,d). In principle for condition (11) and (13) it is possible to results in negative concentration for the depleted species at an el ...
... (11) leads to an overestimation of the charge deposited by a 2%. Boundary conditions (12-13) give a tremendous drop of the charge deposited by a factor of 102 (Figure 2c,d). In principle for condition (11) and (13) it is possible to results in negative concentration for the depleted species at an el ...
Review Final 111 Lect
... (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of the following will result?(Hint: Write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of BaSO4 (s).) a. The concentration of SO42- wi ...
... (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of the following will result?(Hint: Write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of BaSO4 (s).) a. The concentration of SO42- wi ...
Homework Booklet [4,S]
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
Chemistry Test at a Glance
... This assessment includes two tests. You may take either test individually or the full assessment in a single session. The testing time is the amount of time you will have to answer the questions on the test. Test duration includes time for tutorials and directional screens that may be included in th ...
... This assessment includes two tests. You may take either test individually or the full assessment in a single session. The testing time is the amount of time you will have to answer the questions on the test. Test duration includes time for tutorials and directional screens that may be included in th ...
3.091 Summary Lecture Notes, Fall 2009
... o e- discharge tube (vacuum tube with a large voltage (~35,000V’s) applied between two electrodes (cathode and anode (target)) o accelerate e- through a vacuum o e- ‘crash’ into anode (target), ejecting bound e- from core shells o e- from higher orbitals ‘cascade down’, releasing high energy pho ...
... o e- discharge tube (vacuum tube with a large voltage (~35,000V’s) applied between two electrodes (cathode and anode (target)) o accelerate e- through a vacuum o e- ‘crash’ into anode (target), ejecting bound e- from core shells o e- from higher orbitals ‘cascade down’, releasing high energy pho ...
Appendix
... In Chapter 4 we considered the basic mathematical details of a propagation of uncertainty, limiting our treatment to the propagation of measurement error. This treatment is incomplete because it omits other sources of uncertainty that influence the overall uncertainty in our results. Consider, for e ...
... In Chapter 4 we considered the basic mathematical details of a propagation of uncertainty, limiting our treatment to the propagation of measurement error. This treatment is incomplete because it omits other sources of uncertainty that influence the overall uncertainty in our results. Consider, for e ...
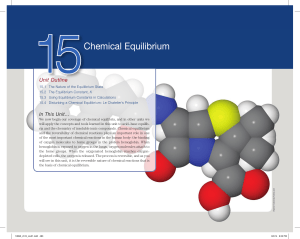
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... Graphical representation of progression toward chemical equilibrium ...
... Graphical representation of progression toward chemical equilibrium ...
Chemistry and electronic properties of metal
... core of the molecule. Oxygen-related levels are 1–3 eV below the centroid of the HOMO. This is in contrast with a previous report that attributed the HOMO to the p bonding of the anhydride group.34 The determination of filled and empty states of a molecular solid via electron spectroscopies can be a ...
... core of the molecule. Oxygen-related levels are 1–3 eV below the centroid of the HOMO. This is in contrast with a previous report that attributed the HOMO to the p bonding of the anhydride group.34 The determination of filled and empty states of a molecular solid via electron spectroscopies can be a ...
Chapter 7: Solutions
... the difference between solute(s) and solvent. Predict the effect of temperature and pressure on the solubility of gases in water and the effect of temperature on the solubility of solids in water. Be able to use the Solubility Rules Table to determine if an ionic compound will significantly dissolve ...
... the difference between solute(s) and solvent. Predict the effect of temperature and pressure on the solubility of gases in water and the effect of temperature on the solubility of solids in water. Be able to use the Solubility Rules Table to determine if an ionic compound will significantly dissolve ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.














![Homework Booklet [4,S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010355871_1-63c750e3d1b58eaaebbb3f5d45651c44-300x300.png)